Abstract
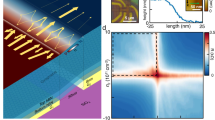
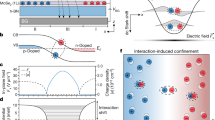
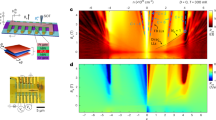
The observation of quantum conductance oscillations in mesoscopic systems has traditionally required the confinement of the carriers to a phase space of reduced dimensionality1,2,3,4. Although electron optics such as lensing5 and focusing6 have been demonstrated experimentally, building a collimated electron interferometer in two unconfined dimensions has remained a challenge owing to the difficulty of creating electrostatic barriers that are sharp on the order of the electron wavelength7. Here, we report the observation of conductance oscillations in extremely narrow graphene heterostructures where a resonant cavity is formed between two electrostatically created bipolar junctions. Analysis of the oscillations confirms that p–n junctions have a collimating effect on ballistically transmitted carriers8. The phase shift observed in the conductance fringes at low magnetic fields is a signature of the perfect transmission of carriers normally incident on the junctions9 and thus constitutes a direct experimental observation of ‘Klein tunnelling’10,11,12.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Wees, B. J. et al. Observation of zero-dimensional states in a one-dimensional electron interferometer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 2523–2526 (1989).
Ji, Y. et al. An electronic Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Nature 422, 415–418 (2003).
Liang, W. et al. Fabry–Perot interference in a nanotube electron waveguide. Nature 411, 665–669 (2001).
Miao, F. et al. Phase-coherent transport in graphene quantum billiards. Science 317, 1530–1533 (2007).
Spector, J., Stormer, H. L., Baldwin, K. W., Pfeiffer, L. N. & West, K. W. Electron focusing in two-dimensional systems by means of an electrostatic lens. Appl. Phys. Lett. 56, 1290–1292 (1990).
van Houten, H. & Beenakker, C. W. J. in Analogies in Optics and Micro Electronics (eds van Haeringen, W. & Lenstra, D.) (Kluwer, 1990).
Washburn, S., Fowler, A. B., Schmid, H. & Kern, D. Possible observation of transmission resonances in GaAs–AlxGa1−x As transistors. Phys. Rev. B 38, 1554–1557 (1988).
Cheianov, V. V. & Fal’ko, V. I. Selective transmission of Dirac electrons and ballistic magnetoresistance of n–p junctions in graphene. Phys. Rev. B 74, 041403(R) (2006).
Shytov, A. V., Rudner, M. S. & Levitov, L. S. Klein backscattering and Fabry–Perot interference in graphene heterojunctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 156804 (2008).
Katsnelson, M. I., Novoselov, K. S. & Geim, A. K. Chiral tunnelling and the Klein paradox in graphene. Nature Phys. 2, 620–625 (2006).
Klein, O. Die Reflexion von Elektronen an einem Potentialsprung nach der relativistischen Dynamik von Dirac. Z. Phys. 53, 157–165 (1929).
Sauter, F. Über das Verhalten eines Elektrons im homogenen elektrischen Feld nach der relativistischen Theorie Diracs. 69 742–764 (1931).
Ando, T. & Nakanishi, T. Impurity scattering in carbon nanotubes: Absence of backscattering. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 67, 1704–1713 (1998).
Cheianov, V. V., Fal’ko, V. I. & Altshuler, B. L. The focusing of electron flow and a Veselago lens in graphene p–n junctions. Science 315, 1252–1255 (2007).
Park, C.-H. et al. Anisotropic behaviours of massless Dirac fermions in graphene under periodic potentials. Nature Phys. 4, 213–217 (2008).
Park, C.-H. et al. Electron beam supercollimation in graphene superlattices. Nano Lett. 8, 2920–2924 (2008).
Garcia-Pomar, J. L., Cortijo, A. & Nieto-Vesperinas, M. Fully valley-polarized electron beams in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 236801 (2008).
Lemme, M. C., Echtermeyer, T. J., Baus, M. & Kurz, H. A graphene field effect device. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 28, 282–284 (2007).
Huard, B. et al. Transport measurements across a tunable potential barrier in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 236803 (2007).
Williams, J. R., DiCarlo, L. & Marcus, C. M. Quantum Hall effect in a gate-controlled p–n junction of graphene. Science 317, 638–641 (2007).
Özyilmaz, B. et al. Electronic transport and quantum Hall effect in bipolar graphene p–n–p junctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 166804 (2007).
Gorbachev, R. V., Mayorov, A. S., Savchenko, A. K., Horsell, D. W. & Guinea, F. Conductance of p–n–p graphene structures with air-bridge top gates. Nano Lett. 8, 1995–1999 (2008).
Liu, G., Velasco, J., Bao, W. & Lau, C. N. Fabrication of graphene p–n–p junctions with contactless top gates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 203103 (2008).
Stander, N., Huard, B. & Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Evidence of Klein tunneling in graphene p–n junctions. Preprint at <http://arxiv.org/abs/0806.2319> (2008).
Meric, I. et al. Current saturation in zero-bandgap, top-gated graphene field-effect transistors. Nature Nanotech. 3, 654–659 (2008).
Zhang, L. M. & Fogler, M. M. Nonlinear screening and ballistic transport in a graphene p–n junction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 116804 (2008).
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 438, 197–200 (2005).
Zhang, Y., Tan, Y. W., Stormer, H. L. & Kim, P. Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry’s phase in graphene. Nature 438, 201–204 (2005).
Ryu, S. et al. Reversible basal plane hydrogenation of graphene. Nano Lett. 8, 4597–4602 (2008).
Bolotin, K. I. et al. Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene. Solid State Commun. 146, 351–355 (2008).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank I. L. Aleiner, K. I. Bolotin, M. Y. Han, E. A. Henriksen, L. S. Levitov and H. L. Stormer for discussions, and I. Meric and M. Y. Han for help with sample preparation. This work is supported by the ONR (No. N000150610138), FENA, NRI, NSEC (No. CHE-0117752) and NYSTAR. Sample preparation was supported by the DOE (DE-FG02-05ER46215).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Informations (PDF 1027 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, A., Kim, P. Quantum interference and Klein tunnelling in graphene heterojunctions. Nature Phys 5, 222–226 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1198
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1198
This article is cited by
-
Giant orbital magnetic moments and paramagnetic shift in artificial relativistic atoms and molecules
Nature Nanotechnology (2023)
-
Ballistic transport spectroscopy of spin-orbit-coupled bands in monolayer graphene on WSe2
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Massive Dirac electrons in a Kronig–Penney potential: dispersion relation and transmission properties
Indian Journal of Physics (2023)
-
Spin-polarized and possible pseudospin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy in kagome metal FeSn
Communications Physics (2022)
-
Gate-tunable Veselago interference in a bipolar graphene microcavity
Nature Communications (2022)