Abstract
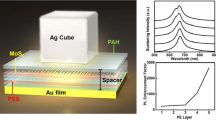
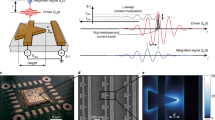
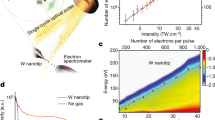
At high intensities, light–matter interactions are controlled by the electric field of the exciting light. For instance, when an intense laser pulse interacts with an atomic gas, individual cycles of the incident electric field ionize gas atoms and steer the resulting attosecond-duration electrical wavepackets1,2. Such field-controlled light–matter interactions form the basis of attosecond science and have recently expanded from gases to solid-state nanostructures3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18. Here, we extend these field-controlled interactions to metallic nanoparticles supporting localized surface plasmon resonances. We demonstrate strong-field, carrier-envelope-phase-sensitive photoemission from arrays of tailored metallic nanoparticles, and we show the influence of the nanoparticle geometry and the plasmon resonance on the phase-sensitive response. Additionally, from a technological standpoint, we push strong-field light–matter interactions to the chip scale. We integrate our plasmonic nanoparticles and experimental geometry in compact, micro-optoelectronic devices that operate out of vacuum and under ambient conditions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corkum, P. B. Plasma perspective on strong-field multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1994–1997 (1993).
Krausz, F. & Ivanov, M. Attosecond physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 163–234 (2009).
Bormann, R., Gulde, M., Weismann, A., Yalunin, S. V. & Ropers, C. Tip-enhanced strong-field photoemission. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 147601 (2010).
Schenk, M., Krüger, M. & Hommelhoff, P. Strong-field above-threshold photoemission from sharp metal tips. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 257601 (2010).
Krüger, M., Schenk, M. & Hommelhoff, P. Attosecond control of electrons emitted from a nanoscale metal tip. Nature 475, 78–81 (2011).
Yalunin, S. V., Gulde, M. & Ropers, C. Strong-field photoemission from surfaces: theoretical approaches. Phys. Rev. B 84, 195426 (2011).
Herink, G., Solli, D. R., Gulde, M. & Ropers, C. Field-driven photoemission from nanostructures quenches the quiver motion. Nature 483, 190–193 (2012).
Krüger, M., Schenk, M., Förster, M. & Hommelhoff, P. Attosecond physics in photoemission from a metal nanotip. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 45, 074006 (2012).
Schertz, F., Schmelzeisen, M., Kreiter, M., Elmers, H.-J. & Schönhense, G. Field emission of electrons generated by the near field of strongly coupled plasmons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 237602 (2012).
Keathley, P. D. et al. Strong-field photoemission from silicon field emitter arrays. Ann. Phys. 525, 144–150 (2013).
Park, D. J. et al. Strong field acceleration and steering of ultrafast electron pulses from a sharp metallic nanotip. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 244803 (2012).
Dombi, P. et al. Ultrafast strong-field photoemission from plasmonic nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 13, 674–678 (2013).
Nagel, P. M. et al. Surface plasmon assisted electron acceleration in photoemission from gold nanopillars. Chem. Phys. 414, 106–111 (2013).
Piglosiewicz, B. et al. Carrier-envelope phase effects on the strong-field photoemission of electrons from metallic nanostructures. Nat. Photon. 8, 37–42 (2014).
Swanwick, M. E. et al. Nanostructured ultrafast silicon-tip optical field-emitter arrays. Nano Lett. 14, 5035–5043 (2014).
Hobbs, R. G. et al. High-density Au nanorod optical field-emitter arrays. Nanotechnology 25, 465304 (2014).
Hobbs, R. G. et al. High-yield, ultrafast, surface plasmon-enhanced, Au nanorod optical field electron emitter arrays. ACS Nano 8, 11474–11482 (2014).
Kusa, F., Echternkamp, K. E., Herink, G., Ropers, C. & Ashihara, S. Optical field emission from resonant gold nanorods driven by femtosecond mid-infrared pulses. AIP Advances 5, 077138 (2015).
Keldysh, L. V. Ionization in the field of a strong electromagnetic wave. Sov. Phys. JETP 20, 1307–1314 (1965).
Büttiker, M. & Landauer, R. Traversal time for tunneling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 1739–1742 (1982).
Martin, Y. C., Hamann, H. F. & Wickramasinghe, H. K. Strength of the electric field in apertureless near-field optical microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 89, 5774–5778 (2001).
Arbouet, A., Houdellier, F., Marty, R. & Girard, C. Interaction of an ultrashort optical pulse with a metallic nanotip: a Green dyadic approach. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 053103 (2012).
Giannini, V., Fernández-Domínguez, A. I., Heck, S. C. & Maier, S. A. Plasmonic nanoantennas: fundamentals and their use in controlling the radiative properties of nanoemitters. Chem. Rev. 111, 3888–3912 (2011).
Biagioni, P., Huang, J.-S. & Hecht, B. Nanoantennas for visible and infrared radiation. Rep. Prog. Phys. 75, 024402 (2012).
Wong, T. K. S. & Ingram, S. G. Observational of Fowler–Nordheim tunnelling at atmospheric pressure using Au/Ti lateral tunnel diodes. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 26, 979–985 (1993).
Driskill-Smith, A. A. G., Hasko, D. G. & Ahmed, H. Nanoscale field emission structures for ultra-low voltage operation at atmospheric pressure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 3159–3161 (1997).
Brimley, S., Miller, M. S. & Hagmann, M. J. Field emission in air and space-charge-limited currents from iridium–iridium oxide tips with gaps below 100 nm. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 094510 (2011).
Han, J.-W., Oh, J. S. & Meyyappan, M. Vacuum nanoelectronics: back to the future?—Gate-insulated nanoscale vacuum channel transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 213505 (2012).
Dogariu, A., Shneider, M. N. & Miles, R. B. Versatile radar measurement of the electron loss rate in air. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 224102 (2013).
Murphy, E. L. & Good, R. H. Jr Thermionic emission, field emission, and the transition region. Phys. Rev. 102, 1464–1473 (1956).
Plech, A., Kotaidis, V., Lorenc, M. & Boneberg, J. Femtosecond laser near-field ablation from gold nanoparticles. Nat. Phys. 2, 44–47 (2006).
Lamprecht, B., Krenn, J. R., Leitner, A. & Aussenegg, F. R. Resonant and off-resonant light-driven plasmons in metal nanoparticles studied by femtosecond-resolution third-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 4421–4424 (1999).
Xu, L. et al. Route to phase control of ultrashort light pulses. Opt. Lett. 21, 2008–2010 (1996).
Paasch-Colberg, T. et al. Solid-state light-phase detector. Nat. Photon. 8, 214–218 (2014).
Acknowledgements
We thank O. D. Mücke for helpful comments and J. Daley for assistance in device fabrication. This work was supported by the United States Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) through grant FA9550-12-1-0499, the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science at DESY, and The Hamburg Center for Ultrafast Imaging: Structure, Dynamics and Control of Matter at the Atomic Scale, an excellence cluster of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. W.P.P. acknowledges earlier support from an NSF graduate research fellowship; P.D.K. acknowledges support from an NDSEG graduate fellowship; and R.G.H. acknowledges support for the device fabrication work from the Center for Excitonics, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the US Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under award number DE-SC0001088. We thank A. Chu and J. Wanapun for additional support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.P.P. and F.X.K. conceived of the experimental concept. W.P.P. and R.G.H. fabricated the devices. W.P.P. constructed the laser source and experimental apparatus and carried out the measurements. W.P.P. developed the model, and W.P.P., R.G.H., P.D.K., K.K.B. and F.X.K. interpreted the results and composed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 2013 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Putnam, W., Hobbs, R., Keathley, P. et al. Optical-field-controlled photoemission from plasmonic nanoparticles. Nature Phys 13, 335–339 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3978
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3978
This article is cited by
-
Ultrafast lasers for attosecond science
Light: Science & Applications (2026)
-
Petahertz electronics
Nature Reviews Physics (2024)
-
On-chip petahertz electronics for single-shot phase detection
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Sub-cycle multidimensional spectroscopy of strongly correlated materials
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
Real-time tracking of coherent oscillations of electrons in a nanodevice by photo-assisted tunnelling
Nature Communications (2024)