Abstract
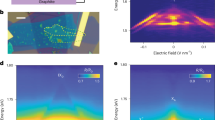
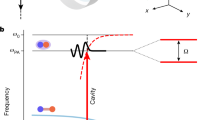
The dynamics of a mobile quantum impurity in a degenerate Fermi system is a fundamental problem in many-body physics. The interest in this field has been renewed due to recent ground-breaking experiments with ultracold Fermi gases1,2,3,4,5. Optical creation of an exciton or a polariton in a two-dimensional electron system embedded in a microcavity constitutes a new frontier for this field due to an interplay between cavity coupling favouring ultralow-mass polariton formation6 and exciton–electron interactions leading to polaron or trion formation7,8. Here, we present cavity spectroscopy of gate-tunable monolayer MoSe2 (ref. 9) exhibiting strongly bound trion and polaron resonances, as well as non-perturbative coupling to a single microcavity mode10,11. As the electron density is increased, the oscillator strength determined from the polariton splitting is gradually transferred from the higher-energy repulsive exciton-polaron resonance to the lower-energy attractive exciton-polaron state. Simultaneous observation of polariton formation in both attractive and repulsive branches indicates a new regime of polaron physics where the polariton impurity mass can be much smaller than that of the electrons. Our findings shed new light on optical response of semiconductors in the presence of free carriers by identifying the Fermi polaron nature of excitonic resonances and constitute a first step in investigation of a new class of degenerate Bose–Fermi mixtures12,13.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Massignan, P., Zaccanti, M. & Bruun, G. M. Polarons, dressed molecules and itinerant ferromagnetism in ultracold Fermi gases. Rep. Prog. Phys. 77, 034401 (2014).
Schirotzek, A., Wu, C.-H., Sommer, A. & Zwierlein, M. W. Observation of Fermi polarons in a tunable Fermi liquid of ultracold atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 230402 (2009).
Schmidt, R., Enss, T., Pietilä, V. & Demler, E. Fermi polarons in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. A 85, 021602 (2012).
Kohstall, C. et al. Metastability and coherence of repulsive polarons in a strongly interacting Fermi mixture. Nature 485, 615–618 (2012).
Koschorreck, M. et al. Attractive and repulsive Fermi polarons in two dimensions. Nature 485, 619–622 (2012).
Carusotto, I. & Ciuti, C. Quantum fluids of light. Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 299–366 (2013).
Esser, A., Zimmermann, R. & Runge, E. Theory of trion spectra in semiconductor nanostructures. Phys. Status Solidi B 227, 317–330 (2001).
Ganchev, B., Drummond, N., Aleiner, I. & Falko, V. Three-particle complexes in two-dimensional semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 107401 (2015).
Xu, X., Yao, W., Xiao, D. & Heinz, T. Spin and pseudospins in layered transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Phys. 10, 343–350 (2014).
Liu, X. et al. Strong light-matter coupling in two-dimensional atomic crystals. Nat. Photon. 9, 30–34 (2015).
Dufferwiel, S. et al. Exciton-polaritons in van der Waals heterostructures embedded in tunable microcavities. Nat. Commun. 6, 8579 (2015).
Laussy, F. P., Kavokin, A. V. & Shelykh, I. A. Exciton-polariton mediated superconductivity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 106402 (2010).
Cotleţ, O., Zeytinoǧlu, S., Sigrist, M., Demler, E. & Imamoǧlu, A. M. C. Superconductivity and other collective phenomena in a hybrid Bose–Fermi mixture formed by a polariton condensate and an electron system in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. B 93, 054510 (2016).
Chernikov, A. et al. Exciton binding energy and nonhydrogenic Rydberg series in monolayer WS2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 076802 (2014).
Srivastava, A. & Imamoglu, A. Signatures of Bloch-band geometry on excitons: nonhydrogenic spectra in transition-metal dichalcogenides. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 166802 (2015).
Zhou, J., Shan, W.-Y., Yao, W. & Xiao, D. Berry phase modification to the energy spectrum of excitons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 166803 (2015).
Wang, G. et al. Exciton states in monolayer MoSe2: impact on interband transitions. 2D Mater. 2, 045005 (2015).
Berkelbach, T. C., Hybertsen, M. S. & Reichman, D. R. Theory of neutral and charged excitons in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides. Phys. Rev. B 88, 045318 (2013).
Chernikov, A. et al. Electrical tuning of exciton binding energies in monolayer WS2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 126802 (2015).
Rapaport, R., Cohen, E., Ron, A., Linder, E. & Pfeiffer, L. N. Negatively charged polaritons in a semiconductor microcavity. Phys. Rev. B 63, 235310 (2001).
Smolka, S. et al. Cavity quantum electrodynamics with many-body states of a two-dimensional electron gas. Science 346, 332–335 (2014).
Jacqmin, T. et al. Direct observation of Dirac cones and a flatband in a honeycomb lattice for polaritons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 116402 (2014).
Suris, R. A. Optical Properties of 2D Systems with Interacting Electrons 111–124 (Springer Netherlands, 2003).
Koudinov, A. V. et al. Suris tetrons: possible spectroscopic evidence for four-particle optical excitations of a two-dimensional electron gas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 147402 (2014).
Duine, R. & MacDonald, A. Itinerant ferromagnetism in an ultracold atom Fermi gas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 230403 (2005).
Ross, J. S. et al. Electrical control of neutral and charged excitons in a monolayer semiconductor. Nat. Commun. 4, 1474 (2013).
Besga, B. et al. Polariton boxes in a tunable fiber cavity. Phys. Rev. Appl. 3, 014008 (2015).
Combescot, R. & Giraud, S. Normal state of highly polarized Fermi gases: full many-body treatment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 050404 (2008).
Vlietinck, J., Ryckebusch, J. & Van Houcke, K. Quasiparticle properties of an impurity in a Fermi gas. Phys. Rev. B 87, 115133 (2013).
Yu, H., Liu, G.-B., Gong, P., Xu, X. & Yao, W. Dirac cones and Dirac saddle points of bright excitons in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Commun. 5, 3876 (2014).
Zomer, P. J., Guimares, M. H. D., Brant, J. C., Tombros, N. & van Wees, B. J. Fast pick up technique for high quality heterostructures of bilayer graphene and hexagonal boron nitride. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 013101 (2014).
Acknowledgements
J. Reichel, A. Kis and R. Schmidt have made invaluable contributions to the experimental and theoretical aspects of this work. The authors also acknowledge many insightful discussions with C. Ciuti, M. Combescot, M. Fleischhauer, L. Glazman, M. Goldstein, F. Grusdt, D. Pimenov and J. von Delft. This work is supported by an ERC Advanced investigator grant (POLTDES), NCCR Quantum Science and Technology (NCCR QSIT), a research instrument of the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF), Harvard-MIT CUA, NSF Grant No. DMR-1308435, M. Rössler, the Walter Haefner Foundation and the ETH Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.S. and A.I. designed and supervised the experiment. M.S. carried out the measurements. P.B. fabricated the sample. T.F. and M.S. designed and assembled the cavity structure. A.S. and M.K. helped with the experiments. O.C., E.D. and A.I. developed the theoretical model. O.C. carried out the calculations. M.S., O.C. and A.I. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 583 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sidler, M., Back, P., Cotlet, O. et al. Fermi polaron-polaritons in charge-tunable atomically thin semiconductors. Nature Phys 13, 255–261 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3949
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3949
This article is cited by
-
The strongly driven Fermi polaron
Nature Physics (2025)
-
Chiral polaron formation on the edge of topological quantum matter
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Feshbach hypothesis of high-Tc superconductivity in cuprates
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Optical signatures of interlayer electron coherence in a bilayer semiconductor
Nature Physics (2025)
-
Single-molecule optoelectronic devices: exciton effect and spectroscopy characterization
Rare Metals (2025)