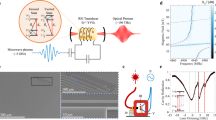
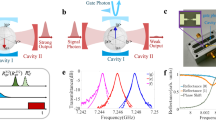
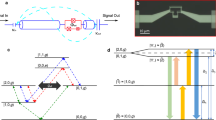
Abstract
Fully controlled coherent coupling of arbitrary harmonic oscillators is an important tool for processing quantum information1. Coupling between quantum harmonic oscillators has previously been demonstrated in several physical systems using a two-level system as a mediating element2,3. Direct interaction at the quantum level has only recently been realized by means of resonant coupling between trapped ions4,5. Here we implement a tunable direct coupling between the microwave harmonics of a superconducting resonator by means of parametric frequency conversion6,7. We accomplish this by coupling the mode currents of two harmonics through a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) and modulating its flux at the difference (∼7 GHz) of the harmonic frequencies. We deterministically prepare a single-photon Fock state8 and coherently manipulate it between multiple modes, effectively controlling it in a superposition of two different ’colours’. This parametric interaction can be described as a beamsplitter-like operation that couples different frequency modes. As such, it could be used to implement linear optical quantum computing protocols9,10 on-chip11.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haroche, S. & Raimond, J. Exploring the Quantum: Atoms, Cavities and Photons (Oxford Univ. Press, 2006).
Rauschenbeutel, A. et al. Controlled entanglement of two field modes in a cavity quantum electrodynamics experiment. Phys. Rev. A 64, 50301 (2001).
Wang, H. et al. Deterministic entanglement of photons in two superconducting microwave resonators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 060401 (2011).
Brown, K. et al. Coupled quantized mechanical oscillators. Nature 471, 196–199 (2011).
Harlander, M., Lechner, R., Brownnutt, M., Blatt, R. & Hänsel, W. Trapped-ion antennae for the transmission of quantum information. Nature 471, 200–203 (2011).
Louisell, W., Yariv, A. & Siegman, A. Quantum fluctuations and noise in parametric processes. I. Phys. Rev. 124, 1646–1654 (1961).
Tucker, J. & Walls, D. Quantum theory of parametric frequency conversion. Ann. Phys. 52, 1–15 (1969).
Wallraff, A. et al. Strong coupling of a single photon to a superconducting qubit using circuit quantum electrodynamics. Nature 431, 162–167 (2004).
Knill, E., Laflamme, R. & Milburn, G. A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46–52 (2001).
Milburn, G. Photons as qubits. Phys. Scr. 2009, 014003 (2009).
Matthews, J., Politi, A., Stefanov, A. & O’Brien, J. Manipulation of multiphoton entanglement in waveguide quantum circuits. Nature Photon. 3, 346–350 (2009).
Huang, J. & Kumar, P. Observation of quantum frequency conversion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 2153–2156 (1992).
Tanzilli, S. et al. A photonic quantum information interface. Nature 437, 116–120 (2005).
Rakher, M., Ma, L., Slattery, O., Tang, X. & Srinivasan, K. Quantum transduction of telecommunications-band single photons from a quantum dot by frequency upconversion. Nature Photon. 4, 786–791 (2010).
Vandevender, A. & Kwiat, P. High efficiency single photon detection via frequency up-conversion. J. Mod. Opt. 51, 1433–1445 (2004).
Gröblacher, S., Hammerer, K., Vanner, M. & Aspelmeyer, M. Observation of strong coupling between a micromechanical resonator and an optical cavity field. Nature 460, 724–727 (2009).
Teufel, J. et al. Circuit cavity electromechanics in the strong-coupling regime. Nature 471, 204–208 (2011).
Wallquist, M. et al. Single-atom cavity QED and optomicromechanics. Phys. Rev. A 81, 23816 (2010).
Niskanen, A. et al. Quantum coherent tunable coupling of superconducting qubits. Science 316, 723 (2007).
Yurke, B. et al. Observation of parametric amplification and deamplification in a Josephson parametric amplifier. Phys. Rev. A 39, 2519–2533 (1989).
Bergeal, N. et al. Phase-preserving amplification near the quantum limit with a Josephson ring modulator. Nature 465, 64–68 (2010).
Castellanos-Beltran, M., Irwin, K., Hilton, G., Vale, L. & Lehnert, K. Amplification and squeezing of quantum noise with a tunable Josephson metamaterial. Nature Phys. 4, 929–931 (2008).
Yamamoto, T. et al. Flux-driven Josephson parametric amplifier. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 042510 (2008).
Chirolli, L., Burkard, G., Kumar, S. & DiVincenzo, D. P. Superconducting resonators as beam splitters for linear-optics quantum computation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 230502 (2010).
Tian, L., Allman, M. & Simmonds, R. Parametric coupling between macroscopic quantum resonators. New J. Phys. 10, 115001 (2008).
Hofheinz, M. et al. Synthesizing arbitrary quantum states in a superconducting resonator. Nature 459, 546–549 (2009).
Palacios-Laloy, A. et al. Tunable resonators for quantum circuits. J. Low Temp. Phys. 151, 1034–1042 (2008).
Sandberg, M. et al. Tuning the field in a microwave resonator faster than the photon lifetime. App. Phys. Lett. 92, 203501 (2008).
Louisell, W. Coupled Mode and Parametric Electronics (Wiley, 1960).
Sillanpää, M., Park, J. & Simmonds, R. Coherent quantum state storage and transfer between two phase qubits via a resonant cavity. Nature 449, 438–442 (2007).
Law, C. K. & Eberly, J. H. Arbitrary control of a quantum electromagnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 1055–1058 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank N. Bergren and L. Ranzani for technical help, and J. Park, F. Altomare and L. Spietz for valuable input.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.Z-B. and F.N. designed the experiment, built the measurement set-up and performed the measurements. M.L., R.W.S., J.A. contributed to the experimental design. L.R.V. contributed to the fabrication process development. J.A. conceived the experiment and supervised the project. All authors participated in the sample fabrication, the writing of the manuscript and the data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 4290 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakka-Bajjani, E., Nguyen, F., Lee, M. et al. Quantum superposition of a single microwave photon in two different ’colour’ states. Nature Phys 7, 599–603 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2035
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2035
This article is cited by
-
Engineering quantum diode in one-dimensional time-varying superconducting circuits
npj Quantum Information (2023)
-
High-fidelity parametric beamsplitting with a parity-protected converter
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Strong parametric dispersive shifts in a statically decoupled two-qubit cavity QED system
Nature Physics (2023)
-
Trade off-free entanglement stabilization in a superconducting qutrit-qubit system
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Dynamical Casimir Effect for Gaussian Boson Sampling
Scientific Reports (2018)