Abstract
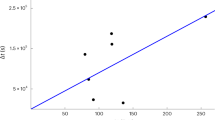
Lorentz-invariance violation (LIV) arises in various quantum-gravity1,2 theories, but typically at Planck energies that are not accessible on Earth. To test LIV, we must turn to astronomical observations2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11. Time-of-flight measurements from astronomical sources have set the present limits on the LIV energy scale. According to existing models, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are accompanied by very high-energy neutrinos12,13. At these energies, the background level in neutrino detectors such as IceCube (currently under construction in Antarctica) is extremely low. We show that the detection of even a single neutrino from the same direction as a GRB, months after the burst, would be statistically significant and imply that the neutrino was associated with the burst. The detection of several delayed neutrinos from different bursts with compatible relations between their delay times, energies and distances would enable us to generically determine (or set limits on) LIV at levels that cannot be reached by any other method.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amelino-Camelia, G. Quantum theory’s last challenge. Nature 408, 661–664 (2000).
Amelino-Camelia, G. et al. Tests of quantum gravity from observations of gamma-ray bursts. Nature 393, 763–765 (1998).
Ellis, J., Mavromatos, N. E., Nanopoulos, D. V. & Sakharov, A. S. Quantum-gravity analysis of gamma-ray bursts using wavelets. Astron. Astrophys. 402, 409–424 (2003).
Boggs, S. E., Wunderer, C. B., Hurley, K. & Coburn, W. Testing Lorentz invariance with GRB 021206. Astrophys. J. Lett. 611, L77–L80 (2004).
Rodríguez Martínez, M., Piran, T. & Oren, Y. GRB 051221A and tests of Lorentz symmetry. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 05(2006)017 (2006).
Ellis, J. et al. Robust limits on Lorentz violation from gamma-ray bursts. Astropart. Phys. 25, 402–411 (2006).
Biller, S. D. et al. Limits to quantum gravity effects on energy dependence of the speed of light from observations of TeV flares in active galaxies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 2108–2111 (1999).
Kaaret, P. Pulsar radiation and quantum gravity. Astron. Astrophys. 345, L32–L34 (1999).
Jacobson, T., Liberati, S. & Mattingly, D. A strong astrophysical constraint on the violation of special relativity by quantum gravity. Nature 424, 1019–1021 (2003).
Jacobson, T., Liberati, S., Mattingly, D. & Stecker, F. W. New limits on Planck scale Lorentz violation in QED. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 021101 (2004).
Stecker, F. W. & Scully, S. T. Lorentz invariance violation and the spectrum and source power of ultrahigh energy cosmic rays. Astropart. Phys. 23, 203–209 (2005).
Waxman, E. & Bahcall, J. High energy neutrinos from cosmological gamma-ray burst fireballs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 2292–2295 (1997).
Vietri, M. On the energy of neutrinos from gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 507, 40–45 (1998).
Gonzalez-Mestres, L. Physics opportunities above the Greisen-Zatsepin-Kuzmin cutoff: Lorentz symmetry violation at the Planck scale. AIP Conf. Proc. 433, 148–158 (1998).
Coleman, S. & Glashow, S. L. High-energy tests of Lorentz invariance. Phys. Rev. D 59, 116008 (1999).
Amelino-Camelia, G. & Piran, T. Planck-scale deformation of Lorentz symmetry as a solution to the ultrahigh energy cosmic ray and the TeV-photon paradoxes. Phys. Rev. D 64, 036005 (2001).
Greisen, K. End to the cosmic-ray spectrum? Phys. Rev. Lett. 16, 748–750 (1966).
Zatsepin, G. T. & Kuzmin, V. A. Upper limit of the spectrum of cosmic rays. JETP Lett. 4, 78–80 (1966).
Ellis, J., Mavromatos, N. E., Nanopoulos, D. V. & Sakharov, A. S. Cosmology: Synchrotron radiation and quantum gravity. Nature 428, (2004).
Rodríguez Martínez, M. & Piran, T. Constraining Lorentz violations with gamma ray bursts. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 04(2006)006 (2006).
Choubey, S. & King, S. F. Gamma ray bursts as probes of neutrino mass, quantum gravity, and dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 67, 073005 (2003).
Piran, T. The physics of gamma-ray bursts. Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 1143–1210 (2004).
Halzen, F. Astroparticle physics with high energy neutrinos: from AMANDA to IceCube. Eur. Phys. J. C 46, 669–687 (2006).
Waxman, E. Extra galactic sources of high energy neutrinos. Phys. Scripta T 121, 147–152 (2005).
Guetta, D. et al. Neutrinos from individual gamma-ray bursts in the BATSE catalog. Astropart. Phys. 20, 429–455 (2004).
Alvarez-Muñiz, J., Halzen, F. & Hooper, D. W. High energy neutrinos from gamma ray bursts: Event rates in neutrino telescopes. Phys. Rev. D 62, 093015 (2000).
Halzen, F. & Hooper, D. W. Neutrino event rates from gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 527, L93–L96 (1999).
Amelino-Camelia, G. Proposal of a second generation of quantum-gravity-motivated Lorentz-Symmetry tests: Sensitivity to effects suppressed quadratically by the Planck scale. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 12, 1633–1639 (2003).
Ahrens, J. et al. Sensitivity of the IceCube detector to astrophysical sources of high energy muon neutrinos. Astropart. Phys. 20, 507–532 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the ISF center of excellence for High Energy Astrophysics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacob, U., Piran, T. Neutrinos from gamma-ray bursts as a tool to explore quantum-gravity-induced Lorentz violation. Nature Phys 3, 87–90 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys506
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys506
This article is cited by
-
Effects on neutrino propagation in space-time foam of D-branes revisited
Journal of High Energy Physics (2024)
-
Could quantum gravity slow down neutrinos?
Nature Astronomy (2023)
-
Neutrinos could hold the key to proving the quantization of spacetime
Nature Astronomy (2023)
-
Lorentz and CPT breaking in gamma-ray burst neutrinos from string theory
Journal of High Energy Physics (2023)
-
Implications of SU(2)L gauge invariance for constraints on Lorentz violation
Journal of High Energy Physics (2021)