Abstract
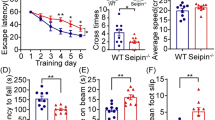
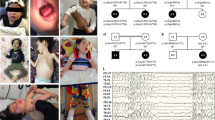
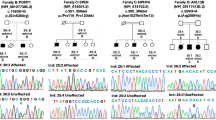
Distal hereditary motor neuropathy (dHMN) or distal spinal muscular atrophy (OMIM #182960) is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by an almost exclusive degeneration of motor nerve fibers, predominantly in the distal part of the limbs1. Silver syndrome (OMIM #270685) is a rare form of hereditary spastic paraparesis mapped to chromosome 11q12–q14 (SPG17) in which spasticity of the legs is accompanied by amyotrophy of the hands and occasionally also the lower limbs2,3. Silver syndrome and most forms of dHMN are autosomal dominantly inherited with incomplete penetrance and a broad variability in clinical expression. A genome-wide scan in an Austrian family with dHMN-V (ref. 4) showed linkage to the locus SPG17, which was confirmed in 16 additional families with a phenotype characteristic of dHMN or Silver syndrome. After refining the critical region to 1 Mb, we sequenced the gene Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy (BSCL2) and identified two heterozygous missense mutations resulting in the amino acid substitutions N88S and S90L. Null mutations in BSCL2, which encodes the protein seipin, were previously shown to be associated with autosomal recessive Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy5 (OMIM #269700). We show that seipin is an integral membrane protein of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The amino acid substitutions N88S and S90L affect glycosylation of seipin and result in aggregate formation leading to neurodegeneration.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harding, A.E. Hereditary spastic paraplegias. Semin. Neurol. 13, 333–336 (1993).
Silver, J.R. Familial spastic paraplegia with amyotrophy of the hands. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 29, 135–144 (1966).
Patel, H. et al. The Silver syndrome variant of hereditary spastic paraplegia maps to chromosome 11q12-q14, with evidence for genetic heterogeneity within this subtype. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69, 209–215 (2001).
Auer-Grumbach, M. et al. Phenotypic and genotypic heterogeneity in hereditary motor neuronopathy type V: a clinical, electrophysiological and genetic study. Brain 123, 1612–1623 (2000).
Magré, J. et al. Identification of the gene altered in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy on chromosome 11q13. Nat. Genet. 28, 3665–370 (2001).
Windpassinger, C. et al. Refinement of the “Silver syndrome locus” on chromosome 11q12-q14 in four families and exclusion of eight candidate genes. Hum. Genet. 114, 99–109 (2003).
Van Maldergem, L. et al. Genotype-phenotype relationships in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy. J. Med. Genet. 39, 722–33 (2002).
Helenius, A. & Aebi, M. Intracellular functions of N-linked glycans. Science 291, 2364–2369 (2001).
Kopito, R.R. Aggresomes, inclusion bodies and protein aggregation. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 524–530 (2000).
Garcia-Mata, R., Gao, Y.-S. & Sztul, E. Hassels with taking out the garbage: Aggravatine aggresomes. Traffic 3, 388–396 (2002).
Johnston, J.A., Ward, C.L. & Kopito, R.R. Aggresomes: A cellular response to misfolded proteins. J. Cell Biol. 143, 1883–1898 (1998).
Christodoulou, K. et al. Mapping of a distal form of spinal muscular atrophy with upper limb predominance to chromosome 7p. Hum. Mol. Genet. 4, 1629–1632 (1995).
Antonellis, A. et al. Glycyl tRNA synthetase mutations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2D and distal spinal muscular atrophy type V. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72, 1293–1299 (2003).
Ryan, M.C., Shooter, E.M. & Notterpeck, L. Aggresome formation in neuropathy models based on peripheral myelin protein 22 mutations. Neurobiol. Dis. 10, 109–118 (2002).
Lee, M.J. et al. Hereditary sensory neuropathy is caused by a mutation in the delta subunit of the cytosolic chaperonin-containing t-complex peptide-1 (Cct4) gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12, 1917–1925 (2003).
Johnston, J.A., Dalton, M.J., Gurney, M.E. & Kopito, R.R. Formation of high molecular weight complexes of mutant Cu, ZN-superoxide dismutase in a mouse model for familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 12571–12576 (2000).
Saliba, R.S., Munro, P.M., Luthert, P.J. & Cheetham, M.E. The cellular fate of mutant rhodopsin: quality control, degradation and aggresome formation. J. Cell Sci. 115, 2907–2918 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank the affected individuals and their family members for their participation; H. Offenbacher, A. Irmler and R. Fischer for their contribution in recruiting the families; A. Krenn and A. Legenstein for technical assistance; and W. Graier and E. Steyrer for critical discussion of the manuscript. This research project was supported by the Muscular Dystrophy Association, USA; the Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung, Austria; the Tom-Wahlig-Stiftung Jena, Germany; the Fachabteilung 6A - Wissenschaft und Forschung of the Land Steiermark; the Birth Defects Foundation, UK; the University of Antwerp, the Fund for Scientific Research - Flanders; the Medical Foundation Queen Elisabeth; the Association Belge contre les Maladies Neuromusculaires, and the Interuniversity Attraction Poles programme of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office, Belgium. I.D. and N.V. are supported by Ph.D. fellowships of the Institute for Science and Technology, Belgium. The Institutes of Medical Biology and Human Genetics and of Medical Biochemistry & Medical Molecular Biology are members of the Institutes of Basic Medical Sciences at the University of Graz and were supported by the infrastructure program of the Austrian ministry of education, science and culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Windpassinger, C., Auer-Grumbach, M., Irobi, J. et al. Heterozygous missense mutations in BSCL2 are associated with distal hereditary motor neuropathy and Silver syndrome. Nat Genet 36, 271–276 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1313
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1313
This article is cited by
-
Liver X receptor-agonist treatment rescues degeneration in a Drosophila model of hereditary spastic paraplegia
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2022)
-
Heterozygous deletion of Seipin in islet beta cells of male mice has an impact on insulin synthesis and secretion through reduced PPARγ expression
Diabetologia (2020)
-
Update on the Genetics of Spastic Paraplegias
Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports (2019)
-
Female adipose tissue-specific Bscl2 knockout mice develop only moderate metabolic dysfunction when housed at thermoneutrality and fed a high-fat diet
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Targeted next-generation sequencing improves diagnosis of hereditary spastic paraplegia in Chinese patients
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2018)