Abstract
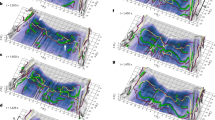
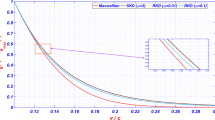
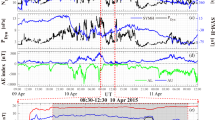
Detection of a separator line that connects magnetic nulls and the determination of the dynamics and plasma environment of such a structure can improve our understanding of the three-dimensional (3D) magnetic reconnection process1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9. However, this type of field and particle configuration has not been directly observed in space plasmas. Here we report the identification of a pair of nulls, the null–null line that connects them, and associated fans and spines in the magnetotail of the Earth using data from the four Cluster spacecraft. With di and de designating the ion and electron inertial lengths, respectively, the separation between the nulls is found to be ∼0.7±0.3di and an associated oscillation is identified as a lower-hybrid wave with wavelength ∼de. This in situ evidence of the full 3D reconnection geometry and associated dynamics provides an important step towards establishing an observational framework of 3D reconnection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Priest, E. R. & Forbes, T. G. Magnetic Reconnection: MHD Theory and Applications (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 2000).
Greene, J. M. Geometrical properties of 3D reconnecting magnetic fields with nulls. J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8583–8590 (1988).
Lau, Y.-T. & Finn, J. M. Three-dimensional kinematic reconnection in the presence of field nulls and closed field lines. Astrophys. J. 350, 672–691 (1990).
Priest, E. R. & Titov, V. S. Magnetic reconnection at three-dimensional null points. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 354, 2951–2992 (1996).
Scholer, M. et al. Onset of collisionless magnetic reconnection in thin current sheets: Three-dimensional particle simulations. Phys. Plasmas 10, 3521–3527 (2003).
Jaroschek, C. H., Treumann, R. A., Lesch, H. & Scholer, M. Fast reconnection in relativistic pair plasmas: Analysis of particle acceleration in self-consistent full particle simulations. Phys. Plasmas 11, 1151–1157 (2004).
Ji, H. et al. Electromagnetic fluctuations during fast reconnection in a laboratory plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 115001 (2004).
Pontin, D. I. & Craig, I. J. D. Dynamic three-dimensional reconnection in a separator geometry with two null points. Astrophys. J 642, 568–578 (2006).
Xiao, C. J. et al. In situ evidence for the structure of the magnetic null in a 3D reconnection event in the Earth’s magnetotail. Nature Phys. 2, 478–483 (2006).
Parnell, C. E., Smith, J. M., Neukirch, T. & Priest, E. R. The structure of three-dimensional magnetic neutral points. Phys. Plasmas 3, 759–770 (1996).
Filippov, B. Observation of a 3D magnetic null point in the solar corona. Sol. Phys. 185, 297–309 (1999).
Escoubet, C. P., Schmidt, R. & Goldstein, M. L. in The Cluster and Phoenix Missions (ed. Escoubet, C. P. et al.) 11–32 (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 1997).
Greene, J. M. Locating three-dimensional roots by a bisection method. J. Comput. Phys. 98, 194–198 (1992).
Zhao, H., Wang, J., Zhang, J. & Xiao, C. J. A new method of identifying 3D null points in solar vector magnetic fields. Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 5, 443–447 (2005).
Balogh, A. et al. The cluster magnetic field investigation: Overview of in-flight performance and initial results. Ann. Geophys. 19, 1207–1217 (2001).
Reme, H. et al. First multispacecraft ion measurements in and near the Earth’s magnetosphere with the identical Cluster ion spectrometry (CIS) experiment. Ann. Geophys. 19, 1303–1354 (2001).
Runov, A. et al. Current sheet structure near magnetic X-line observed by cluster. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, 1579 (2003).
Wygant, J. R. et al. Cluster observations of an intense normal component of the electric field at a thin reconnecting current sheet in the tail and its role in the shock-like acceleration of the ion fluid into the separatrix region. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09206 (2005).
Wilber, M. et al. Cluster observations of velocity space-restricted ion distributions near the plasma sheet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, L24802 (2004).
Cattell, C. et al. Cluster observations of electron holes in association with magnetotail reconnection and comparison to simulations. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A01211 (2004).
Birn, J. et al. Geospace environmental modeling (GEM) magnetic reconnection challenge. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 3715–3719 (2001).
Øieroset, M. et al. In situ detection of collisionless reconnection in the earth’s magnetotail. Nature 412, 414–417 (2001).
Deimling, A. Nonlinear Functional analysis (Spring, New York, 1985).
Dunlop, M. W., Southwood, D. J., Glassmeier, K.-H. & Neubauer, F. M. Analysis of multipoint magnetometer. Adv. Space Res. 8, 273–277 (1988).
Chanteur, G. in Analysis Methods for Multi-Spacecraft Data (eds Paschmann, G. & Daly, P. W.) 349–369 (ESA Publications Division, Noordwijk, 1998).
Bale, S. D., Mozer, F. S. & Phan, T. Observation of lower hybrid drift instability in the diffusion region at a reconnecting magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, 2180 (2002).
Vaivads, A. et al. Cluster observations of lower hybrid turbulence within thin layers at the magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, L03804 (2004).
Carter, T. A. et al. Measurement of lower-hybrid drift turbulence in a reconnecting current sheet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 015001 (2002).
Chaston, C. C. et al. Drift-kinetic alfvén waves observed near a reconnection X line in the earth’s magnetopause. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 065002 (2005).
Grinsted, A., Moore, J. C. & Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Processes Geophys. 11, 561–566 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the NSFC Programs (grant Nos 40390150, 40504021, 10233050, 10575018, 40536030, 40425004 and 40228006) and the National Basic Research Programme of China (grant No 2006CB806300), as well as the CAS Project KJCX2-YW-T04 and the China Double Star-Cluster Science Team. C.J.X. also thanks A. Grinsted at the University of Lapland for supporting the MatLab wavelet coherence package.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.J.X., X.G.W., and Z.Y.P. are first authors with equal contributions to theoretical and data analysis. Z.W.M. has also made important contributions to the paper, and H.Z., G.P.Z. and J.X.W. have developed analysis tools and participated in the analysis. Other coauthors have provided the Cluster observation data and been involved in discussions. M.G.K. has also made significant contributions to the final revision of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, C., Wang, X., Pu, Z. et al. Satellite observations of separator-line geometry of three-dimensional magnetic reconnection. Nature Phys 3, 609–613 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys650
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys650
This article is cited by
-
Evolution of clustered magnetic nulls in a turbulent-like reconnection region in the magnetotail
Science Bulletin (2016)
-
Extreme ultraviolet imaging of three-dimensional magnetic reconnection in a solar eruption
Nature Communications (2015)
-
Three-Year Global Survey of Coronal Null Points from Potential-Field-Source-Surface (PFSS) Modeling and Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) Observations
Solar Physics (2015)
-
Concentration of electrostatic solitary waves around magnetic nulls within magnetic reconnection diffusion region: single-event-based statistics
Earth, Planets and Space (2014)
-
Recent progresses in theoretical studies and satellite observations for collisionless magnetic reconnection
Chinese Science Bulletin (2012)