Abstract
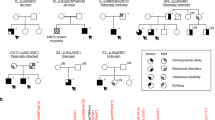
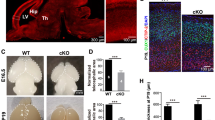
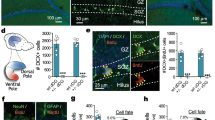
Disruption of human neural precursor proliferation can give rise to a small brain (microcephaly), and failure of neurons to migrate properly can lead to an abnormal arrest of cerebral cortical neurons in proliferative zones near the lateral ventricles (periventricular heterotopia). Here we show that an autosomal recessive condition characterized by microcephaly and periventricular heterotopia1 maps to chromosome 20 and is caused by mutations in the gene ADP-ribosylation factor guanine nucleotide-exchange factor-2 (ARFGEF2). By northern-blot analysis, we found that mouse Arfgef2 mRNA levels are highest during embryonic periods of ongoing neuronal proliferation and migration, and by in situ hybridization, we found that the mRNA is widely distributed throughout the embryonic central nervous system (CNS). ARFGEF2 encodes the large (>200 kDa) brefeldin A (BFA)-inhibited GEF2 protein (BIG2), which is required for vesicle and membrane trafficking from the trans-Golgi network (TGN). Inhibition of BIG2 by BFA, or by a dominant negative ARFGEF2 cDNA, decreases cell proliferation in vitro, suggesting a cell-autonomous regulation of neural expansion. Inhibition of BIG2 also disturbed the intracellular localization of such molecules as E-cadherin and β-catenin by preventing their transport from the Golgi apparatus to the cell surface. Our findings show that vesicle trafficking is an important regulator of proliferation and migration during human cerebral cortical development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheen, V.L. et al. Autosomal recessive form of periventricular heterotopia. Neurology 60, 1108–1112 (2003).
Yamaji, R. et al. Identification and localization of two brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins for ADP-ribosylation factors in a macromolecular complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2567–2572 (2000).
Pacheco-Rodriguez, G., Moss, J. & Vaughan, M. BIG1 and BIG2: brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins for ADP-ribosylation factors. Methods Enzymol. 345, 397–404 (2002).
Togawa, A., Morinaga, N., Ogasawara, M., Moss, J. & Vaughan, M. Purification and cloning of a brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein for ADP-ribosylation factors. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 12308–12315 (1999).
Shinotsuka, C., Waguri, S., Wakasugi, M., Uchiyama, Y. & Nakayama, K. Dominant-negative mutant of BIG2, an ARF-guanine nucleotide exchange factor, specifically affects membrane trafficking from the trans-Golgi network through inhibiting membrane association of AP-1 and GGA coat proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 294, 254–260 (2002).
Shinotsuka, C., Yoshida, Y., Kawamoto, K., Takatsu, H. & Nakayama, K. Overexpression of an ADP-ribosylation factor-guanine nucleotide exchange factor, BIG2, uncouples brefeldin A-induced adaptor protein-1 coat dissociation and membrane tubulation. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 9468–9473 (2002).
Shevell, D.E. et al. EMB30 is essential for normal cell division, cell expansion, and cell adhesion in Arabidopsis and encodes a protein that has similarity to Sec7. Cell 77, 1051–1062 (1994).
Bonifacino, J.S. & Jackson, C.L. Endosome-specific localization and function of the ARF activator GNOM. Cell 112, 141–142 (2003).
Geldner, N. et al. The Arabidopsis GNOM ARF-GEF mediates endosomal recycling, auxin transport, and auxin-dependent plant growth. Cell 112, 219–230 (2003).
Poon, P.P., Nothwehr, S.F., Singer, R.A. & Johnston, G.C. The Gcs1 and Age2 ArfGAP proteins provide overlapping essential function for transport from the yeast trans-Golgi network. J. Cell Biol. 155, 1239–1250 (2001).
Ruthel, G. & Banker, G. Role of moving growth cone-like “wave” structures in the outgrowth of cultured hippocampal axons and dendrites. J. Neurobiol. 39, 97–106 (1999).
Jareb, M. & Banker, G. Inhibition of axonal growth by brefeldin A in hippocampal neurons in culture. J. Neurosci. 17, 8955–8963 (1997).
Reynolds, B.A. & Weiss, S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science 255, 1707–1710 (1992).
Wichterle, H., Garcia-Verdugo, J.M. & Alvarez-Buylla, A. Direct evidence for homotypic, glia-independent neuronal migration. Neuron 18, 779–791 (1997).
Doms, R.W., Russ, G. & Yewdell, J.W. Brefeldin A redistributes resident and itinerant Golgi proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 109, 61–72 (1989).
Schroeter, E.H., Kisslinger, J.A. & Kopan, R. Notch-1 signalling requires ligand-induced proteolytic release of intracellular domain. Nature 393, 382–386 (1998).
Peng, C.Y., Manning, L., Albertson, R. & Doe, C.Q. The tumour-suppressor genes lgl and dlg regulate basal protein targeting in Drosophila neuroblasts. Nature 408, 596–600 (2000).
Klymkowsky, M.W. & Parr, B. The body language of cells: the intimate connection between cell adhesion and behavior. Cell 83, 5–8 (1995).
Chenn, A. & Walsh, C.A. Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural precursors. Science 297, 365–369 (2002).
Roberts, E. et al. Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly: an analysis of locus heterogeneity and phenotypic variation. J. Med. Genet. 39, 718–721 (2002).
Bond, J. et al. ASPM is a major determinant of cerebral cortical size. Nat. Genet. 32, 316–320 (2002).
Sheen, V.L. & Walsh, C.A. Developmental genetic malformations of the cerebral cortex. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 3, 433–441 (2003).
Fox, J.W. et al. Mutations in filamin 1 prevent migration of cerebral cortical neurons in human periventricular heterotopia. Neuron 21, 1315–1325 (1998).
Kruglyak, L., Daly, M.J., Reeve-Daly, M.P. & Lander, E.S. Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 58, 1347–1363 (1996).
Berger, U.V. & Hediger, M.A. Differential distribution of the glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in tanycytes of the third ventricle. J. Comp. Neurol. 433, 101–114 (2001).
Borghesani, P.R. et al. BDNF stimulates migration of cerebellar granule cells. Development 129, 1435–1442 (2002).
Sheen, V.L., Arnold, M.W., Wang, Y. & Macklis, J.D. Neural precursor differentiation following transplantation into neocortex is dependent on intrinsic developmental state and receptor competence. Exp. Neurol. 158, 47–62 (1999).
Sheen, V.L. & Macklis, J.D. Apoptotic mechanisms in targeted neuronal cell death by chromophore-activated photolysis. Exp. Neurol. 130, 67–81 (1994).
Lu, Q. et al. delta-catenin, an adhesive junction-associated protein which promotes cell scattering. J. Cell Biol. 144, 519–532 (1999).
Sheen, V.L. et al. Filamin A and Filamin B are co-expressed within neurons during periods of neuronal migration and can physically interact. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 2845–2854 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Nakayama and H.-W. Shin for providing the BIG-2 dominant-negative and wild-type constructs. This work was supported by grants to C.A.W. from the US National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the March of Dimes and the McKnight Foundation. C.A.W. is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. V.L.S. is supported by a grant from the US National Institute of Mental Health and is a Charles A. Dana fellow and Clinical Investigators Training Program fellow for the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and the Harvard/Massachusetts Institute of Technology Division of Health Sciences and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheen, V., Ganesh, V., Topcu, M. et al. Mutations in ARFGEF2 implicate vesicle trafficking in neural progenitor proliferation and migration in the human cerebral cortex. Nat Genet 36, 69–76 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1276
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1276
This article is cited by
-
Expression analysis of type I ARF small GTPases ARF1-3 during mouse brain development
Molecular Biology Reports (2024)
-
Inhibition of Foxp4 Disrupts Cadherin-based Adhesion of Radial Glial Cells, Leading to Abnormal Differentiation and Migration of Cortical Neurons in Mice
Neuroscience Bulletin (2023)
-
How mechanisms of stem cell polarity shape the human cerebral cortex
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2022)
-
Golgipathies reveal the critical role of the sorting machinery in brain and skeletal development
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Dominant ARF3 variants disrupt Golgi integrity and cause a neurodevelopmental disorder recapitulated in zebrafish
Nature Communications (2022)