Abstract
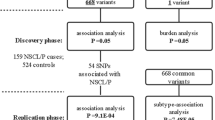
We conducted a genome-wide association study for nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate (NSCL/P) in 401 affected individuals and 1,323 controls, with replication in an independent sample of 793 NSCL/P triads. We report two new loci associated with NSCL/P at 17q22 (rs227731, combined P = 1.07 × 10−8, relative risk in homozygotes = 1.84, 95% CI 1.34–2.53) and 10q25.3 (rs7078160, combined P = 1.92 × 10−8, relative risk in homozygotes = 2.17, 95% CI 1.32–3.56).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Accessions
NCBI Reference Sequence
References
Birnbaum, S. et al. Nat. Genet. 41, 473–477 (2009).
Rahimov, F. et al. Nat. Genet. 40, 1341–1347 (2008).
Guo, C.Y. et al. Genet. Epidemiol. 33, 54–62 (2009).
Zhang, Z. et al. Development 129, 4135–4146 (2002).
Suzuki, S. et al. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 84, 406–411 (2009).
Hallonet, M. et al. Genes Dev. 13, 3106–3114 (1999).
Petersen, B. et al. Am. J. Med. Genet. 77, 60–62 (1998).
Mulcahy, M.T. et al. Clin. Genet. 21, 33–35 (1982).
Welsh, I.C. et al. Mech. Dev. 124, 746–761 (2007).
Goodnough, L.H. et al. Dev. Dyn. 236, 1918–1928 (2007).
Vieira, A.R. et al. PLoS Genet. 1, e64 (2005).
Drieschner, N. et al. Gene 403, 110–117 (2007).
Yunis, E. et al. Hum. Genet. 48, 241–244 (1979).
Magee, A.C. et al. Clin. Genet. 54, 65–69 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank all affected individuals and their families for their participation in this study as well as the German support group for people with cleft lip and/or palate (Deutsche Selbsthilfevereinigung für Lippen-Gaumen-Fehlbildungen e.V.). We acknowledge our collaborating clinical partners, all colleagues who contributed to the European Collaboration on Craniofacial Anomalies (EUROCRAN) project, our laboratory technicians and colleagues responsible for database management (for a complete list of all individuals see Supplementary Note). The study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (FOR 423 and individual grants MA 2546/3-1, KR 1912/7-1, NO 246/6-1 and WI 1555/5-1). The Heinz Nixdorf Recall cohort was established with the generous support of the Heinz Nixdorf Foundation, Germany (Chairman: G. Schmidt). POPGEN biobank is financed by the local Ministry of Science, Economy and Transport of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The Kooperative Gesundheitforschung in der Region Augsburg (KORA) research platform was initiated and financed by the Helmholtz Center Munich, German Research Center for Environmental Health, which is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research and by the state of Bavaria. The work of KORA is supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) in the context of the German National Genome Research Network (NGFN-2 and NGFN-plus). The EUROCRAN study was supported by the European Commission FP5 (contract no. QLG1-CT-2000-01019), and the ITALCLEFT study was supported by a FAR-2008 grant from the University of Ferrara, Italy. N.A.d.A. is supported by the Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa (CNPq), Brasil. T.A.C. is supported by a grant from the Ministry of Higher Education, Syrian Arab Republic. Additional acknowledgments are found in the Supplementary Note.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.M., F.-J.K., T.F.W., P.P. and M.M.N. initiated the study. E.M., S. Birnbaum, K.U.L., P.H., M. Knapp, M.R., P.A.M. and M.M.N. contributed to the study design. M.M.N., E.M., S.C., P.H., K.U.L. and S. Birnbaum coordinated the work and prepared the manuscript, with feedback from the other authors. S. Birnbaum., H.R., A.P., C.L., G.S., M. Scheer., B. Braumann, R.H.R., A.H., S.P., B. Blaumeiser, R.P.S.-T., F.-J.K., M.R. and P.A.M. clinically characterized the cleft families and collected blood samples. S.M., M. Krawczak, S.S., T.M. and E.M. characterized and recruited the controls. K.U.L., C.B., M.F., N.A.d.A., T.A.C., S. Barth, N.K. and J.B. prepared the DNA and performed the molecular genetic experiments. M. Knapp., S.H., M. Steffens and M.M. conducted the statistical analysis. M.M.N., E.M., M. Knapp., T.F.W., S. Birnbaum, K.U.L., M.R. and P.P. analyzed and interpreted the data.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3, Supplementary Tables 1–4, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Note (PDF 602 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mangold, E., Ludwig, K., Birnbaum, S. et al. Genome-wide association study identifies two susceptibility loci for nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Nat Genet 42, 24–26 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.506
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.506
This article is cited by
-
Genetic association and functional validation of ZFP36L2 in non-syndromic orofacial cleft subtypes
Journal of Human Genetics (2024)
-
Global perspectives in orofacial cleft management and research
British Dental Journal (2023)
-
Using whole exome sequencing to identify susceptibility genes associated with nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2023)
-
Rare variant modifier analysis identifies variants in SEC24D associated with orofacial cleft subtypes
Human Genetics (2023)
-
Allele-specific transcription factor binding in a cellular model of orofacial clefting
Scientific Reports (2022)