Abstract
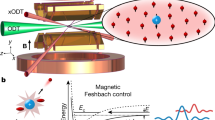
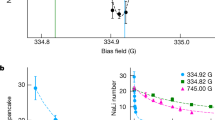
The capability to tune the strength of the elastic interparticle interaction is crucial for many experiments with ultracold gases. Magnetic Feshbach resonances1,2 are widely harnessed for this purpose, but future experiments3,4,5,6,7,8 would benefit from extra flexibility, in particular from the capability to spatially modulate the interaction strength on short length scales. Optical Feshbach resonances9,10,11,12,13,14,15 do offer this possibility in principle, but in alkali atoms they induce rapid loss of particles due to light-induced inelastic collisions. Here, we report experiments that demonstrate that light near-resonant with a molecular bound-to-bound transition in 87Rb can be used to shift the magnetic field at which a magnetic Feshbach resonance occurs. This enables us to tune the interaction strength with laser light, but with considerably less loss than using an optical Feshbach resonance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tiesinga, E., Verhaar, B. J. & Stoof, H. T. C. Threshold and resonance phenomena in ultracold ground-state collisions. Phys. Rev. A 47, 4114–4122 (1993).
Inouye, S., Andrews, M. R., Stenger, J., Miesner, H.-J., Stamper-Kurn, D. M. & Ketterle, W. Observation of Feshbach resonances in a Bose–Einstein condensate. Nature 392, 151–154 (1998).
Garay, L. J., Anglin, J. R., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Sonic analog of gravitational black holes in Bose–Einstein condensates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 4643–4647 (2000).
Carusotto, I., Fagnocchi, S., Recati, A., Balbinot, R. & Fabbri, A. Numerical observation of Hawking radiation from acoustic black holes in atomic Bose–Einstein condensates. New J. Phys. 10, 103001 (2008).
Rodas-Verde, M. I., Michinel, H. & Pérez-García, V. M. Controllable soliton emission from a Bose–Einstein condensate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 153903 (2005).
Dong, G., Hu, B. & Lu, W. Ground-state properties of a Bose–Einstein condensate tuned by a far-off-resonant optical field. Phys. Rev. A 74, 063601 (2006).
Abdullaev, F. K., Gammal, A., Salerno, M. & Tomio, L. Localized modes of binary mixtures of Bose–Einstein condensates in nonlinear optical lattices. Phys. Rev. A 77, 023615 (2008).
Deng, X.-L., Porras, D. & Cirac, J. I. Quantum phases of interacting phonons in ion traps. Phys. Rev. A 77, 033403 (2008).
Fedichev, P. O., Kagan, Y., Shlyapnikov, G. V. & Walraven, J. T. M. Influence of nearly resonant light on the scattering length in low-temperature atomic gases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2913–2916 (1996).
Bohn, J. L. & Julienne, P. S. Prospects for influencing scattering lengths with far-off-resonant light. Phys. Rev. A 56, 1486–1491 (1997).
Fatemi, F. K., Jones, K. M. & Lett, P. D. Observation of optically induced Feshbach resonances in collisions of cold atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 4462–4465 (2000).
Theis, M. et al. Tuning the scattering length with an optically induced Feshbach resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 123001 (2004).
Thalhammer, G., Theis, M., Winkler, K., Grimm, R. & Hecker Denschlag, J. Inducing an optical Feshbach resonance via stimulated Raman coupling. Phys. Rev. A 71, 033403 (2005).
Jones, K. M., Tiesinga, E., Lett, P. D. & Julienne, P. S. Ultracold photoassociation spectroscopy: Long-range molecules and atomic scattering. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 483–535 (2006).
Enomoto, K., Kasa, K., Kitagawa, M. & Takahashi, Y. Optical Feshbach resonance using the intercombination transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 203201 (2008).
Volz, T. et al. Preparation of a quantum state with one molecule at each site of an optical lattice. Nature Phys. 2, 692–695 (2006).
Autler, S. H. & Townes, C. H. Stark effect in rapidly varying fields. Phys. Rev. 100, 703–722 (1955).
Mackie, M., Fenty, M., Savage, D. & Kesselman, J. Cross-molecular coupling in combined photoassociation and Feshbach resonances. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 040401 (2008).
van Abeelen, F. A., Heinzen, D. J. & Verhaar, B. J. Photoassociation as a probe of Feshbach resonances in cold-atom scattering. Phys. Rev. A 57, R4102–R4105 (1998).
Junker, M. et al. Photoassociation of a Bose–Einstein condensate near a Feshbach resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 060406 (2008).
Marte, A. et al. Feshbach resonances in rubidium 87: Precision measurement and analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 283202 (2002).
Castin, Y. & Dum, R. Bose–Einstein condensates in time dependent traps. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 5315–5319 (1996).
Volz, T., Dürr, S., Ernst, S., Marte, A. & Rempe, G. Characterization of elastic scattering near a Feshbach resonance in 87Rb. Phys. Rev. A 68, 010702(R) (2003).
Smirne, G. et al. Collisional relaxation of Feshbach molecules and three-body recombination in 87Rb Bose–Einstein condensates. Phys. Rev. A 75, 020702(R) (2007).
Kraemer, T. et al. Evidence for Efimov quantum states in an ultracold gas of caesium atoms. Nature 440, 315–318 (2006).
Timmermans, E., Tommasini, P., Hussein, M. & Kerman, A. Feshbach resonances in atomic Bose–Einstein condensates. Phys. Rep. 315, 199–230 (1999).
van Abeelen, F. A. & Verhaar, B. J. Time-dependent Feshbach resonance scattering and anomalous decay of a Na Bose–Einstein condensate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1550–1553 (1999).
Dürr, S., Volz, T., Marte, A. & Rempe, G. Observation of molecules produced from a Bose–Einstein condensate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 020406 (2004).
Dürr, S., Volz, T. & Rempe, G. Dissociation of ultracold molecules with Feshbach resonances. Phys. Rev. A 70, 031601(R) (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Bernhardt and K. Predehl for providing light from their frequency comb. We acknowledge fruitful discussions with T. Bergeman, J. I. Cirac, D. Heinzen, C.-C. Tsai and T. Volz. This work was supported by the German Excellence Initiative through the Nanosystems Initiative Munich and by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft through SFB 631.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauer, D., Lettner, M., Vo, C. et al. Control of a magnetic Feshbach resonance with laser light. Nature Phys 5, 339–342 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1232
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1232
This article is cited by
-
A solvable model for symmetry-breaking phase transitions
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Strongly correlated Fermions strongly coupled to light
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Experimental realization of a Rydberg optical Feshbach resonance in a quantum many-body system
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Self-trapping under two-dimensional spin-orbit coupling and spatially growing repulsive nonlinearity
Frontiers of Physics (2018)
-
Localized spatially nonlinear matter waves in atomic-molecular Bose-Einstein condensates with space-modulated nonlinearity
Scientific Reports (2016)