Abstract
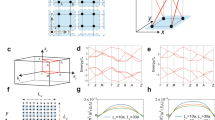
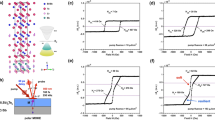
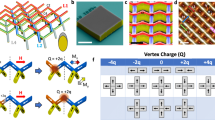
Topological insulators embody a state of bulk matter characterizedby spin-momentum-locked surface states that span the bulk bandgap1,2,3,4,5,6,7. This highly unusual surface spin environment provides a rich ground for uncovering new phenomena 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24. Understanding the response of a topological surface to strong Coulomb perturbations represents a frontier in discovering the interacting and emergent many-body physics of topological surfaces. Here we present the first controlled study of topological insulator surfaces under Coulomb and magnetic perturbations. We have used time-resolved deposition of iron, with a large Coulomb charge and significant magnetic moment, to systematically modify the topological spin structure of the Bi2Se3 surface. We observe that such perturbation leads to the creation of odd multiples of Dirac fermions and that magnetic interactions break time-reversal symmetry in the presence of band hybridizations. We present a theoretical model to account for the observed electron dynamics of the topological surface. Taken collectively, these results are a critical guide in controlling electron mobility and quantum behaviour of topological surfaces, not only for device applications but also in setting the stage for creating exotic particles such as axions or imaging monopoles on the surface.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moore, J. E. Topological insulators: The next generation. Nature Phys. 5, 378–380 (2009).
Hasan, M. Z. & Kane, C. L. Topological insulators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 3045–3067 (2010).
Fu, L., Kane, C. L. & Mele, E. J. Topological insulators in three dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 106803 (2007).
Hsieh, D. et al. A topological Dirac insulator in a quantum spin Hall phase. Nature 452, 970–974 (2008).
Hsieh, D. et al. Observation of unconventional quantum spin textures in topological insulators. Science 323, 919–922 (2009).
Hsieh, D. et al. A tunable topological insulator in the spin helical Dirac transport regime. Nature 460, 1101–1105 (2009).
Xia, Y. et al. Observation of a large-gap topological-insulator class with a single Dirac cone on the surface. Nature Phys. 5, 398–402 (2009).
Xia, Y. et al. Electrons on the surface of Bi2Se3 form a topologically-ordered two dimensional gas with a non-trivial Berry’s phase. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/0812.2078 (2008).
Hor, Y. S. et al. Development of ferromagnetism in the magnetically doped topological insulator Bi2−xMnxTe3 . Phys. Rev. B 81, 195203 (2010).
Hsieh, D. et al. Observation of time-reversal-protected single-Dirac-cone topological-insulator states in Bi2Te3 and Sb2Te3 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 146401 (2009).
Biswas, R. R. & Balatsky, A. V. Impurity-induced states on the surface of 3D topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 81, 233405 (2010).
Garate, I. & Franz, M. Inverse spin-galvanic effect in a topological-insulator/ferromagnet interface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 146802 (2010).
Fu, L. & Kane, C. L. Probing neutral Majorana fermion edge modes with charge transport. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 216403 (2009).
Law, K. T., Lee, P. A. & Ng, T. K. Majorana fermion induced resonant Andreev reflection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 237001 (2009).
Qi, X-L. et al. Inducing a magnetic monopole with topological surface states. Science 323, 1184–1187 (2009).
Seradjeh, B., Moore, J. E. & Franz, M. Exciton condensation and charge fractionalization in a topological insulator film. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 066402 (2009).
Tse, W-K. & MacDonald, A. H. Giant magneto-optical Kerr effect and universal Faraday effect in thin-film topological insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 057401 (2010).
Zhang, H. et al. Model Hamiltonian for topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 82, 045122 (2010).
Lee, D-H. Surface states of topological insulators: The Dirac fermion in curved two-dimensional spaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 196804 (2009).
Hasan, M. Z. et al. Warping the cone on a topological insulator. Physics 2, 108 (2009).
Fu, L. & Berg, E. Odd-parity topological superconductors: Theory and application to CuxBi2Se3 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 097001 (2010).
Wray, L. A., Xu, S-Y., Xia, Y., Hor, Y. S., Qian, D., Fedorov, A. V., Lin, H., Bansil, A., Cava, R. J. & Hasan, M. Z. Observation of topological order in a superconducting doped topological insulator. Nature Phys. 6, 855–859 (2010).
Xia, Y. et al. Topological control: Systematic control of topological insulator Dirac fermion density on the surface of Bi2Te3. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/0907.3089 (2009).
Ye, F. et al. Spin helix of magnetic impurities in two-dimensional helical metal. Europhys. Lett. 90, 47001 (2010).
Kawaminami, M. & Okazaki, A. Neutron diffraction study of Fe7Se8. II. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 29, 649–655 (1970).
Liu, Q. et al. Magnetic impurities on the surface of a topological insulator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 156603 (2009).
Wahl, P. et al. Exchange interaction between single magnetic adatoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 056601 (2007).
Mermin, N. D. & Wagner, H. Absence of ferromagnetism or antiferromagnetism in one- or two-dimensional isotropic Heisenberg models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 17, 1133–1136 (1966).
Zhang, R-J. & Willis, R. F. Thickness-dependent Curie temperatures of ultrathin magnetic films: Effect of the range of spin–spin interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 2665–2668 (2001).
Blaha, P. et al. Computer Code WIEN2K (Vienna Univ. Technology, 2001).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge discussions with R. R. Biswas and D. Haldane. The synchrotron X-ray-based measurements and theoretical computations are supported by the Basic Energy Sciences of the US DOE (DE-FG-02-05ER46200, AC03-76SF00098 and DE-FG02-07ER46352). Materials growth and characterization are supported by NSF/DMR-0819860 and NSF-DMR-1006492. M.Z.H. acknowledges extra support from the A. P. Sloan Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.A.W., S-Y.X. and Y.X. contributed equally to the experiment with assistance from D.H. and M.Z.H.; A.V.F. provided beamline assistance; Y.S.H. and R.J.C. provided single-crystal samples; H.L. and A.B. carried out the calculations with assistance from M.Z.H.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 457 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wray, L., Xu, SY., Xia, Y. et al. A topological insulator surface under strong Coulomb, magnetic and disorder perturbations. Nature Phys 7, 32–37 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1838
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1838
This article is cited by
-
Proximity induced band gap opening in topological-magnetic heterostructure (Ni80Fe20/p-TlBiSe2/p-Si) under ambient condition
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
A novel method to realize quantum spin-phonon Hall insulator in a one-dimensional superconducting resonator lattice
Quantum Information Processing (2023)
-
Intrinsic magnetic topological materials
Frontiers of Physics (2023)
-
Shubnikov-de Haas (SdH) Oscillation in Self-Flux Grown Rhombohedral Single-Crystalline Bismuth
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism (2023)
-
Driving ultrafast spin and energy modulation in quantum well states via photo-induced electric fields
npj Quantum Materials (2022)