Abstract
Objective:
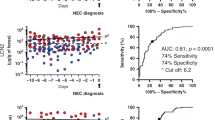
Neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) have higher calprotectin levels in stool than do healthy neonates. However, it is not known whether high stool calprotectin at the onset of bowel symptoms identifies neonates who truly have NEC vs other bowel disorders.
Study Design:
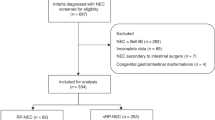
Neonates were eligible for this study when an x-ray was ordered to 'rule-out NEC'. Stool calprotectin was quantified at that time and in a follow-up stool. Each episode was later categorized as NEC or not NEC. The location of calprotectin in the bowel was determined by immunohistochemistry.
Results:
Neonates with NEC had higher initial and follow-up stool calprotectin levels than did neonates without NEC. Calprotectin in bowel from neonates with NEC was within neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs).
Conclusion:
At the onset of signs concerning for NEC, fecal calprotectin is likely to be higher in neonates with NEC. Calprotectin in their stools is exported from neutrophils via NETs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neu J . Necrotizing enterocolitis: the mystery goes on. Neonatology 2014; 106 (4): 289–295.
Gordon PV, Swanson JR . Necrotizing enterocolitis is one disease with many origins and potential means of prevention. Pathophysiology 2014; 21 (1): 13–19.
Lambert DK, Christensen RD, Baer VL, Henry E, Gordon PV, Besner GE et al. Fulminant necrotizing enterocolitis in a multihospital healthcare system. J Perinatol 2012; 32 (3): 194–199.
Sharma R, Hudak ML . A clinical perspective of necrotizing enterocolitis: past, present, and future. Clin Perinatol 2013; 40 (1): 27–51.
Ng PC, Chan KY, Poon TC . Biomarkers for prediction and diagnosis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Clin Perinatol 2013; 40 (1): 149–159.
Alibrahim B, Aljasser MI, Salh B . Fecal calprotectin use in inflammatory bowel disease and beyond: a mini-review. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 29 (3): 157–163.
Menees SB, Powell C, Kurlander J, Goel A, Chey WD . A meta-analysis of the utility of C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, fecal calprotectin, and fecal lactoferrin to exclude inflammatory bowel disease in adults with IBS. Am J Gastroenterol 2015; 110 (3): 444–454.
Bin-Nun A, Booms C, Sabag N, Mevorach R, Algur N, Hammerman C . Rapid fecal calprotectin (FC) analysis: point of care testing for diagnosing early necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Perinatol 2015; 32 (4): 337–342.
Waugh N, Cummins E, Royle P, Kandala NB, Shyangdan D, Arasaradnam R et al. Faecal calprotectin testing for differentiating amongst inflammatory and non-inflammatory bowel diseases: systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2013; 17 (55): xv–xix, 1–211.
Carroll D, Corfield A, Spicer R, Cairns P . Faecal calprotectin concentrations and diagnosis of necrotising enterocolitis. Lancet 2003; 361 (9354): 310–311.
Wright EK, De Cruz P, Gearry R, Day AS, Kamm MA . Fecal biomarkers in the diagnosis and monitoring of Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014; 20 (9): 1668–1677.
D'Inca R, Caccaro R . Measuring disease activity in Crohn's disease: what is currently available to the clinician. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 2014; 7: 151–161.
Josefsson S, Bunn SK, Domellof M . Fecal calprotectin in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2007; 44 (4): 407–413.
Yang Q, Smith PB, Goldberg RN, Cotten CM . Dynamic change of fecal calprotectin in very low birth weight infants during the first month of life. Neonatology 2008; 94 (4): 267–271.
Thuijls G, Derikx JP, van Wijck K, Zimmermann LJ, Degraeuwe PL, Mulder TL et al. Non-invasive markers for early diagnosis and determination of the severity of necrotizing enterocolitis. Ann Surg 2010; 251 (6): 1174–1180.
Aydemir O, Aydemir C, Sarikabadayi YU, Emre Canpolat F, Erdeve O, Biyikli Z et al. Fecal calprotectin levels are increased in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012; 25 (11): 2237–2241.
Dabritz J, Jenke A, Wirth S, Foell D . Fecal phagocyte-specific S100A12 for diagnosing necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 2012; 161 (6): 1059–1064.
Zoppelli L, Guttel C, Bittrich HJ, Andree C, Wirth S, Jenke A . Fecal calprotectin concentrations in premature infants have a lower limit and show postnatal and gestational age dependence. Neonatology 2012; 102 (1): 68–74.
Selimoglu MA, Temel I, Yildirim C, Ozyaln F, Aktas M, Karabiber H . The role of fecal calprotectin and lactoferrin in the diagnosis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2012; 13 (4): 452–454.
Aydemir G, Cekmez F, Tanju IA, Canpolat FE, Genc FA, Yildirim S et al. Increased fecal calprotectin in preterm infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. Clin Lab 2012; 58 (7–8): 841–844.
Reisinger KW, Van der Zee DC, Brouwers HA, Kramer BW, van Heurn LW, Buurman WA et al. Noninvasive measurement of fecal calprotectin and serum amyloid A combined with intestinal fatty acid-binding protein in necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 2012; 47 (9): 1640–1645.
Jenke AC, Postberg J, Mariel B, Hensel K, Foell D, Dabritz J et al. S100A12 and hBD2 correlate with the composition of the fecal microflora in ELBW infants and expansion of E. coli is associated with NEC. Biomed Res Int 2013; 2013: 150372.
Reisinger KW, Kramer BW, Van der Zee DC, Brouwers HA, Buurman WA, van Heurn E et al. Non-invasive serum amyloid A (SAA) measurement and plasma platelets for accurate prediction of surgical intervention in severe necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). PLoS One 2014; 9 (6): e90834.
Yoon JM, Park JY, Ko KO, Lim JW, Cheon EJ, Kim HJ . Fecal calprotectin concentration in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Korean J Pediatr 2014; 57 (8): 351–356.
Albanna EA, Ahmed HS, Awad HA . Stool calprotectin in necrotizing enterocolitis. J Clin Neonatol 2014; 3 (1): 16–19.
Yost CC, Cody MJ, Harris ES, Thornton NL, McInturff AM, Martinez ML et al. Impaired neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation: a novel innate immune deficiency of human neonates. Blood 2009; 113 (25): 6419–6427.
Yost CC . Toward the 'ideal' inhibitor of NETs. Blood 2014; 123 (16): 2439–2440.
Urban CF, Ermert D, Schmid M, Abu-Abed U, Goosmann C, Nacken W et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contain calprotectin, a cytosolic protein complex involved in host defense against Candida albicans. PLoS Pathog 2009; 5 (10): e1000639.
Patel AL, Trivedi S, Bhandari NP, Ruf A, Scala CM, Witowitch G et al. Reducing necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants using quality-improvement methods. J Perinatol 2014; 34 (11): 850–857.
Henry E, Christensen RD, Sheffield MJ, Eggert LD, Carroll PD, Minton SD et al. Why do four NICUs using identical RBC transfusion guidelines have different gestational age-adjusted RBC transfusion rates? J Perinatol 2015; 35 (2): 132–136.
Christensen RD, Carroll PD, Josephson CD . Evidence-based advances in transfusion practice in neonatal intensive care units. Neonatology 2014; 106 (3): 245–253.
Baer VL, Lambert DK, Carroll PD, Gerday E, Christensen RD . Using umbilical cord blood for the initial blood tests of VLBW neonates results in higher hemoglobin and fewer RBC transfusions. J Perinatol 2013; 33 (5): 363–365.
McInturff AM, Cody MJ, Elliott EA, Glenn JW, Rowley JW, Rondina MT et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation via induction of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Blood 2012; 120 (15): 3118–3125.
Hutter JJ Jr, Hathaway WE, Wayne ER . Hematologic abnormalities in severe neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 1976; 88 (6): 1026–1031.
Kling PJ, Hutter JJ . Hematologic abnormalities in severe neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: 25 years later. J Perinatol 2003; 23 (7): 523–530.
Remon J, Kampanatkosol R, Kaul RR, Muraskas JK, Christensen RD, Maheshwari A . Acute drop in blood monocyte count differentiates NEC from other causes of feeding intolerance. J Perinatol 2014; 34 (7): 549–554.
Maheshwari A, Schelonka RL, Dimmitt RA, Carlo WA, Munoz-Hernandez B, Das A et al. Cytokines associated with necrotizing enterocolitis in extremely-low-birth-weight infants. Pediatr Res 2014; 76 (1): 100–108.
Ho TT, Groer MW, Luciano AA, Schwartz A, Ji M, Miladinovic BS et al. Red blood cell transfusions increase fecal calprotectin levels in premature infants. J Perinatol 2015; 35 (10): 837–841.
Gordon PV, Swanson JR, Clark R, Spitzer A . The complete blood cell count in a refined cohort of preterm NEC: the improtance of gestational age and day of diagnosis when using the CBC to estimate mortality. J Perinatol 2015; 36 (2): 121–125.
Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004; 303 (5663): 1532–1535.
Steinberg BE, Grinstein S . Unconventional roles of the NADPH oxidase: signaling, ion homeostasis, and cell death. Sci STKE 2007; 2007 (379): pe11.
Acknowledgements
We thank Diana Lim from the University of Utah Molecular Medicine Program for assistance with graphics. Research grants from the McKay-Dee Hospital Foundation and from Sigma Theta Tau International Honor Society of Nursing provided partial funding for the project. ARUP Laboratories, Salt Lake City, Utah, provided partial funding for the calprotectin assays. This work was supported, in part, by the US National Institutes of Health (K08HD049699 to CY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest. RS and JL are employees of ARUP Laboratories where the calprotectin assays were run.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Perinatology website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MacQueen, B., Christensen, R., Yost, C. et al. Elevated fecal calprotectin levels during necrotizing enterocolitis are associated with activated neutrophils extruding neutrophil extracellular traps. J Perinatol 36, 862–869 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2016.105
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2016.105
This article is cited by
-
Lipocalin 2 links inflammation and ankylosis in the clinical overlap of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS)
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2020)
-
Development of an improved murine model of necrotizing enterocolitis shows the importance of neutrophils in NEC pathogenesis
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Intestinal dysbiosis and necrotizing enterocolitis: assessment for causality using Bradford Hill criteria
Pediatric Research (2020)
-
Markers of neutrophil activation and extracellular traps formation are predictive of appendicitis in mice and humans: a pilot study
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Pediatric immunothrombosis—Understudied… but what potential!
Pediatric Research (2019)