Abstract
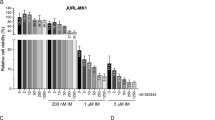
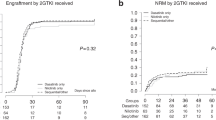
Grb2-associated binder 2 (Gab2) serves as a critical amplifier in the signaling network of Bcr-Abl, the driver of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Despite the success of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in CML treatment, TKI resistance, caused by mutations in Bcr-Abl or aberrant activity of its network partners, remains a clinical problem. Using inducible expression and knockdown systems, we analyzed the role of Gab2 in Bcr-Abl signaling in human CML cells, especially with respect to TKI sensitivity. We show for the first time that Gab2 signaling protects CML cells from various Bcr-Abl inhibitors (imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib and GNF-2), whereas Gab2 knockdown or haploinsufficiency leads to increased TKI sensitivity. We dissected the underlying molecular mechanism using various Gab2 mutants and kinase inhibitors and identified the Shp2/Ras/ERK and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR axes as the two critical signaling pathways. Gab2-mediated TKI resistance was associated with persistent phosphorylation of Gab2 Y452, a PI3K recruitment site, and consistent with this finding, the protective effect of Gab2 was completely abolished by the combination of dasatinib with the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235. The identification of Gab2 as a novel modulator of TKI sensitivity in CML suggests that Gab2 could be exploited as a biomarker and therapeutic target in TKI-resistant disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Hare T, Deininger MW, Eide CA, Clackson T, Druker BJ . Targeting the BCR-ABL signaling pathway in therapy-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 212–221.
Pendergast AM, Quilliam LA, Cripe LD, Bassing CH, Dai Z, Li N et al. BCR-ABL-induced oncogenesis is mediated by direct interaction with the SH2 domain of the GRB-2 adaptor protein. Cell 1993; 75: 175–185.
Hantschel O, Superti-Furga G . Regulation of the c-Abl and Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 33–44.
Sattler M, Mohi MG, Pride YB, Quinnan LR, Malouf NA, Podar K et al. Critical role for Gab2 in transformation by BCR/ABL. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 479–492.
Brehme M, Hantschel O, Colinge J, Kaupe I, Planyavsky M, Kocher T et al. Charting the molecular network of the drug target Bcr-Abl. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009; 106: 7414–7419.
Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2408–2417.
Sharma SV, Gajowniczek P, Way IP, Lee DY, Jiang J, Yuza Y et al. A common signaling cascade may underlie "addiction" to the Src, BCR-ABL, and EGF receptor oncogenes. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 425–435.
Bixby D, Talpaz M . Seeking the causes and solutions to imatinib-resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2011; 25: 7–22.
Quintas-Cardama A, Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE . Mechanisms of primary and secondary resistance to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Control 2009; 16: 122–131.
Zhang J, Adrian FJ, Jahnke W, Cowan-Jacob SW, Li AG, Iacob RE et al. Targeting Bcr-Abl by combining allosteric with ATP-binding-site inhibitors. Nature 2010; 463: 501–506.
Donato NJ, Wu JY, Stapley J, Gallick G, Lin H, Arlinghaus R et al. BCR-ABL independence and LYN kinase overexpression in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells selected for resistance to STI571. Blood 2003; 101: 690–698.
Grosso S, Puissant A, Dufies M, Colosetti P, Jacquel A, Lebrigand K et al. Gene expression profiling of imatinib and PD166326-resistant CML cell lines identifies Fyn as a gene associated with resistance to BCR-ABL inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8: 1924–1933.
Scherr M, Chaturvedi A, Battmer K, Dallmann I, Schultheis B, Ganser A et al. Enhanced sensitivity to inhibition of SHP2, STAT5, and Gab2 expression in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Blood 2006; 107: 3279–3287.
Wöhrle FU, Daly RJ, Brummer T . Function, regulation and pathological roles of the Gab/DOS docking proteins. Cell Commun Signal 2009; 7: 22.
Harkiolaki M, Tsirka T, Lewitzky M, Simister PC, Joshi D, Bird LE et al. Distinct binding modes of two epitopes in Gab2 that interact with the SH3C domain of Grb2. Structure 2009; 17: 809–822.
Wada T, Nakashima T, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Gasser J, Hara H, Schett G et al. The molecular scaffold Gab2 is a crucial component of RANK signaling and osteoclastogenesis. Nat Med 2005; 11: 394–399.
Gu H, Saito K, Klaman LD, Shen J, Fleming T, Wang Y et al. Essential role for Gab2 in the allergic response. Nature 2001; 412: 186–190.
Li G, Wang Z, Miskimen KL, Zhang Y, Tse W, Bunting KD . Gab2 promotes hematopoietic stem cell maintenance and self-renewal synergistically with STAT5. PLoS One 2010; 5: e9152.
Zhang Y, Diaz-Flores E, Li G, Wang Z, Kang Z, Haviernikova E et al. Abnormal hematopoiesis in Gab2 mutant mice. Blood 2007; 110: 116–124.
Lynch DK, Daly RJ . PKB-mediated negative feedback tightly regulates mitogenic signalling via Gab2. EMBO J 2002; 21: 72–82.
Brummer T, Larance M, Abreu MT, Lyons RJ, Timpson P, Emmerich CH et al. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of 14-3-3 terminates signalling by the Gab2 docking protein. EMBO J 2008; 27: 2305–2316.
Abreu MT, Hughes WE, Mele K, Lyons RJ, Rickwood D, Browne BC et al. Gab2 regulates cytoskeletal organization and migration of mammary epithelial cells by modulating RhoA activation. Mol Biol Cell 2011; 22: 105–116.
Mohi MG, Williams IR, Dearolf CR, Chan G, Kutok JL, Cohen S et al. Prognostic, therapeutic, and mechanistic implications of a mouse model of leukemia evoked by Shp2 (PTPN11) mutations. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 179–191.
Xu D, Wang S, Yu WM, Chan G, Araki T, Bunting KD et al. A germline gain-of-function mutation in Ptpn11 (Shp-2) phosphatase induces myeloproliferative disease by aberrant activation of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 2010; 116: 3611–3621.
Aumann K, Lassmann S, Schopflin A, May AM, Wohrle FU, Zeiser R et al. The immunohistochemical staining pattern of Gab2 correlates with distinct stages of chronic myeloid leukemia. Hum Pathol 2011; 42: 719–726.
Brummer T, Schramek D, Hayes VM, Bennett HL, Caldon CE, Musgrove EA et al. Increased proliferation and altered growth factor dependence of human mammary epithelial cells overexpressing the Gab2 docking protein. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 626–637.
Radich JP, Dai H, Mao M, Oehler V, Schelter J, Druker B et al. Gene expression changes associated with progression and response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006; 103: 2794–2799.
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB et al. Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18 000 cancer gene expression profiles. Neoplasia 2007; 9: 166–180.
Quintas-Cardama A, Qiu YH, Post SM, Zhang Y, Creighton CJ, Cortes J et al. Reverse phase protein array profiling reveals distinct proteomic signatures associated with chronic myeloid leukemia progression and with chronic phase in the CD34-positive compartment. Cancer 2012; e-pub ahead of print 19 April 2012; doi:10.1002/cncr.27568.
Barretina J, Caponigro G, Stransky N, Venkatesan K, Margolin AA, Kim S et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012; 483: 603–607.
Dorsey JF, Cunnick JM, Mane SM, Wu J . Regulation of the Erk2-Elk1 signaling pathway and megakaryocytic differentiation of Bcr-Abl(+) K562 leukemic cells by Gab2. Blood 2002; 99: 1388–1397.
Herr R, Wohrle FU, Danke C, Berens C, Brummer T . A novel MCF-10A line allowing conditional oncogene expression in 3D culture. Cell Commun Signal 2011; 9: 17.
Wu J, Meng F, Lu H, Kong L, Bornmann W, Peng Z et al. Lyn regulates BCR-ABL and Gab2 tyrosine phosphorylation and c-Cbl protein stability in imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood 2008; 111: 3821–3829.
Dai Y, Rahmani M, Corey SJ, Dent P, Grant S . A Bcr/Abl-independent, Lyn-dependent form of imatinib mesylate (STI-571) resistance is associated with altered expression of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 34227–34239.
Burchert A, Wang Y, Cai D, von Bubnoff N, Paschka P, Muller-Brusselbach S et al. Compensatory PI3-kinase/Akt/mTor activation regulates imatinib resistance development. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1774–1782.
Bennett HL, Brummer T, Jeanes A, Yap AS, Daly RJ . Gab2 and Src co-operate in human mammary epithelial cells to promote growth factor independence and disruption of acinar morphogenesis. Oncogene 2008; 27: 2693–2704.
O’Hare T, Eide CA, Deininger MW . Bcr-Abl kinase domain mutations, drug resistance, and the road to a cure for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2007; 110: 2242–2249.
Samanta A, Perazzona B, Chakraborty S, Sun X, Modi H, Bhatia R et al. Janus kinase 2 regulates Bcr-Abl signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2011; 25: 463–472.
Roelz R, Pilz IH, Mutschler M, Pahl HL . Of mice and men: human RNA polymerase III promoter U6 is more efficient than its murine homologue for shRNA expression from a lentiviral vector in both human and murine progenitor cells. Exp Hematol 2010; 38: 792–797.
Hiwase DK, White DL, Powell JA, Saunders VA, Zrim SA, Frede AK et al. Blocking cytokine signaling along with intense Bcr-Abl kinase inhibition induces apoptosis in primary CML progenitors. Leukemia 2010; 24: 771–778.
Maira SM, Stauffer F, Brueggen J, Furet P, Schnell C, Fritsch C et al. Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 1851–1863.
Mohi MG, Boulton C, Gu TL, Sternberg DW, Neuberg D, Griffin JD et al. Combination of rapamycin and protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) inhibitors for the treatment of leukemias caused by oncogenic PTKs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004; 101: 3130–3135.
Warsch W, Kollmann K, Eckelhart E, Fajmann S, Cerny-Reiterer S, Holbl A et al. High STAT5 levels mediate imatinib resistance and indicate disease progression in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011; 117: 3409–3420.
Wu J, Meng F, Kong LY, Peng Z, Ying Y, Bornmann WG et al. Association between imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutation-negative leukemia and persistent activation of LYN kinase. J Natl Cancer Inst 2008; 100: 926–939.
Futami M, Zhu QS, Whichard ZL, Xia L, Ke Y, Neel BG et al. G-CSF receptor activation of the Src kinase Lyn is mediated by Gab2 recruitment of the Shp2 phosphatase. Blood 2011; 118: 1077–1086.
Schmidt T, Kharabi Masouleh B, Loges S, Cauwenberghs S, Fraisl P, Maes C et al. Loss or inhibition of stromal-derived PlGF prolongs survival of mice with imatinib-resistant Bcr-Abl1(+) leukemia. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 740–753.
Peng Z, Luo HW, Yuan Y, Shi J, Huang SF, Li CL et al. Growth of chronic myeloid leukemia cells is inhibited by infection with Ad-SH2-HA adenovirus that disrupts Grb2-Bcr-Abl complexes. Oncol Rep 2011; 25: 1381–1388.
Modi H, Li L, Chu S, Rossi J, Yee JK, Bhatia R . Inhibition of Grb2 expression demonstrates an important role in BCR-ABL-mediated MAPK activation and transformation of primary human hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 2011; 25: 305–312.
Cheng AM, Saxton TM, Sakai R, Kulkarni S, Mbamalu G, Vogel W et al. Mammalian Grb2 regulates multiple steps in embryonic development and malignant transformation. Cell 1998; 95: 793–803.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Alexander Kühnemund and members of the Brummer laboratory for helpful discussions, Andreas Geissler for advice on the caspase assays and Katja Thurig, Christine Capri and Jennifer Schwarz for technical assistance. TB is supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) through the Emmy-Noether-Program (BR3662/1-1) and EXC 294 BIOSS. FUW is funded by the Excellence Initiative of the DFG (GSC-4; Spemann Graduate School for Biology and Medicine) and EXC 294 BIOSS. RZ is supported by the DFG (ZE 872/1–1 and Heisenberg Fellowship ZE 872/2–1). SL, MW, RZ and TB are also supported by the DFG funded Collaborative Research Center 850. HLP gratefully acknowledges support by the DFG (Pa 611/5-1 and Pa 611/6-1) as well as the NIH (PO1 CA108671). RJD is supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. DS is supported by the Austrian Academy of Sciences through an APART fellowship. KA is supported by a fellowship of the medical faculty of the University of Freiburg.
Author contributions
FUW, SH, SS and SB performed all cellular and biochemical experiments. KA conducted the IHC analyses. KA, SL, HLP, MW, CFW and RZ provided clinical samples and expertise. PA, DS and JMP provided critical reagents and mice. All authors contributed to the design, analysis and discussion of experiments. TB wrote the manuscript together with FUW, SH and RJD. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wöhrle, F., Halbach, S., Aumann, K. et al. Gab2 signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia cells confers resistance to multiple Bcr-Abl inhibitors. Leukemia 27, 118–129 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.222
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.222
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mast cell deficiency prevents BCR::ABL1 induced splenomegaly and cytokine elevation in a CML mouse model
Leukemia (2023)
-
Gab2 deficiency prevents Flt3-ITD driven acute myeloid leukemia in vivo
Leukemia (2022)
-
SRSF1 mediates cytokine-induced impaired imatinib sensitivity in chronic myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2020)
-
BRAF inhibition upregulates a variety of receptor tyrosine kinases and their downstream effector Gab2 in colorectal cancer cell lines
Oncogene (2018)
-
Protein-Dysregulationen in humanen und murinen myeloproliferativen Neoplasien
Der Pathologe (2018)