Abstract
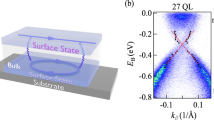
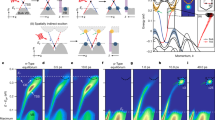
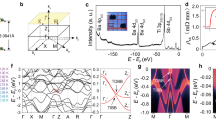
Recent experiments and theories have suggested that strong spin–orbit coupling effects in certain band insulators can give rise to a new phase of quantum matter, the so-called topological insulator, which can show macroscopic quantum-entanglement effects1,2,3,4,5,6,7. Such systems feature two-dimensional surface states whose electrodynamic properties are described not by the conventional Maxwell equations but rather by an attached axion field, originally proposed to describe interacting quarks8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15. It has been proposed that a topological insulator2 with a single Dirac cone interfaced with a superconductor can form the most elementary unit for performing fault-tolerant quantum computation14. Here we present an angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy study that reveals the first observation of such a topological state of matter featuring a single surface Dirac cone realized in the naturally occurring Bi2Se3 class of materials. Our results, supported by our theoretical calculations, demonstrate that undoped Bi2Se3 can serve as the parent matrix compound for the long-sought topological device where in-plane carrier transport would have a purely quantum topological origin. Our study further suggests that the undoped compound reached via n-to-p doping should show topological transport phenomena even at room temperature.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

 .
.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu, L., Kane, C. L. & Mele, E. J. Topological insulators in three dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 106803 (2007).
Moore, J. E. & Balents, L. Topological invariants of time-reversal-invariant band structures. Phys. Rev. B 75, 121306(R) (2007).
Zhang, S.-C. Topological states of quantum matter. Physics 1, 6 (2008).
Konig, M. et al. Quantum spin Hall insulator state in HgTe quantum wells. Science 318, 766–770 (2007).
Hsieh, D. et al. A topological Dirac insulator in a quantum spin Hall phase. Nature 452, 970–974 (2008).
Hsieh, D. et al. Observation of unconventional quantum spin textures in topological insulators. Science 323, 919–922 (2009).
Fu, L. & Kane, C. L. Topological insulators with inversion symmetry. Phys. Rev. B 76, 045302 (2007).
Wilczek, F. Two applications of axion electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 1799–1802 (1987).
Franz, M. High-energy physics in a new guise. Physics 1, 36 (2008).
Qi, X.-L., Li, R., Zang, J. & Zhang, S.-C. Inducing a magnetic monopole with topological surface states. Science 323, 1184–1187 (2009).
Qi, X.-L. et al. Topological field theory of time-reversal invariant insulators. Phys. Rev. B 78, 195424 (2008).
Ran, Y., Zhang, Y. & Vishwanath, A. One-dimensional topologically protected modes in topological insulators with lattice dislocations. Nature Phys.doi:10.1038/nphys1220 (2009).
Moore, J. E., Ran, Y. & Wen, X.-G. Topological surface states in three-dimensional magnetic insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 186805 (2008).
Fu, L. & Kane, C. L. Superconducting proximity effect and Majorana fermions at the surface of a topological insulator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 096407 (2008).
Seradjeh, B., Moore, J. E. & Franz, M. Exciton condensation and charge fractionalization in a topological insulator film. Preprint at <http://arxiv.org/abs/0902.1147v1> (2009).
Geim, A. K. & Novoselov, K. S. The rise of graphene. Nature Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007).
DiSalvo, F. J. Thermoelectric cooling and power generation. Science 285, 703–706 (1999).
Wyckoff, R. W. G. Crystal Structures (Krieger, 1986).
Hyde, G. R. et al. Electronic properties of Bi2Se3 crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 35, 1719–1728 (1974).
Larson, P. et al. Electronic structure of Bi2X3 (X=S, Se, T) compounds: Comparison of theoretical calculations with photoemission studies. Phys. Rev. B 65, 085108 (2002).
Greanya, V. A. et al. Determination of the valence band dispersions for Bi2Se3 using angle resolved photoemission. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 6658–6661 (2002).
Mooser, E. & Pearson, W. B. New semiconducting compounds. Phys. Rev. 101, 492–493 (1956).
Black, J. et al. Electrical and optical properties of some M2V−BN3VI−B semiconductors. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2, 240–251 (1957).
Mishra, S. K., Satpathy, S. & Jepsen, O. Electronic structure and thermoelectric properties of bismuth telluride and bismuth selenide. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 9, 461–479 (1997).
LaShell, S., McDougal, B. A. & Jensen, E. Spin splitting of an Au(111) surface state band observed with angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3419–3422 (1996).
Hoesch, M. et al. Spin structure of the Shockley surface state on Au(111). Phys. Rev. B 69, 241401 (2004).
Hufner, S. Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Springer, 1995).
Blaha, P. et al. Computer Code WIEN2K (Vienna Univ. Technology, 2001).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank N. P. Ong, B.A. Bernevig, D. Haldane and D.A. Huse for discussions. The synchrotron X-ray experiments are supported by the DOE-BES (contract DE-FG02-05ER46200) and materials synthesis is supported by the NSF-MRSEC (NSF-DMR-0819860) at Princeton Center for Complex Materials at Princeton University. Theoretical work is supported by the US Department of Energy, Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences contract DEFG02-07ER46352, and benefited from the allocation of supercomputer time at NERSC and Northeastern University’s Advanced Scientific Computation Center (ASCC). D.Q. was partly supported by the NNSF-China (grant No. 10874116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.X., D.Q. and D.H., carried out the experiment with the assistance of L.W. and A.P. D.G., Y.S.H. and R.J.C. provided the samples. H.L., Y.X. and A.B. carried out the theoretical calculations and the data analysis. M.Z.H. conceived the idea for the Bi2X3 topological class before any theoretical proposal and was responsible for overall project direction, planning and management.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 847 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Y., Qian, D., Hsieh, D. et al. Observation of a large-gap topological-insulator class with a single Dirac cone on the surface. Nature Phys 5, 398–402 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1274
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1274
This article is cited by
-
Room temperature nonlocal detection of charge-spin interconversion in a topological insulator
npj 2D Materials and Applications (2024)
-
Topological Insulator TlBiSe2/GaN Vertical Heterojunction Diode for High Responsive Broadband UV to Near-Infrared Photodetector
Journal of Electronic Materials (2024)
-
Realization of practical eightfold fermions and fourfold van Hove singularity in TaCo2Te2
npj Quantum Materials (2023)
-
Evidence for unconventional superconductivity and nontrivial topology in PdTe
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Topological magnon-photon interaction for cavity magnonics
Communications Physics (2023)