Abstract
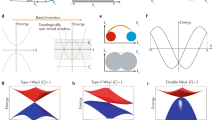
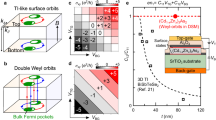
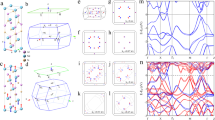
Weyl semimetal is a new quantum state of matter1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 hosting the condensed matter physics counterpart of the relativistic Weyl fermions13 originally introduced in high-energy physics. The Weyl semimetal phase realized in the TaAs class of materials features multiple Fermi arcs arising from topological surface states10,11,14,15,16 and exhibits novel quantum phenomena, such as a chiral anomaly-induced negative magnetoresistance17,18,19 and possibly emergent supersymmetry20. Recently it was proposed theoretically that a new type (type-II) of Weyl fermion21,22 that arises due to the breaking of Lorentz invariance, which does not have a counterpart in high-energy physics, can emerge as topologically protected touching between electron and hole pockets. Here, we report direct experimental evidence of topological Fermi arcs in the predicted type-II Weyl semimetal MoTe2 (refs 23,24,25). The topological surface states are confirmed by directly observing the surface states using bulk- and surface-sensitive angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, and the quasi-particle interference pattern between the putative topological Fermi arcs in scanning tunnelling microscopy. By establishing MoTe2 as an experimental realization of a type-II Weyl semimetal, our work opens up opportunities for probing the physical properties of this exciting new state.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nielsen, H. B. & Ninomiya, M. The Adler-Bell-Jackiw anomaly and Weyl fermions in a crystal. Phys. Lett. B 130, 389–396 (1983).
Wan, X., Turner, A. M., Vishwanath, A. & Savrasov, S. Y. Topological semimetal and Fermi-arc surface states in the electronic structure of pyrochlore iridates. Phys. Rev. B 83, 205101 (2011).
Burkov, A. A. & Balents, L. Weyl semimetal in a topological insulator multilayer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 127205 (2011).
Xu, G., Weng, H., Wang, Z., Dai, X. & Fang, Z. Chern semimetal and the quantized anomalous Hall effect in HgCr2Se4 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 186806 (2011).
Yang, K. Y., Lu, Y. M. & Ran, Y. Quantum Hall effects in a Weyl semimetal: possible application in pyrochlore iridates. Phys. Rev. B 84, 075129 (2011).
Hosur, P. & Qi, X. Recent developments in transport phenomena in Weyl semimetals. C. R. Phys. 14, 857–870 (2013).
Zhang, H., Wang, J., Xu, G., Xu, Y. & Zhang, S. C. Topological states in ferromagnetic CdO/EuO superlattices and quantum wells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 096804 (2014).
Liu, J. & Vanderbilt, D. Weyl semimetals from noncentrosymmetric topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 90, 155316 (2014).
Hirayama, M., Okugawa, R., Ishibashi, S., Murakami, S. & Miyake, T. Weyl node and spin texture in trigonal tellurium and selenium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 206401 (2015).
Weng, H., Fang, C., Fang, Z., Bernevig, B. A. & Dai, X. Weyl semimetal phase in noncentrosymmetric transition-metal monophosphides. Phys. Rev. X 5, 011029 (2015).
Huang, S.-M. et al. A Weyl Fermion semimetal with surface Fermi arcs in the transition metal monopnictide TaAs class. Nat. Commun. 6, 7373 (2015).
Ruan, J. et al. Symmetry-protected ideal Weyl semimetal in HgTe-class materials. Nat. Commun. 7, 11136 (2016).
Weyl, H. Elektron und gravitation I. Z. Phys. 56, 330–352 (1929).
Xu, S.-Y. et al. Discovery of a Weyl fermion semimetal and topological Fermi arcs. Science 349, 613–617 (2015).
Lv, B. Q. et al. Experimental discovery of Weyl semimetal TaAs. Phys. Rev. X 5, 031013 (2015).
Yang, L. X. et al. Weyl semimetal phase in the non-centrosymmetric compound TaAs. Nat. Phys. 11, 728–732 (2015).
Son, D. T. & Spivak, B. Z. Chiral anomaly and classical negative magnetoresistance of Weyl metals. Phys. Rev. B 88, 104412 (2013).
Huang, X. et al. Observation of the chiral-anomaly-induced negative magnetoresistance in 3D Weyl semimetal TaAs. Phys. Rev. X 5, 031023 (2015).
Zhang, C. et al. Signatures of the Adler-Bell-Jackiw chiral anomaly in a Weyl fermion semimetal. Nat. Commun. 7, 10735 (2016).
Jian, S. K., Jiang, Y. F. & Yao, H. Emergent spacetime supersymmetry in 3D Weyl semimetals and 2D Dirac semimetals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 237001 (2015).
Soluyanov, A. A. et al. Type-II Weyl semimetals. Nature 527, 495–498 (2015).
Xu, Y., Zhang, F. & Zhang, C. Structured Weyl points in spin-orbit coupled fermionic superfluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 265304 (2015).
Sun, Y., Wu, S. C., Ali, M. N., Felser, C. & Yan, B. Prediction of Weyl semimetal in orthorhombic MoTe2 . Phys. Rev. B 92, 161107 (2015).
Wang, Z. et al. MoTe2: a type-II Weyl topological metal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 056805 (2016).
Kourtis, S., Li, J., Wang, Z., Yazdani, A. & Bernevig, B. A. Universal signatures of Fermi arcs in quasiparticle interference on the surface of Weyl semimetals. Phys. Rev. B 93, 041109 (2016).
Ali, M. N. et al. Large, non-saturating magnetoresistance in WTe2 . Nature 514, 205–208 (2014).
Chang, T.-R. et al. Prediction of an arc-tunable Weyl fermion metallic state in MoxW1−xTe2 . Nat. Commun. 7, 10639 (2016).
Qi, Y. et al. Superconductivity in Weyl semimetal candidate MoTe2 . Nat. Commun. 7, 11038 (2016).
Pletikosić, I., Ali, M. N., Fedorov, A. V., Cava, R. J. & Valla, T. Electronic structure basis for the extraordinary magntoresistance in WTe2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 216601 (2014).
Wu, Y. et al. Temperature-induced Lifshiftz transition in WTe2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 166602 (2015).
Jiang, J. et al. Signature of strong spin-orbital coupling in the large nonsaturating magnetoresistance material WTe2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 166601 (2015).
Beloposki, I. et al. Fermi arc electronic structure and Chern numbers in the type-II Weyl semimetal candidate MoxW1−xTe2 . Phys. Rev. B 94, 085127 (2016).
Clarke, R., Marseglia, E. & Hughes, H. P. A low-temperature structural phase transition in β-MoTe2 . Phil. Mag. B 38, 121–126 (1978).
Manolikas, C., Van Landuyt, J. & Amelinckx, S. Electron microscopy and electron diffraction study of the domain structures, the dislocation fine structure, and the phase transformations in β-MoTe2 . Phys. Status Solidi 53, 327–338 (1979).
Keum, D. H. et al. Bandgap opening in few-layered monoclinic MoTe2 . Nat. Phys. 11, 482–486 (2015).
Wang, J. et al. Power-law decay of standing waves on the surface of topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 84, 235447 (2011).
Zhang, T. et al. Experimental demonstration of topological surface states protected by time-reversal symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 266803 (2009).
Huang, L. et al. Spectroscopic evidence for a type II Weyl semimetallic state in MoTe2 . Nat. Mater. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmat4685 (2016).
Xu, S.-Y. et al. Discovery of Lorentz-violating Weyl fermion semimetal state in LaAlGe materials. Preprint at http://arXiv.org/abs/1603.07318 (2016).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169 (1996).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 11274191, 11334006), Ministry of Science and Technology of China (no. 2015CB92100, 2016YFA0301004 and 2012CB932301) and Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program (no. 2012Z02285). The Advanced Light Source is supported by the Director, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, of the US Department of Energy under contract no. DE-AC02-05CH11231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.Z., X.C. and Y.W. conceived the research project. K.D. and K.Z. grew and characterized the samples under the supervision of Y.W. K.D., G.W., K.Z., S.D., E.W., M.Y. and Hongyun Z. performed the ARPES measurements and analysed the ARPES data. J.D. and A.F. provided support for the ARPES experiments. P.D. and Z.X. performed the STM measurements. Haijun Z. performed the first-principles calculations presented in the manuscript. H.H. and W.D. repeated the calculation. K.D., H.Yao, Y.W., X.C. and S.Z. wrote the manuscript, and all authors commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 1501 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, K., Wan, G., Deng, P. et al. Experimental observation of topological Fermi arcs in type-II Weyl semimetal MoTe2. Nature Phys 12, 1105–1110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3871
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3871
This article is cited by
-
Electric quadrupole second-harmonic generation revealing dual magnetic orders in a magnetic Weyl semimetal
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
Tilted Dirac superconductor at quantum criticality: restoration of Lorentz symmetry
Journal of High Energy Physics (2024)
-
Light control with Weyl semimetals
eLight (2023)
-
Spinful hinge states in the higher-order topological insulators WTe2
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Two step I to II type transitions in layered Weyl semi-metals and their impact on superconductivity
Scientific Reports (2023)