Abstract
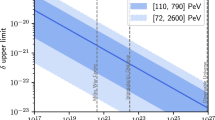
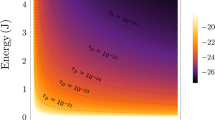
Wheeler’s ‘spacetime-foam’1 picture of quantum gravity (QG) suggests spacetime fuzziness (fluctuations leading to non-deterministic effects) at distances comparable to the Planck length, LPl ≈ 1.62 × 10−33 cm, the inverse (in natural units) of the Planck energy, EPl ≈ 1.22 × 1019 GeV. The resulting non-deterministic motion of photons on the Planck scale is expected to produce energy-dependent stochastic fluctuations in their speed. Such a stochastic deviation from the well-measured speed of light at low photon energies, c, should be contrasted with the possibility of an energy-dependent systematic, deterministic deviation. Such a systematic deviation, on which observations by the Fermi satellite set Planck-scale limits for linear energy dependence2, is more easily searched for than stochastic deviations. Here, for the first time, we place Planck-scale limits on the more generic spacetime-foam prediction of energy-dependent fuzziness in the speed of photons. Using high-energy observations from the Fermi Large Area Telescope (LAT) of gamma-ray burst GRB090510, we test a model in which photon speeds are distributed normally around c with a standard deviation proportional to the photon energy. We constrain the model’s characteristic energy scale beyond the Planck scale at >2.8EPl(>1.6EPl), at 95% (99%) confidence. Our results set a benchmark constraint to be reckoned with by any QG model that features spacetime quantization.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wheeler, J. in Relativity, Groups and Topology (eds DeWitt, C. M. & DeWitt, B. S.) 467–500 (Gordon and Breach, 1964).
Abdo, A. A. et al. A limit on the variation of the speed of light arising from quantum gravity effects. Nature 462, 331–334 (2009).
Amelino-Camelia, G. Quantum-spacetime phenomenology. Living Rev. Relativ. 16, 5 (2013).
Amelino-Camelia, G. Gravity-wave interferometers as quantum-gravity detectors. Nature 398, 216–218 (1999).
Christiansen, W., Ng, Y. J. & van Dam, H. Probing spacetime foam with extragalactic sources. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 051301 (2006).
Amelino-Camelia, G. & Smolin, L. Prospects for constraining quantum gravity dispersion with near term observations. Phys. Rev. D 80, 084017 (2009).
Jacob, U. & Piran, T. Lorentz-violation-induced arrival delays of cosmological particles. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 01, 031 (2008).
Majid, S. & Ruegg, H. Bicrossproduct structure of κ-Poincare group and non-commutative geometry. Phys. Lett. B 334, 348–354 (1994).
Madore, J., Schraml, S., Schupp, P. & Wess, J. Gauge theory on noncommutative spaces. Eur. Phys. J. C16, 161–167 (2000).
Amelino-Camelia, G., Ellis, J., Mavromatos, N. E., Nanopoulos, D. V. & Sarker, S. Tests of quantum gravity from observations of γ-ray bursts. Nature 393, 763–765 (1998).
Cucchiara, A. et al. A photometric redshift of z ∼ 9.4 for GRB 090429B. Astrophys. J. 736, 7 (2011).
McBreen, S. et al. Optical and near-infrared follow-up observations of four Fermi/LAT GRBs: redshifts, afterglows, energetics, and host galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 516, A71 (2010).
Ackermann, M. et al. Fermi observations of GRB 090510: A short-hard gamma-ray burst with an additional, hard power-law component from 10 keV to GeV energies. Astrophys. J. 716, 1178–1190 (2010).
Ackermann, M. et al. The first Fermi-LAT gamma-ray burst catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 209, 11 (2013).
Vasileiou, V. et al. Constraints on Lorentz invariance violation from Fermi-Large Area Telescope observations of gamma-ray bursts. Phys. Rev. D 87, 122001 (2013).
Atwood, W. B. et al. The large area telescope on the Fermi gamma-ray space telescope mission. Astrophys. J. 697, 1071–1102 (2009).
Martınez, M. & Errando, M. A new approach to study energy-dependent arrival delays on photons from astrophysical sources. Astropart. Phys. 31, 226–232 (2009).
Abramowski, A. et al. Search for Lorentz Invariance breaking with a likelihood fit of the PKS 2155-304 flare data taken on MJD 53944. Astropart. Phys. 34, 738–747 (2011).
Feldman, G. J. & Cousins, R. D. Unified approach to the classical statistical analysis of small signals. Phys. Rev. D 57, 3873–3889 (1998).
Lieu, R. & Hillman, L. W. The phase coherence of light from extragalactic sources: Direct evidence against first-order Planck-scale fluctuations in time and space. Astrophys. J. 585, L77–L80 (2003).
Tamburini, F., Cuofano, C., Della Valle, M. & Gilmozzi, R. No quantum gravity signature from the farthest quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 533, A71 (2011).
Actis, M. et al. Design concepts for the Cherenkov Telescope Array CTA: An advanced facility for ground-based high-energy gamma-ray astronomy. Exp. Astron. 32, 193–316 (2011).
Inoue, S. et al. Gamma-ray burst science in the era of the Cherenkov Telescope Array. Astropart. Phys. 43, 252–275 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The Fermi-LAT Collaboration acknowledges support for LAT development, operation and data analysis from NASA and DOE (United States), CEA/Irfu and IN2P3/CNRS (France), ASI and INFN (Italy), MEXT, KEK and JAXA (Japan), and the K. A. Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and the National Space Board (Sweden). Science analysis support in the operations phase from INAF (Italy) and CNES (France) is also gratefully acknowledged. This research was supported by an ERC advanced grant (GRBs), by the I-CORE (grant No 1829/12), by the joint ISF-NSFC program (T.P.) and by the Templeton Foundation (G.A-C.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed significantly to this work. V.V. and J.G. have focused mainly on the data analysis and deriving the limits, whereas T.P. and G.A-C. have focused mainly on the theory parts.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 2116 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasileiou, V., Granot, J., Piran, T. et al. A Planck-scale limit on spacetime fuzziness and stochastic Lorentz invariance violation. Nature Phys 11, 344–346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3270
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3270
This article is cited by
-
Quantum gravitational decoherence from fluctuating minimal length and deformation parameter at the Planck scale
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Single extra dimension from κ-Poincaré and gauge invariance
Journal of High Energy Physics (2021)
-
The variation of photon speed with photon frequency in quantum gravity
Indian Journal of Physics (2018)
-
Spacetime fuzziness in focus
Nature Physics (2015)