Abstract
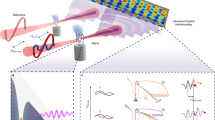
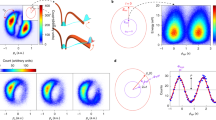
Attosecond physics offers new insights into ultrafast quantum phenomena involving electron dynamics on the fastest measurable timescales. The rapid progress in this field enables us to re-visit one of the most fundamental strong-field phenomena: field-induced tunnel ionization1,2,3. In this work, we employ high-harmonic generation to probe the electron wavefunction during field-induced tunnelling through a potential barrier. By using a combination of strong and weak driving laser fields, we modulate the atomic potential barrier on optical subcycle timescales. This induces a temporal interferometer between attosecond bursts originating from consecutive laser half-cycles. Our study provides direct insight into the basic properties of field-induced tunnelling, following the evolution of the electronic wavefunction within a temporal window of approximately 200 attoseconds.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uiberacker, M. et al. Attosecond real-time observation of electron tunnelling in atoms. Nature 446, 627–632 (2007).
Eckle, P. et al. Attosecond ionization and tunneling delay time measurements in helium. Science 322, 1525–1529 (2008).
Shafir, D. et al. Resolving the time when an electron exits a tunnelling barrier. Nature 485, 343–346 (2012).
Sokolovski, D. & Baskin, L. Traversal time in quantum scattering. Phys. Rev. A 36, 4604–4611 (1987).
Landauer, R. & Martin, T. Barrier interaction time in tunneling. Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 217–228 (1994).
Keldysh, L. Ionization in the field of a strong electromagnetic wave. Sov. Phys. JETP 20, 1307–1314 (1965).
Corkum, P. & Krausz, F. Attosecond science. Nature Phys. 3, 381–387 (2007).
Baltuška, A. et al. Attosecond control of electronic processes by intense light fields. Nature 421, 611–615 (2003).
Fittinghoff, D. N., Bolton, P. R., Chang, B. & Kulander, K. C. Observation of nonsequential double ionization of helium with optical tunneling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2642–2645 (1992).
Arissian, L. et al. Direct test of laser tunneling with electron momentum imaging. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 133002 (2010).
Serbinenko, V. & Smirnova, O. Multidimensional high harmonic spectroscopy: A semi-classical perspective on measuring multielectron rearrangement upon ionization. J. Phys. B 46, 171001 (2013).
Litvinyuk, I. V. et al. Shakeup excitation during optical tunnel ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 033003 (2005).
Bryan, W. et al. Atomic excitation during recollision-free ultrafast multi-electron tunnel ionization. Nature Phys. 2, 379–383 (2006).
Büttiker, M. & Landauer, R. Traversal time for tunneling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 1739–1742 (1982).
Dudovich, N. et al. Measuring and controlling the birth of attosecond XUV pulses. Nature Phys. 2, 781–786 (2006).
Steinberg, A. M., Kwiat, P. G. & Chiao, R. Y. Measurement of the single-photon tunneling time. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 708–711 (1993).
Corkum, P. B. Plasma perspective on strong field multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1994–1997 (1993).
Dahlström, J., L’Huillier, A. & Mauritsson, J. Quantum mechanical approach to probing the birth of attosecond pulses using a two-colour field. J. Phys. B 44, 095602 (2011).
Lewenstein, M., Balcou, P., Ivanov, M. Y., L’Huillier, A. & Corkum, P. B. Theory of high-harmonic generation by low-frequency laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 49, 2117–2132 (1994).
Salières, P. et al. Feynman’s path-integral approach for intense-laser-atom interactions. Science 292, 902–905 (2001).
Soifer, H. et al. Spatio-spectral analysis of ionization times in high-harmonic generation. Chem. Phys. 414, 176–183 (2013).
Mairesse, Y. et al. Attosecond synchronization of high-harmonic soft X-rays. Science 302, 1540–1543 (2003).
Zhao, J. & Lein, M. Determination of ionization and tunneling times in high-order harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 043901 (2013).
Torlina, L. & Smirnova, O. Time-dependent analytical R-matrix approach for strong-field dynamics. II. One-electron systems. Phys. Rev. A 86, 043408 (2012).
Ivanov, M. Y., Spanner, M. & Smirnova, O. Anatomy of strong field ionization. J. Mod. Opt. 52, 165–184 (2005).
Mairesse, Y. et al. High harmonic spectroscopy of multichannel dynamics in strong-field ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 213601 (2010).
Rohringer, N. & Santra, R. Multichannel coherence in strong-field ionization. Phys. Rev. A 79, 053402 (2009).
Smirnova, O. et al. High harmonic interferometry of multi-electron dynamics in molecules. Nature 460, 972–977 (2009).
Torlina, L., Ivanov, M., Walters, Z. B. & Smirnova, O. Time-dependent analytical R-matrix approach for strong-field dynamics. II. Many-electron systems. Phys. Rev. A 86, 043409 (2012).
Weinkauf, R., Schlag, E., Martinez, T. & Levine, R. Nonstationary electronic states and site-selective reactivity. J. Phys. Chem. A 101, 7702–7710 (1997).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank O. Raz, J. M. Dahlström and M. Yu. Ivanov for valuable discussions. N.D. is the incumbent of the Robin Chemers Neustein Professorial Chair. N.D. acknowledges the Minerva Foundation, the Israeli Science Foundation, the Crown Center of Photonics and the European Research Council for financial support. N.D. and O.S. acknowledge the German-Israeli Foundation. L.T. and O.S. acknowledge the support of DFG grant SM 292/2-3. F.M. and O.S. acknowledge the support of the DFG grant SM 292/3-1. D.S.B. and O.S. acknowledge the support of Einstein foundation project A-211-55 Attosecond Electron Dynamics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
O.P., G.O., H.S., B.D.B. and A.J.U. performed the experiments. O.P., G.O., F.M., O.S. and N.D. analysed and interpreted the data. Simulations were implemented by O.P., V.S., A.G.H., D.S.B. and F.M. This project was supervised by N.D. and O.S. All authors discussed the results and wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 2672 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedatzur, O., Orenstein, G., Serbinenko, V. et al. Attosecond tunnelling interferometry. Nature Phys 11, 815–819 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3436
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3436
This article is cited by
-
Observation of interband Berry phase in laser-driven crystals
Nature (2024)
-
Spatiotemporal imaging and shaping of electron wave functions using novel attoclock interferometry
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Photon-statistics force in ultrafast electron dynamics
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
Attosecond field emission
Nature (2023)
-
High-order harmonic generation from a thin film crystal perturbed by a quasi-static terahertz field
Nature Communications (2023)