Abstract
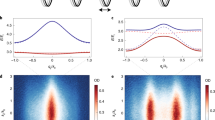
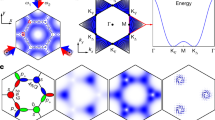
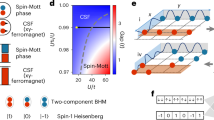
Orbital physics plays a significant role for a vast number of important phenomena in complex condensed-matter systems, including high-temperature superconductivity and unconventional magnetism. In contrast, phenomena in superfluids—in particular in ultracold quantum gases—are typically well described by the lowest orbital and a real order parameter1. Here, we report on the observation of a multi-orbital superfluid phase with a complex order parameter in binary spin mixtures. In this unconventional superfluid, the local phase angle of the complex order parameter is continuously twisted between neighbouring lattice sites. The nature of this twisted superfluid quantum phase is an interaction-induced admixture of the p-orbital contributions favoured by the graphene-like band structure of the hexagonal optical lattice used in the experiment. We observe a second-order quantum phase transition between the normal superfluid and the twisted superfluid phase, which is accompanied by a symmetry breaking in momentum space. The experimental results are consistent with calculated phase diagrams and reveal fundamentally new aspects of orbital superfluidity in quantum gas mixtures. Our studies might bridge the gap between conventional superfluidity and complex phenomena of orbital physics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 November 2011
In the version of this Letter originally published online, the square-root signs in the formula in Fig. 3a were displayed incorrectly. This has been corrected in all versions of the Letter.
References
Pitaevskii, L. P. & Stringari, S. Bose–Einstein Condensation (Oxford Univ.Press, 2003).
Geim, A. K. & Novoselov, K. S. The rise of graphene. Nature Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007).
Du, X., Skachko, I., Duerr, F., Luican, A. & Andrei, E. Y. Fractional quantum Hall effect and insulating phase of Dirac electrons in graphene. Nature 462, 192–195 (2009).
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 438, 197–200 (2005).
Zhang, Y., Tan, J. W., Stormer, H. L. & Kim, P. Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry’s phase in graphene. Nature 438, 201–204 (2005).
Soltan-Panahi, P. et al. Multi-component quantum gases in spin-dependent hexagonal lattices. Nature Phys. 7, 434–440 (2011).
Zhu, A-L., Wang, B. & Duan, L-M. Simulation and detection of Dirac fermions with cold atoms in an optical lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 260402 (2007).
Wu, C. & Das Sarma, S. p x,y-orbital counterpart of graphene: Cold atoms in the honeycomb optical lattice. Phys. Rev. B 77, 235107 (2008).
Lee, K. L., Grémaud, B., Han, R., Englert, B-G. & Miniatura, C. Ultracold fermions in a graphene-type optical lattice. Phys. Rev. A 80, 043411 (2009).
Greiner, M., Mandel, O., Esslinger, T., Hänsch, T. W. & Bloch, I. Quantum phase transition from a superfluid to a Mott insulator in a gas of ultracold atoms. Nature 415, 39–44 (2002).
Jördens, R., Strohmaier, N., Günter, K., Moritz, H. & Esslinger, T. A Mott insulator of fermionic atoms in an optical lattice. Nature 455, 204–207 (2008).
Schneider, U. et al. Metallic and insulating phases of repulsively interacting fermions in a 3D optical lattice. Science 322, 1520–1525 (2008).
Struck, J. et al. Quantum simulation of frustrated magnetism in triangular optical lattices. Science 333, 996–999 (2011).
Bloch, I., Dalibard, J. & Zwerger, W. Many-body physics with ultracold gases. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 885–964 (2008).
Will, S. et al. Time-resolved observation of coherent multi-body interactions in quantum phase revivals. Nature 465, 197–201 (2010).
Best, T. et al. Role of interactions in 87Rb–40K Bose–Fermi mixtures in a 3D optical lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 030408 (2009).
Lühmann, D-S., Bongs, K., Sengstock, K. & Pfannkuche, D. Self-trapping of bosons and fermions in optical lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 050402 (2008).
Lutchyn, R. M., Tewari, S. & Das Sarma, S. Loss of superfluidity by fermions in the boson Hubbard model on an optical lattice. Phys. Rev. A 79, 011606 (2009).
Müller, T., Fölling, S., Widera, A. & Bloch, I. State preparation and dynamics of ultracold atoms in higher lattice orbitals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 200405 (2007).
Wirth, G., Ölschläger, M. & Hemmerich, A. Evidence for orbital superfluidity in the P-band of a bipartite optical square lattice. Nature Phys. 7, 147–153 (2011).
Ölschläger, M., Wirth, G. & Hemmerich, A. Unconventional superfluid order in the F band of a bipartite optical square lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 015302 (2011).
Isacsson, A. & Girvin, S. M. Multiflavor bosonic Hubbard models in the first excited Bloch band of an optical lattice. Phys. Rev. A 72, 053604 (2005).
Wu, C., Liu, W. V., Moore, J. & Das Sarma, S. State preparation and dynamics of ultracold atoms in higher lattice orbitals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190406 (2006).
Liu, W. V. & Wu, C. Atomic matter of nonzero-momentum Bose–Einstein condensation and orbital current order. Phys. Rev. A 74, 013607 (2006).
Zhou, Q., Porto, J. V. & Das Sarma, S. Condensates induced by interband coupling in a double-well lattice. Inter-band coupling induced novel condensates in a double-well lattice. Phys. Rev. B 83, 195106 (2011).
Schmaljohann, H. et al. Dynamics of F=2 spinor Bose–Einstein condensates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 040402 (2004).
Acknowledgements
The work has been funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft grants FOR 801 and GRK 1355 as well as by the Landesexzellenzinitiative Hamburg, which is supported by the Joachim Herz Stiftung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The experimental work and data analysis were done by P.S-P., J.S., D-S.L., P.W. and K.S. D-S.L. and P.S-P. carried out the theoretical calculations. P.S-P. and D-S.L. wrote the manuscript with substantial contributions by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soltan-Panahi, P., Lühmann, DS., Struck, J. et al. Quantum phase transition to unconventional multi-orbital superfluidity in optical lattices. Nature Phys 8, 71–75 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2128
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2128
This article is cited by
-
A p-orbital honeycomb-Kagome lattice realized in a two-dimensional metal-organic framework
Communications Chemistry (2023)
-
Photonic quadrupole topological insulator using orbital-induced synthetic flux
Nature Communications (2022)
-
The mixing-demixing phase diagram of ultracold heteronuclear mixtures in a ring trimer
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
The phase-separation mechanism of a binary mixture in a ring trimer
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Analytical approach to quantum phase transitions of ultracold Bose gases in bipartite optical lattices using the generalized Green’s function method
Frontiers of Physics (2018)