Abstract
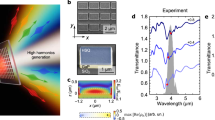
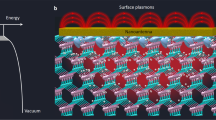
Plasmonic antennas can enhance the intensity of a nanojoule laser pulse by localizing the electric field in their proximity1. It has been proposed that the field can become strong enough to convert the fundamental laser frequency into high-order harmonics through an extremely nonlinear interaction with gas atoms that occupy the nanoscopic volume surrounding the antennas2,3,4. However, the small number of gas atoms that can occupy this volume limits the generation of high harmonics5,6,7. Here we use an array of monopole nano-antennas to demonstrate plasmon-assisted high-harmonic generation directly from the supporting crystalline silicon substrate. The high density of the substrate compared with a gas allows macroscopic buildup of harmonic emission. Despite the sparse coverage of antennas on the surface, harmonic emission is ten times brighter than without antennas. Imaging the high-harmonic radiation will allow nanometre and attosecond measurement of the plasmonic field8 thereby enabling more sensitive plasmon sensors9 while opening a new path to extreme-ultraviolet-frequency combs10.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stockman, M. I. Nanoplasmonics: the physics behind the applications. Phys. Today 64, 39–44 (February, 2011).
Kim, S. et al. High-harmonic generation by resonant plasmon field enhancement. Nature 453, 757–760 (2008).
Park, I.-Y. et al. Plasmonic generation of ultrashort extreme-ultraviolet light pulses. Nat. Photon. 5, 677–681 (2011).
Park, I.-Y. et al. Generation of EUV radiation by plasmonic field enhancement using nano-structured bowties and funnel-waveguides. Ann. Phys. (Leipz.) 525, 87–96 (2013).
Sivis, M. et al. Nanostructure-enhanced atomic line emission. Nature 485, E1–E3 (2012).
Sivis, M. et al. Extreme-ultraviolet light generation in plasmonic nanostructures. Nat. Phys. 9, 304–309 (2013).
Raschke, M. B. High-harmonic generation with plasmonics: feasible or unphysical? Ann. Phys. (Leipz.) 525, A40–A42 (2013).
Feist, J., Homer Reid, M. T. & Kling, M. F. Nanoplasmonic near-field synthesis. Phys. Rev. A 87, 033816 (2013).
Stewart, M. E. et al. Nanostructured plasmonic sensors. Chem. Rev. 108, 494–521 (2008).
Cingöz, A. et al. Direct frequency comb spectroscopy in the extreme ultraviolet. Nature 482, 68–71 (2012).
Li, X. F. et al. Multiple-harmonic generation in rare gases at high laser intensity. Phys. Rev. A 39, 5751–5761 (1989).
Pfeifer, T., Spielmann, C. & Gerber, G. Femtosecond x-ray science. Rep. Prog. Phys. 69, 443–505 (2006).
Ghimire, S. et al. Observation of high-order harmonic generation in a bulk crystal. Nat. Phys. 7, 138–141 (2011).
Schubert, O. et al. Sub-cycle control of terahertz high-harmonic generation by dynamical Bloch oscillations. Nat. Photon. 8, 119–123 (2014).
Luu, T. T. et al. Extreme ultraviolet high-harmonic spectroscopy of solids. Nature 521, 498–502 (2015).
Vampa, G. et al. Generation of high harmonics from silicon. Preprint at http://arXiv.org/abs/1605.06345 (2016).
Han, S. et al. High-harmonic generation by field enhanced femtosecond pulses in metal-sapphire nanostructure. Nat. Commun 7, 13105 (2016).
Boyd, R. W. Nonlinear Optics (Academic, 2003).
Pfullmann, N. et al. Bow-tie nano-antenna assisted generation of extreme ultraviolet radiation. New J. Phys. 15, 093027 (2013).
Pfullmann, N. et al. Nano-antenna-assisted harmonic generation. Appl. Phys. B 113, 75–79 (2013).
Guler, U., Shalaev, V. M. & Boltasseva, A. Nanoparticle plasmonics: going practical with transition metal nitrides. Mater. Today 18, 227–237 (April, 2015).
Barwick, B., Flannigan, D. J. & Zewail, A. H. Photon-induced near-field electron microscopy. Nature 462, 902–906 (2009).
Kawata, S., Inouye, Y. & Verma, P. Plasmonics for near-field nano-imaging and superlensing. Nat. Photon. 3, 388–394 (2009).
Zhang, B. et al. High contrast 3D imaging of surfaces near the wavelength limit using tabletop EUV ptychography. Ultramicroscopy 158, 98–104 (2015).
Chapman, H. N. et al. Femtosecond diffractive imaging with a soft-X-ray free-electron laser. Nat. Phys. 2, 839–843 (2006).
Förg, B. et al. Attosecond nanoscale near-field sampling. Nat. Commun. 7, 11717 (2016).
Kim, K. T. et al. Petahertz optical oscilloscope. Nat. Photon. 7, 958–962 (2013).
Dudovich, N. et al. Measuring and controlling the birth of attosecond XUV pulses. Nat. Phys. 2, 781–786 (2006).
Vampa, G. et al. Linking high harmonics from gases and solids. Nature 522, 462–464 (2015).
Ciappina, M. F. et al. High-order-harmonic generation from inhomogeneous fields. Phys. Rev. A 85, 033828 (2012).
Yu, N. & Capasso, F. Flat optics with designer metasurfaces. Nat. Mater. 13, 139–150 (2014).
Barbry, M. et al. Atomistic near-field nanoplasmonics: reaching atomic-scale resolution in nanooptics. Nano Lett. 15, 3410–3419 (2015).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Crane and B. Avery for technical support. G.V. thanks M. Sivis for insightful discussions. This material is based on work supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under award number FA9550-16-1-0109 and the AFOSR MURI grant number FA9550-15-1-0037. The authors also acknowledge financial support from the NRC, NSERC and CFI/ORF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.V. and P.B.C. conceived the experiment; G.V. and T.J.H. performed the high-harmonic measurements; B.G.G. and S.S.M. designed the nano-antennas; B.G.G., A.O. and E.L.-S. fabricated the antennas; A.S. and A.Y.N. maintained the laser source; D.M.V., P.B.C. and P.B. supervised the experiment; all authors contributed to the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 615 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vampa, G., Ghamsari, B., Siadat Mousavi, S. et al. Plasmon-enhanced high-harmonic generation from silicon. Nature Phys 13, 659–662 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys4087
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys4087
This article is cited by
-
Giant near-field nonlinear electrophotonic effects in an angstrom-scale plasmonic junction
Nature Communications (2026)
-
The attoscience of strong-field-driven solids
Nature Reviews Physics (2024)
-
Many-body enhancement of high-harmonic generation in monolayer MoS2
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Sub-cycle multidimensional spectroscopy of strongly correlated materials
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
Tuneable Terahertz Surface Plasmons Excitation in a Metal-Air-Metal Symmetrical Structure by Relativistic Electron Beam
Plasmonics (2024)