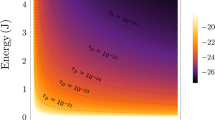
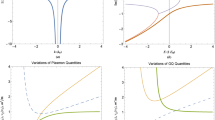
Abstract
Different approaches to quantum gravity, such as string theory1,2 and loop quantum gravity, as well as doubly special relativity3 and gedanken experiments in black-hole physics4,5,6, all indicate the existence of a minimal measurable length7,8 of the order of the Planck length,  . This observation has motivated the proposal of generalized uncertainty relations, which imply changes in the energy spectrum of quantum systems. As a consequence, quantum gravitational effects could be revealed by experiments able to test deviations from standard quantum mechanics9,10,11, such as those recently proposed on macroscopic mechanical oscillators12. Here we exploit the sub-millikelvin cooling of the normal modes of the ton-scale gravitational wave detector AURIGA, to place an upper limit for possible Planck-scale modifications on the ground-state energy of an oscillator. Our analysis calls for the development of a satisfactory treatment of multi-particle states in the framework of quantum gravity models.
. This observation has motivated the proposal of generalized uncertainty relations, which imply changes in the energy spectrum of quantum systems. As a consequence, quantum gravitational effects could be revealed by experiments able to test deviations from standard quantum mechanics9,10,11, such as those recently proposed on macroscopic mechanical oscillators12. Here we exploit the sub-millikelvin cooling of the normal modes of the ton-scale gravitational wave detector AURIGA, to place an upper limit for possible Planck-scale modifications on the ground-state energy of an oscillator. Our analysis calls for the development of a satisfactory treatment of multi-particle states in the framework of quantum gravity models.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amati, D., Ciafaloni, M. & Veneziano, G. Superstring collisions at Planckian energies. Phys. Lett. B 197, 81–88 (1987).
Gross, D. J. & Mende, P. F. String theory beyond the Planck scale. Nucl. Phys. B 303, 407–454 (1988).
Amelino-Camelia, G. Doubly special relativity: First results and key open problems. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 11, 1643–1669 (2002).
Maggiore, M. A generalized uncertainty principle in quantum gravity. Phys. Lett. B 304, 65–69 (1993).
Scardigli, F. Generalized uncertainty principle in quantum gravity from micro-black hole gedanken experiment. Phys. Lett. B 452, 39–44 (1999).
Jizba, P., Kleinert, H. & Scardigli, F. Uncertainty relation on a world crystal and its applications to micro black holes. Phys. Rev. D 81, 084030 (2010).
Garay, L. G. Quantum gravity and minimum length. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 10, 145–165 (1995).
Hossenfelder, S. Minimal length scale scenarios for quantum gravity. Living Rev. Relativ. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/arXiv:1203.6191 (2012).
Das, S. & Vagenas, E. C. Universality of quantum gravity corrections. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 221301 (2008).
Ali, A. F., Das, S. & Vagenas, E. C. Discreteness of space from the generalized uncertainty principle. Phys. Lett. B 678, 497–499 (2009).
Ali, A. F., Das, S. & Vagenas, E. C. A proposal for testing quantum gravity in the lab. Phys. Rev. D 84, 044013 (2011).
Pikovski, I., Vanner, M. R., Aspelmeyer, M., Kim, M. S. & Brukner, Č. Probing Planck-scale physics with quantum optics. Nature Phys. 8, 393–397 (2012).
Amelino-Camelia, G., Ellis, J., Mavromatos, N. E., Nanopoulos, D. V. & Sarkar, S. Tests of quantum gravity from observations of gamma-ray bursts. Nature 393, 763–765 (1998).
Jacob, U. & Piran, T. Neutrinos from gamma-ray bursts as a tool to explore quantum-gravity-induced Lorentz violation. Nature Phys. 7, 87–90 (2007).
Tamburini, F., Cuofano, C., Della Valle, M. & Gilmozzi, R. No quantum gravity signature from the farthest quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 533, 1–5 (2011).
Abdo, A. A. et al. A limit on the variation of the speed of light arising from quantum gravity effects. Nature 462, 331–334 (2009).
O’Connell, A. D. et al. Quantum ground state and single-phonon control of a mechanical resonator. Nature 464, 697–713 (2010).
Teufel, J. D. et al. Sideband cooling of micromechanical motion to the quantum ground state. Nature 475, 359–363 (2011).
Chan, J. et al. Laser cooling of a nanomechanical oscillator into its quantum ground state. Nature 478, 89–92 (2011).
Safavi-Naeini, A. H. et al. Observation of quantum motion of a nanomechanical resonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 033602 (2012).
Hossenfelder, S. Multiparticle states in deformed special relativity. Phys. Rev. D 75, 105005 (2007).
Quesne, C. & Tkachuk, V. M. Composite system in deformed space with minimal length. Phys. Rev. A 81, 012106 (2010).
Maggiore, M. The algebraic structure of the generalized uncertainty principle. Phys. Lett. B 319, 83–86 (1993).
Kempf, A., Mangano, G. & Mann, R. B. Hilbert space representation of the minimal length uncertainty relation. Phys. Rev. D 52, 1108–1118 (1995).
Sathyaprakash, B.S. & Schutz, B. F. Physics, astrophysics and cosmology with gravitational waves. Living Rev. Relativ. 12, 1–141 (2009).
Allen, Z. A. et al. First search for gravitational wave bursts with a network of detectors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 5046–5050 (2000).
Vinante, A. et al. Feedback cooling of the normal modes of a massive electromechanical system to submillikelvin temperature. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 033601 (2008).
Vinante, A. et al. Stabilization and optimization of a two-stage d.c. SQUID coupled to a high Q resonator. Physica C 368, 176–180 (2002).
Baggio, L. et al. 3-mode detection for widening the bandwidth of resonant gravitational wave detectors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 241101 (2005).
Selected Articles from the 9th Edoardo Amaldi Meeting and the 2011 Numerical Relativity and Data Analysis Meeting (AMALDI 9/NRDA 2011) Class. Quant. Grav. 29, 120301–129603 (Special issue, 2012).
Cerdonio, M. & Losurdo, G. Gravitational waves: from discovery to astronomy. La Riv. Nuovo Cimento 35, 389–480 (2012).
Amelino-Camelia, G. Gravity-wave interferometers as quantum-gravity detectors. Nature 398, 216–218 (1999).
Hogan, C. J. Interferometers as probes of Planckian quantum geometry. Phys. Rev. D 85, 064007 (2012).
Acknowledgements
F. Marin and F. Marino thank D. Seminara and M. Inguscio for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F. Marin conceived the work, which was further developed with F. Marino and all other authors. F. Marin and F. Marino wrote the manuscript with input from all of the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1025 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marin, F., Marino, F., Bonaldi, M. et al. Gravitational bar detectors set limits to Planck-scale physics on macroscopic variables. Nature Phys 9, 71–73 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2503
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2503
This article is cited by
-
First-order quantum corrections of tunneling radiation in modified Schwarzschild–Rindler black hole
General Relativity and Gravitation (2024)
-
Effective GUP-modified Raychaudhuri equation and black hole singularity: four models
Journal of High Energy Physics (2021)
-
On quantum gravity tests with composite particles
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Kepler Problem in Space with Deformed Lorentz-Covariant Poisson Brackets
Foundations of Physics (2020)
-
Creation and control of multi-phonon Fock states in a bulk acoustic-wave resonator
Nature (2018)