Abstract
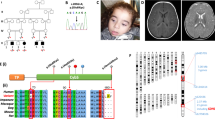
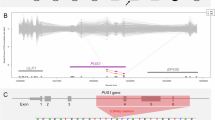
The iron–sulfur (Fe–S) cluster (ISC) biogenesis pathway is indispensable for many fundamental biological processes and pathogenic variations in genes encoding several components of the Fe–S biogenesis machinery, such as NFU1, BOLA3, IBA57 and ISCA2 are already implicated in causing four types of multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndromes (MMDS). We report on two unrelated families, with two affected children each with early onset neurological deterioration, seizures, extensive white matter abnormalities, cortical migrational abnormalities, lactic acidosis and early demise. Exome sequencing of two affected individuals, one from each family, revealed a homozygous c.259G>A [p.(Glu87Lys)] variant in ISCA1 and Mendelian segregation was confirmed in both families. The ISCA1 variant lies in the only shared region of homozygosity between the two families suggesting the possibility of a founder effect. In silico functional analyses and structural modeling of the protein predict the identified ISCA1 variant to be detrimental to protein stability and function. Notably the phenotype observed in all affected subjects with the ISCA1 pathogenic variant is similar to that previously described in all four types of MMDS. Our findings suggest association of a pathogenic variant in ISCA1 with another MMDS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Netz, D. J., Mascarenhas, J., Stehling, O., Pierik, A. J. & Lill, R. Maturation of cytosolic and nuclear iron-sulfur proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 24, 303–312 (2014).
Rouault, T. A. & Tong, W. H. Iron-sulphur cluster biogenesis and mitochondrial iron homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 345–351 (2005).
Lill, R. & Muhlenhoff, U. Maturation of iron-sulfur proteins in eukaryotes: mechanisms, connected processes, and diseases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 669–700 (2008).
Baker, P. R. 2nd, Friederich, M. W., Swanson, M. A., Shaikh, T., Bhattacharya, K., Scharer, G. H. et al. Variant non ketotic hyperglycinemia is caused by mutations in LIAS, BOLA3 and the novel gene GLRX5. Brain 137, 366–379 (2014).
Cameron, J. M., Janer, A., Levandovskiy, V., Mackay, N., Rouault, T. A., Tong, W. H. et al. Mutations in iron-sulfur cluster scaffold genes NFU1 and BOLA3 cause a fatal deficiency of multiple respiratory chain and 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase enzymes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 89, 486–495 (2011).
Banci, L., Brancaccio, D., Ciofi-Baffoni, S., Del Conte, R., Gadepalli, R., Mikolajczyk, M. et al. [2Fe-2S] cluster transfer in iron-sulfur protein biogenesis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 6203–6208 (2014).
Navarro-Sastre, A., Tort, F., Stehling, O., Uzarska, M. A., Arranz, J. A., Del Toro, M. et al. A fatal mitochondrial disease is associated with defective NFU1 function in the maturation of a subset of mitochondrial Fe-S proteins. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 89, 656–667 (2011).
Al-Hassnan, Z. N., Al-Dosary, M., Alfadhel, M., Faqeih, E. A., Alsagob, M., Kenana, R. et al. ISCA2 mutation causes infantile neurodegenerative mitochondrial disorder. J. Med. Genet. 52, 186–194 (2015).
Ajit Bolar, N., Vanlander, A. V., Wilbrecht, C., Van der Aa, N., Smet, J., De Paepe, B. et al. Mutation of the iron-sulfur cluster assembly gene IBA57 causes severe myopathy and encephalopathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 22, 2590–2602 (2013).
Ahting, U., Mayr, J. A., Vanlander, A. V., Hardy, S. A., Santra, S., Makowski, C. et al. Clinical, biochemical, and genetic spectrum of seven patients with NFU1 deficiency. Front. Genet. 6, 123 (2015).
Girisha, K. M., Shukla, A., Trujillano, D., Bhavani, G. S., Hebbar, M., Kadavigere, R. et al. A homozygous nonsense variant in IFT52 is associated with a human skeletal ciliopathy. Clin. Genet. 90, 536–539 (2016).
Wang, K., Li, M. & Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, e164 (2010).
Guo, Y., Ding, X., Shen, Y., Lyon, G. J. & Wang, K. SeqMule: automated pipeline for analysis of human exome/genome sequencing data. Sci. Rep. 5, 14283 (2015).
Danecek, P., Auton, A., Abecasis, G., Albers, C. A., Banks, E., DePristo, M. A. et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 27, 2156–2158 (2011).
Vigeland, M. D., Gjotterud, K. S. & Selmer, K. K. FILTUS: a desktop GUI for fast and efficient detection of disease-causing variants, including a novel autozygosity detector. Bioinformatics 32, 1592–1594 (2016).
Biasini, M., Bienert, S., Waterhouse, A., Arnold, K., Studer, G., Schmidt, T. et al. SWISS-MODEL: modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, W252–W258 (2014).
Sievers, F., Wilm, A., Dineen, D., Gibson, T. J., Karplus, K., Li, W. et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 539 (2011).
Ashkenazy, H., Abadi, S., Martz, E., Chay, O., Mayrose, I., Pupko, T. et al. ConSurf 2016: an improved methodology to estimate and visualize evolutionary conservation in macromolecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, W344–W350 (2016).
Lek, M., Karczewski, K. J., Minikel, E. V., Samocha, K. E., Banks, E., Fennell, T. et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60706 humans. Nature 536, 285–291 (2016).
Tang, H. & Thomas, P. D. PANTHER-PSEP: predicting disease-causing genetic variants using position-specific evolutionary preservation. Bioinformatics 32, 2230–2232 (2016).
Kircher, M., Witten, D. M., Jain, P., O’Roak, B. J., Cooper, G. M. & Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 46, 310–315 (2014).
Bromberg, Y. & Rost, B. SNAP: predict effect of non-synonymous polymorphisms on function. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 3823–3835 (2007).
Hecht, M., Bromberg, Y. & Rost, B. Better prediction of functional effects for sequence variants. BMC Genomics 16 (Suppl 8), S1 (2015).
Muhlenhoff, U., Richter, N., Pines, O., Pierik, A. J. & Lill, R. Specialized function of yeast Isa1 and Isa2 proteins in the maturation of mitochondrial [4Fe-4S] proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 41205–41216 (2011).
Sheftel, A. D., Wilbrecht, C., Stehling, O., Niggemeyer, B., Elsasser, H. P., Muhlenhoff, U. et al. The human mitochondrial ISCA1, ISCA2, and IBA57 proteins are required for [4Fe-4S] protein maturation. Mol. Biol. Cell. 23, 1157–1166 (2012).
Brancaccio, D., Gallo, A., Mikolajczyk, M., Zovo, K., Palumaa, P., Novellino, E. et al. Formation of [4Fe-4S] clusters in the mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster assembly machinery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 16240–16250 (2014).
Song, D., Tu, Z. & Lee, F. S. Human ISCA1 interacts with IOP1/NARFL and functions in both cytosolic and mitochondrial iron-sulfur protein biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 35297–35307 (2009).
Acknowledgements
We thank the families who cooperated with the evaluation of the subjects and consented for participation in this study. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health funded the project titled ‘Genetic Diagnosis of Heritable Neurodevelopmental Disorders in India: Investigating the Use of Whole-Exome Sequencing and Genetic Counseling to Address the High Burden of Neurodevelopmental Disorders’ (1R21NS094047-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, A., Hebbar, M., Srivastava, A. et al. Homozygous p.(Glu87Lys) variant in ISCA1 is associated with a multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome. J Hum Genet 62, 723–727 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2017.35
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2017.35
This article is cited by
-
Ferroptosis is a novel pathogenic mechanism of FDXR-related disease via disruption of the NRF2 pathway
Cell Death Discovery (2025)
-
Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation Attenuates Cognitive Deficits and Alzheimer’s Disease-Type Pathologies via ISCA1-Mediated Mitochondrial Modulation in APP/PS1 Mice
Neuroscience Bulletin (2024)
-
Novel IBA57 mutations in two chinese patients and literature review of multiple mitochondrial dysfunction syndrome
Metabolic Brain Disease (2022)
-
Multilocus disease-causing genomic variations for Mendelian disorders: role of systematic phenotyping and implications on genetic counselling
European Journal of Human Genetics (2021)
-
A novel ISCA2 variant responsible for an early-onset neurodegenerative mitochondrial disorder: a case report of multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome 4
BMC Neurology (2019)