Abstract
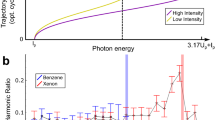
High-harmonic spectroscopy provides a unique insight into the electronic structure of atoms and molecules1,2,3,4,5. Although attosecond science holds the promise of accessing the timescale of electron–electron interactions, until now, their signature has not been seen in high-harmonic spectroscopy. We have recorded high-harmonic spectra of atoms to beyond 160 eV, using a new, almost ideal laser source with a wavelength of 1.8 μm and a pulse duration of less than two optical cycles. We show that we can relate these spectra to differential photoionization cross-sections measured with synchrotron sources. In addition, we show that the high-harmonic spectra contain features due to collective multi-electron effects involving inner-shell electrons, in particular the giant resonance in xenon. We develop a new theoretical model based on the strong-field approximation and show that it is in agreement with the experimental observations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 March 2011
In the version of this Letter originally published online, the affiliation for the first author, A. D. Shiner, was given incorrectly. This has now been corrected for all versions of the Letter.
References
Itatani, J. et al. Tomographic imaging of molecular orbitals. Nature 432, 867–871 (2004).
Le, A-T., Lucchese, R. R., Tonzani, S., Morishita, T. & Lin, C. D. Quantitative rescattering theory for high-order harmonic generation from molecules. Phys. Rev. A 80, 013401 (2009).
Mairesse, Y., Levesque, J., Dudovich, N., Corkum, P. B. & Villeneuve, D. M. High harmonic generation from aligned molecules—amplitude and polarization. J. Mod. Optics 55, 2591–2602 (2008).
Wörner, H. J., Niikura, H., Bertrand, J. B., Corkum, P. B. & Villeneuve, D. M. Observation of electronic structure minima in high-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 103901 (2009).
Haessler, S. et al. Attosecond imaging of molecular electronic wavepackets. Nature Phys. 6, 200–206 (2010).
Berkowitz, J. Photoabsorption, Photoionization and Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Academic, 1979).
Kimura, K., Katsumata, S., Achiba, Y., Yamazaki, T. & Iwata, S. Handbook of HeI Photoelectron Spectra (Japan Scientific Societies Press, 1981).
Becker, U. & Shirley, D. A. (eds) VUV and Soft X-Ray Photoionization (Plenum Press, 1996).
Torres, R. et al. Probing orbital structure of polyatomic molecules by high-order harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 203007 (2007).
Baker, S. et al. Probing proton dynamics in molecules on an attosecond timescale. Science 312, 424–427 (2006).
Smirnova, O. et al. High harmonic interferometry of multi-electron dynamics in molecules. Nature 460, 972–977 (2009).
Wörner, H. J., Bertrand, J. B., Kartashov, D. V., Corkum, P. B. & Villeneuve, D. M. Following a chemical reaction using high-harmonic spectroscopy. Nature 466, 604–607 (2010).
Corkum, P. B. Plasma perspective on strong field multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1994–1997 (1993).
Le, A-T., Lucchese, R. R., Lee, M. T. & Lin, C. D. Probing molecular frame photoionization via laser generated high-order harmonics from aligned molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 203001 (2009).
Frolov, M. V. et al. Analytic description of the high-energy plateau in harmonic generation by atoms: Can the harmonic power increase with increasing laser wavelengths? Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 243901 (2009).
Ganeev, R. A. High-order harmonic generation in a laser plasma: A review of recent achievements. J. Phys. B 40, R213–R253 (2007).
Frolov, M. V., Manakov, N. L. & Starace, A. F. Potential barrier effects in high-order harmonic generation by transition-metal ions. Phys. Rev. A 82, 023424 (2010).
Schmidt, B. E. et al. Compression of 1.8 μm laser pulses to sub two optical cycles with bulk material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 121109 (2010).
Frolov, M. V., Manakov, N. L., Sarantseva, T. S. & Starace, A. F. Analytic formulae for high harmonic generation. J. Phys. B 42, 035601 (2009).
Landau, L. D. & Lifshitz, E. M. Quantum Mechanics Non-Relativistic Theory 3 edn (Course of Theoretical Physics, vol. 3, Pergamon Press, 1977).
Huang, K. N., Johnson, W. R. & Cheng, K. T. Theoretical photoionization parameters for the noble gases argon, krypton, and xenon. At. Nucl. Data Tables 26, 33–45 (1981).
Minemoto, S. et al. Retrieving photorecombination cross sections of atoms from high-order harmonic spectra. Phys. Rev. A 78, 061402(R) (2008).
Amusia, M. Y. & Connerade, J-P. The theory of collective motion probed by light. Rep. Prog. Phys. 63, 41–70 (2000).
Becker, U. et al. Subshell photoionization of Xe between 40 and 1,000 eV. Phys. Rev. A 39, 3902–3911 (1989).
Kutzner, M., Radojević, V. & Kelly, H. P. Extended photoionization calculations for xenon. Phys. Rev. A 40, 5052–5057 (1989).
Popmintchev, T. et al. Phase matching of high harmonic generation in the soft and hard X-ray regions of the spectrum. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 10516–10521 (2009).
Vozzi, C. et al. High-order harmonics generated by 1.5 μm parametric source. J. Mod. Opt. 57, 1008–1013 (2010).
Schultze, M. et al. Delay in photoemission. Science 328, 1658–1662 (2010).
Shiner, A. D. et al. Wavelength scaling of high harmonic generation efficiency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 073902 (2009).
Farrell, J. P., McFarland, B. K., Bucksbaum, P. H. & Gühr, M. Calibration of a high harmonic spectrometer by laser induced plasma emission. Opt. Express 17, 15134–15144 (2009).
Fahlman, A., Krause, M. O., Carlson, T. A. & Svensson, A. Xe 5s, 5p correlation satellites in the region of strong interchannel interactions, 28–75 eV. Phys. Rev. A 30, 812–819 (1984).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank laser technicians F. Poitras and A. Laramée for their dedicated work on the laser system, and gratefully acknowledge financial support from NSERC, AFOSR, CIPI and FQRNT. We thank U. Becker, M. Spanner and T. Starace for illuminating discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.D.S. and B.E.S. contributed equally to this work. B.E.S., F.L. and J-C.K. developed the laser source. A.D.S., B.E.S. and C.T.H. carried out the experiments. H.J.W. interpreted the xenon results. A.D.S. analysed the data. S.P. and D.M.V. provided the theoretical parts. A.D.S., H.J.W., P.B.C. and D.M.V. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 739 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiner, A., Schmidt, B., Trallero-Herrero, C. et al. Probing collective multi-electron dynamics in xenon with high-harmonic spectroscopy. Nature Phys 7, 464–467 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1940
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1940
This article is cited by
-
Topological high-harmonic spectroscopy
Communications Physics (2024)
-
Investigation of interference structure with different field intensication in linearly polarized laser field
Optical Review (2024)
-
Coulomb and Quantum Interference Effects in the Spectra of High-Order Harmonics Generated by Aligned Molecules
Radiophysics and Quantum Electronics (2023)
-
Atomic partial wave meter by attosecond coincidence metrology
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Field-free molecular orientation by delay- and polarization-optimized two fs pulses
Scientific Reports (2020)