Abstract
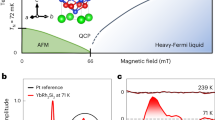
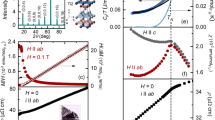
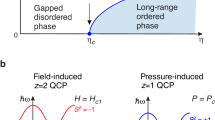
A continuous phase transition driven to zero temperature by a non-thermal parameter, such as pressure, terminates in a quantum critical point (QCP). At present, two main theoretical approaches are available for antiferromagnetic QCPs in heavy-fermion systems. The conventional one is the quantum generalization of finite-temperature phase transitions, which reproduces the physical properties in many cases1,2,3,4,5. More recent unconventional models incorporate a breakdown of the Kondo effect, giving rise to a Fermi-surface reconstruction6,7,8— YbRh2Si2 is a prototype of this category5,9,10,11. In YbRh2Si2, the antiferromagnetic transition temperature merges with the Kondo breakdown at the QCP. Here, we study the evolution of the quantum criticality in YbRh2Si2 under chemical pressure. Surprisingly, for positive pressure we find the signature of the Kondo breakdown within the magnetically ordered phase, whereas negative pressure induces their separation, leaving an intermediate spin-liquid-type ground state over an extended range. This behaviour suggests a new quantum phase arising from the interplay of the Kondo breakdown and the antiferromagnetic QCP.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

 and TN(H) in the susceptibility.
and TN(H) in the susceptibility.
 in magnetoresistance and magnetization.
in magnetoresistance and magnetization.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hertz, J. A. Quantum critical phenomena. Phys. Rev. B 14, 1165–1184 (1976).
Millis, A. J. Effect of a nonzero temperature on quantum critical-points in itinerant fermion systems. Phys. Rev. B 48, 7183–7196 (1993).
Moriya, T. & Takimoto, T. Anomalous properties around magnetic instability in heavy electron systems. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 64, 960–969 (1995).
Löhneysen, H. v., Rosch, A., Vojta, M. & Wölfle, P. Fermi-liquid instabilities at magnetic quantum phase transitions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79, 1015–1075 (2007).
Gegenwart, P., Si, Q. & Steglich, F. Quantum criticality in heavy-fermion metals. Nature Phys. 4, 186–197 (2008).
Si, Q., Rabello, M. S., Ingersent, K. & Smith, J. L. Locally critical quantum phase transitions in strongly correlated metals. Nature 413, 804–808 (2001).
Coleman, P., Pépin, C., Si, Q. & Ramazashvili, R. How do Fermi liquids get heavy and die? J. Phys. Condens. Matter 13, R723–R738 (2001).
Senthil, T., Vojta, M. & Sachdev, S. Weak magnetism and non-Fermi liquids near heavy-fermion critical points. Phys. Rev. B 69, 035111 (2004).
Custers, J. et al. The break-up of heavy electrons at a quantum critical point. Nature 424, 524–527 (2003).
Park, T. et al. Isotropic quantum scattering and unconventional superconductivity. Nature 456, 366–368 (2008).
Schröder, A. et al. Onset of antiferromagnetism in heavy-fermion metals. Nature 407, 351–355 (2000).
Trovarelli, O. et al. YbRh2Si2: Pronounced non-Fermi-liquid effects above a low-lying magnetic phase transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 626–629 (2000).
Paschen, S. et al. Hall-effect evolution across a heavy-fermion quantum critical point. Nature 432, 881–885 (2004).
Gegenwart, P. et al. Multiple energy scales at a quantum critical point. Science 315, 969–971 (2007).
Coleman, P., Marston, J. B. & Schofield, A. J. Transport anomalies in a simplified model for a heavy-electron quantum critical point. Phys. Rev. B 72, 245111 (2005).
Harrison, N. et al. Fermi surface of CeIn3 above the Néel critical field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 056401 (2007).
Goh, S. K. et al. Fermi-surface reconstruction in CeRh1−xCoxIn5 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 056402 (2008).
Goltsev, A. V. & Abd-Elmeguid, M. M. Origin of the pressure dependence of the Kondo temperature in Ce- and Yb-based heavy-fermion compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 17, S813–S821 (2005).
Tokiwa, Y. et al. Field-induced suppression of the heavy-fermion state in YbRh2Si2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 226402 (2005).
Weickert, F., Gegenwart, P., Ferstl, J., Geibel, C. & Steglich, F. Low-temperature electrical resistivity of Yb1−xLaxRh2Si2 . Physica B 378–380, 72–73 (2006).
Westerkamp, T., Gegenwart, P., Krellner, C., Geibel, C. & Steglich, F. Low-temperature magnetic susceptibility of Yb(Rh1−xMx)2Si2 (M=Ir, Co) single crystals. Physica B 403, 1236–1238 (2008).
Pépin, C. Selective Mott transition and heavy fermions. Phys. Rev. B 77, 245129 (2008).
Niklowitz, P. G., Knebel, G., Flouquet, J., Bud’ko, S. L. & Canfield, P. C. Field-induced non-Fermi-liquid resistivity of stoichiometric YbAgGe single crystals. Phys. Rev. B 73, 125101 (2006).
Tokiwa, Y. et al. Low-temperature thermodynamic properties of the heavy-fermion compound YbAgGe close to the field-induced quantum critical point. Phys. Rev. B 73, 094435 (2006).
Doiron-Leyraud, N. et al. Fermi-liquid breakdown in the paramagnetic phase of a pure metal. Nature 425, 595–599 (2003).
Nakatsuji, S. et al. Superconductivity and quantum criticality in the heavy-fermion system β-YbAlB4 . Nature Phys. 4, 603–607 (2008).
Nevidomskyy, A. H. & Coleman, P. Layered Kondo lattice model for quantum critical β-YbAlB4 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 077202 (2009).
Sakakibara, T., Mitamura, H., Tayama, T. & Amitsuka, H. Faraday force magnetometer for high-sensitivity magnetization measurements at very low temperatures and high fields. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 33, 5067–5072 (1994).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank P. Coleman and Q. Si for motivating discussions. We acknowledge partial support by the DFG Research Group 960 ‘Quantum Phase Transitions’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.F. set up, carried out and analysed the resistivity measurements. T.W. set up, carried out and analysed the a.c.-susceptibility measurements. M.B. set up, carried out and analysed the magnetization measurements. C.K. and C.G. grew the single crystals for the study. F.S., P.G., S.W. and N.O. planned and headed the project. S.F. wrote the paper with assistance from F.S., N.O, M.B., P.G. and S.W.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 306 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedemann, S., Westerkamp, T., Brando, M. et al. Detaching the antiferromagnetic quantum critical point from the Fermi-surface reconstruction in YbRh2Si2. Nature Phys 5, 465–469 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1299
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1299
This article is cited by
-
Evidence for charge delocalization crossover in the quantum critical superconductor CeRhIn5
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Terahertz control of many-body dynamics in quantum materials
Nature Reviews Materials (2023)
-
Thermoelectric signature of quantum critical phase in a doped spin-liquid candidate
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Critical slowing down near a magnetic quantum phase transition with fermionic breakdown
Nature Physics (2023)
-
Transport evidence for decoupled nematic and magnetic criticality in iron chalcogenides
Communications Physics (2022)