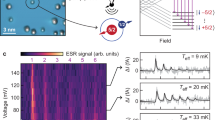
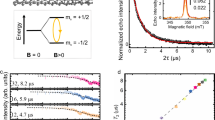
Abstract
For coherent electron spins, hyperfine coupling to nuclei in the host material can either be a dominant source of unwanted spin decoherence1,2,3 or, if controlled effectively, a resource enabling storage and retrieval of quantum information4,5,6,7. To investigate the effect of a controllable nuclear environment on the evolution of confined electron spins, we have fabricated and measured gate-defined double quantum dots with integrated charge sensors made from single-walled carbon nanotubes with a variable concentration of 13C (nuclear spin I=1/2) among the majority zero-nuclear-spin 12C atoms. We observe strong isotope effects in spin-blockaded transport, and from the magnetic field dependence estimate the hyperfine coupling in 13C nanotubes to be of the order of 100 μeV, two orders of magnitude larger than anticipated8,9. 13C-enhanced nanotubes are an interesting system for spin-based quantum information processing and memory: the 13C nuclei differ from those in the substrate, are naturally confined to one dimension, lack quadrupolar coupling and have a readily controllable concentration from less than one to 105 per electron.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khaetskii, A. V., Loss, D. & Glazman, L. Electron spin decoherence in quantum dots due to interaction with nuclei. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 186802 (2002).
Petta, J. R. et al. Coherent manipulation of coupled electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots. Science 309, 2180–2184 (2005).
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Driven coherent oscillations of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Nature 442, 766–771 (2006).
Kane, B. E. A silicon-based nuclear spin quantum computer. Nature 393, 133–137 (1998).
Taylor, J. M., Marcus, C. M. & Lukin, M. D. Long-lived memory for mesoscopic quantum bits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 206803 (2003).
Gurudev Dutt, M. V. et al. Quantum register based on individual electronics and nuclear spin qubits in diamond. Science 316, 1312–1316 (2007).
Hanson, R., Dobrovitski, V. V., Feiguin, A. E., Gwyat, O. & Awschalom, D. D. Coherent dynamics of a single spin interacting with an adjustable spin bath. Science 320, 352–355 (2008).
Yazyev, O. V. Hyperfine interactions in graphene and related carbon nanostructures. Nano Lett. 8, 1011–1015 (2008).
Pennington, C. H. & Stenger, V. A. Nuclear magnetic resonance of C60 and fulleride superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 68, 855–910 (1996).
Ono, K., Austing, D. G., Tokura, Y. & Tarucha, S. Current rectification by Pauli exclusion in a weakly coupled double quantum dot system. Science 297, 1313–1317 (2002).
Hanson, R. et al. Spins in few-electron quantum dots. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79, 1217–1265 (2007).
Merkulov, I. A., Efros, Al. L. & Rosen, M. Electron spin relaxation by nuclei in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 65, 205309 (2002).
Coish, W. A., Fischer, J. & Loss, D. Exponential decay in a spin bath. Phys. Rev. B 77, 125329 (2008).
Biercuk, M. J., Garaj, S., Mason, N., Chow, J. M. & Marcus, C. M. Gate-defined quantum dots on carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 5, 1267–1271 (2005).
Sapmaz, S., Meyer, C., Beliczynski, P., Jarillo-Herrero, P. & Kouwenhoven, L. P. Excited state spectroscopy in carbon nanotube double quantum dots. Nano Lett. 6, 1350–1355 (2006).
Gräber, M. R. et al. Molecular states in carbon nanotube double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 74, 075427 (2006).
Buitelaar, M. R. et al. Pauli spin blockade in carbon nanotube double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 77, 245439 (2008).
Jørgensen, H. I. et al. Singlet-triplet physics and shell filling in carbon nanotube double quantum dots. Nature Phys. 4, 536–539 (2008).
Liu, L. & Fan, S. Isotope labeling of carbon nanotubes and formation of 12C and 13C nanotube junctions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 11502–11503 (2001).
Johnson, A. C., Petta, J. R., Marcus, C. M., Hanson, M. P. & Gossard, A. C. Singlet-triplet spin blockade and charge sensing in a few-electron double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 72, 165308 (2005).
Hu, Y. et al. A Ge/Si heterostructure nanowire-based double quantum dot with integrated charge sensor. Nature Nanotech. 2, 622–625 (2007).
Jouravlev, O. N. & Nazarov, Y. V. Electron transport in a double quantum dot governed by a nuclear magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 176804 (2006).
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Control and detection of singlet-triplet mixing in a random nuclear field. Science 309, 1346–1350 (2005).
Pfund, A., Shorubalko, I., Ensslin, K. & Leturcq, R. Suppression of spin relaxation in an InAs nanowire double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 036801 (2007).
Kuemmeth, F., Ilani, S., Ralph, D. C. & McEuen, P. L. Coupling of spin and orbital motion of electrons in carbon nanotubes. Nature 452, 448–452 (2008).
Baugh, J., Kitamura, Y., Ono, K. & Tarucha, S. Large nuclear Overhauser fields detected in vertically coupled double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 096804 (2007).
Reilly, D. J. et al. Exchange control of nuclear spin diffusion in a double quantum dot. Preprint at <http://arxiv.org/abs/0803.3082> (2008).
Rudner, M. S. & Levitov, L. S. Self-polarization and dynamical cooling of nuclear spins in double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 036602 (2007).
Braunecker, B., Simon, P. & Loss, D. Nuclear magnetism and electronic order in 13C nanotubes. Preprint at <http://arxiv.org/abs/0808.1685> (2008).
Farmer, D. B. & Gordon, R. G. Atomic layer deposition on suspended single-walled carbon nanotubes via gas-phase noncovalent functionalization. Nano Lett. 6, 699–703 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Biercuk, K. Flensberg, L. Kouwenhoven, D. Loss, E. Rashba and O. Yazyev for discussions, and D. Reilly for experimental assistance. This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation under grant no. NIRT 0210736 and the NSF-NNIN Program, ARO/iARPA, the Department of Defense, Harvard’s Center for Nanoscale Systems. H.O.H.C. acknowledges support from the NSF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 173 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Churchill, H., Bestwick, A., Harlow, J. et al. Electron–nuclear interaction in 13C nanotube double quantum dots. Nature Phys 5, 321–326 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1247
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1247
This article is cited by
-
Atomic-like charge qubit in a carbon nanotube enabling electric and magnetic field nano-sensing
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Electrical control of a long-lived spin qubit in a Si/SiGe quantum dot
Nature Nanotechnology (2014)
-
Observation and spectroscopy of a two-electron Wigner molecule in an ultraclean carbon nanotube
Nature Physics (2013)
-
Tuning organic magnetoresistance in polymer-fullerene blends by controlling spin reaction pathways
Nature Communications (2013)
-
Electrical control of single hole spins in nanowire quantum dots
Nature Nanotechnology (2013)