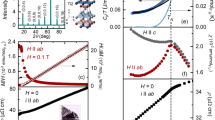
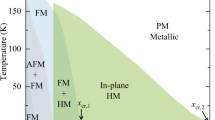
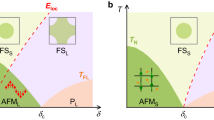
Abstract
In contrast to classical phase transitions driven by temperature,a quantum critical point (QCP) defines a transition at zero temperature that is driven by non-thermal parameters1,2,3. In the known quantum critical d-electron systems, tuning the electronic bandwidth by means of changing the applied pressure or unit-cell dimensions, or tuning the d-state population, is used to drive the criticality4,5,6. Here we describe how a novel chemical parameter, the breaking of bonds in Ge–Ge dimers that occurs within the intermetallic framework in SrCo2(Ge1−xPx)2, results in the appearance of a ferromagnetic (FM) QCP. Although both SrCo2P2 and SrCo2Ge2 are paramagnetic, weak itinerant ferromagnetism unexpectedly develops during the course of the dimer breaking, and a QCP is observed at the onset of the FM phase. The use of chemical bond breaking as a tuning parameter to induce QCP opens an avenue for designing and studying novel magnetic materials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stewart, G. R. Non-Fermi-liquid behavior in d- and f-electron metals. Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 797–855 (2001).
Stewart, G. R. Addendum: Non-Fermi-liquid behavior in d- and f-electron metals. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 743–753 (2006).
Löhneysen, H. v., Rosch, A., Vojta, M. & Wölfle, P. Fermi-liquid instabilities at magnetic quantum phase transitions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79, 1015–1075 (2007).
Sokolov, D. A., Aronson, M. C., Gannon, W. & Fisk, Z. Critical phenomena and the quantum critical point of ferromagnetic Zr1−xNbxZn2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 116404 (2006).
Smith, R. P. et al. Marginal breakdown of the Fermi-liquid state on the border of metallic ferromagnetism. Nature 455, 1220–1223 (2008).
Pfleiderer, C., Julian, S. R. & Lonzarich, G. G. Non-Fermi-liquid nature of the normal state of itinerant-electron ferromagnets. Nature 414, 427–430 (2001).
Custers, J. et al. The break-up of heavy electrons at a quantum critical point. Nature 424, 524–527 (2003).
Rotter, M., Tegel, M. & Johrendt, D. Superconductivity at 38 K in the iron arsenide Ba1−xKxFe2As2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 107006 (2008).
Hoffmann, R. & Zheng, C. Making and breaking bonds in the solid state: The thorium chromium silicide (ThCr2Si2) structure. J. Phys. Chem. 89, 4175–4181 (1985).
Just, G. & Paufler, P. On the coordination of ThCr2Si2BaAl4-type compounds within the field of free parameters. J. Alloys Comp. 232, 1–25 (1996).
Analytis, J. G. et al. Fermi surface of SrFe2P2 determined by the de Haas– van Alphen effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 076401 (2009).
Coldea, A. I. et al. Topological change of the Fermi surface in ternary iron pnictides with reduced c/a ratio: A de Haas–van Alphen study of CaFe2P2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 026404 (2009).
Yildirim, T. Strong coupling of the Fe-spin state and the As–As hybridization in iron-pnictide superconductors from first-principle calculations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 037003 (2009).
Huhnt, C., Schlabitz, W., Wurth, A., Mewis, A. & Reehuis, M. First-order phase transitions in EuCo2P2 and SrNi2P2 . Phys. Rev. B 56, 13796–13804 (1997).
Reehuis, M., Jeitschko, W., Kotzyba, G., Zimmer, B. & Hu, X. Antiferromagnetic order in the ThCr2Si2 type phosphides CaCo2P2 and CeCo2P2 . J. Alloys Comp. 266, 54–60 (1998).
Chefki, M. et al. Pressure-induced transition of the sublattice magnetization in EuCo2P2: Change from local moment Eu (4f) to itinerant Co (3d) magnetism. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 802–805 (1998).
Canfield, P. C. et al. Structural, magnetic and superconducting phase transitions in CaFe2As2 under ambient and applied pressure. Physica C 469, 404–412 (2009).
Jia, S., Williams, A. J., Stephens, P. W. & Cava, R. J. Lattice collapse and the magnetic phase diagram of Sr1−xCaxCo2P2 . Phys. Rev. B 80, 165107 (2009).
Reehuis, M. & Jeitschko, W. Structure and magnetic properties of the phosphides CaCo2P2 and LnT2P2 with ThCr2Si2 structure and LnTP with PbFCl structure (Ln=lanthanoids, T=Fe, Co, Ni) +. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 51, 961–968 (1990).
Arrott, A. Criterion for ferromagnetism from observations of magnetic isotherms. Phys. Rev. 108, 1394–1396 (1957).
Moriya, T. Spin Fluctuations in Itinerant Electron Magnetism (Springer, 1985).
Millis, A. J. Effect of a nonzero temperature on quantum critical points in itinerant fermion systems. Phys. Rev. B 48, 7183–7196 (1993).
Mydosh, J. A. Spin Glass: An Experimental Introduction (Taylor and Francis, 1993).
Pawina, J. Bachelor Thesis, Princeton Univ. (2010).
Siggelkow, L., Hlukhyy, V. & Fässler, T. F. Synthesis, structure and chemical bonding of CaCo2Si2 and BaCo2Ge2—two new compounds with ThCr2Si2 structure type. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 636, 378–384 (2010).
Hoffmann, R. Solids and Surfaces: A Chemist’s View of Bonding in Extended Strutures (VCH, 1988).
McQueen, T. M. et al. Intrinsic properties of stoichiometric LaFePO. Phys. Rev. B 78, 024521 (2008).
Larson, A. C. & Von Dreele, R. B. General Structure Analysis System (GSAS). Report No. 86 (Los Alamos National Laboratory LAUR, 2000).
Toby, B. H. EXPGUI, a graphical user interface for GSAS. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 34, 210–213 (2001).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank J. Xiong and D. X. Qu for experimental assistance, as well as N. Ni for helpful discussion. The work at Princeton was supported by the US Department of Energy, Division of Basic Energy Sciences, Grant No. DE-FG02-98ER45706. Use of the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory was supported by the US Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.J. and S.J. synthesized the materials. M.R.S. and B.H.T. performed the synchrotron XRD. S.J., J.G.C. and N.P.O. performed the thermodynamic measurements. S.J., P.J. and R.J.C. analysed the data. S.J. and R.J.C. wrote the paper. R.J.C. designed the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, S., Jiramongkolchai, P., Suchomel, M. et al. Ferromagnetic quantum critical point induced by dimer-breaking in SrCo2(Ge1−xPx)2. Nature Phys 7, 207–210 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1868
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1868