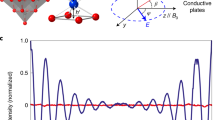
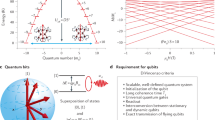
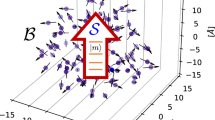
Abstract
Tunable electron spins in solid media are among the most promising candidates for qubits1. In this context, molecular nanomagnets have been proposed as hardware for quantum computation2. The flexibility in their synthesis represents a distinct advantage over other spin systems, enabling the systematic production of samples with desirable properties, for example, with a view to implementing quantum logic gates3,4. Here, we report the observation of quantum interference associated with tunnelling trajectories between states of different total spin length in a dimeric molecular nanomagnet. We argue that the interference is a consequence of the unique characteristics of a molecular Mn12 wheel, which behaves as a molecular dimer with weak ferromagnetic exchange coupling: each half of the molecule acts as a single-molecule magnet, whereas the weak coupling between the two halves gives rise to an extra internal spin degree of freedom within the molecule—that is, its total spin may fluctuate. More importantly, the observation of quantum interference provides clear evidence for quantum-mechanical superpositions involving entangled states shared between both halves of the wheel.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loss, D. & DiVincenzo, D. P. Quantum computation with quantum dots. Phys. Rev. A 57, 120–126 (1998).
Leuenberger, M. & Loss, D. Quantum computing in molecular magnets. Nature 410, 789–793 (2001).
Wernsdorfer, W., Aliaga-Alcade, N., Hendrickson, D. N. & Christou, G. Exchange-biased quantum tunneling in a supramolecular dimer of single-molecule magnets. Nature 416, 406–409 (2002).
Hill, S., Edwards, R. S., Aliaga-Alcade, N. & Christou, G. Quantum coherence in an exchange-coupled dimer of single-molecule magnets. Science 302, 1015–1018 (2003).
Prokof ’ev, N. V. & Stamp, P. C. E. Theory of the spin bath. Rep. Prog. Phys. 63, 669–726 (2000).
Chudnovsky, E. M. Universal decoherence in solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 120405 (2004).
del Barco, E., Kent, A. D., Yang, E. C. & Hendrickson, D. N. Quantum superposition of high spin states in the single molecule magnet Ni4 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 157202 (2004).
Wernsdorfer, W., Mailly, D., Timco, G. A. & Winpenny, R. E. P. Resonant photon absorption and hole burning in Cr7Ni antiferromagnetic rings. Phys. Rev. B 72, 060409 (2005).
Waldmann, O., Dobe, C., Mutka, H., Furrer, A. & Güdel, H. U. Neel-vector tunneling in antiferromagnetic molecular clusters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 057202 (2005).
Bal, M. et al. Non-equilibrium magnetization dynamics in the Fe8 single-molecule magnet induced by high-intensity microwave radiation. Europhys. Lett. 71, 110–116 (2005).
Ardavan, A. et al. Will spin-relaxation times in molecular magnets permit quantum information processing? Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 057201 (2007).
Friedman, J. R., Sarachik, M. P., Tejada, J. & Ziolo, R. Macroscopic measurements of resonant magnetization tunneling in high-spin molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 3830–3833 (1996).
Thomas, L. et al. Macroscopic quantum tunneling of magnetization in a single crystal of nanomagnets. Nature 383, 145–147 (1996).
Bokacheva, L., Kent, A. D. & Walters, M. A. Crossover between thermally assisted and pure quantum tunneling in molecular magnet Mn12-acetate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 4803–4806 (2000).
Wernsdorfer, W. & Sessoli, R. Quantum phase interference and parity effects in magnetic molecular clusters. Science 284, 133–135 (1999).
del Barco, E., Kent, A. D., Rumberger, E. M., Hendrickson, D. N. & Christou, G. Symmetry of magnetic quantum tunneling in single molecule magnet Mn12-acetate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 047203 (2003).
del Barco, E. et al. Magnetic quantum tunneling in the single-molecule magnet Mn12-acetate. J. Low. Temp. Phys. 140, 119–174 (2005).
Chudnovsky, E. M. & Tejada, J. Quantum Tunneling of the Magnetization (Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 1983).
Carretta, S. et al. Quantum oscillations of the total spin in a heterometallic antiferromagnetic ring: Evidence from neutron spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 167401 (2007).
Chiolero, A. & Loss, D. Macroscopic quantum coherence in ferrimagnets. Phys. Rev. B 56, 738–746 (1997).
Meier, F. & Loss, D. Electron and nuclear spin dynamics in antiferromagnetic molecular rings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5373–5376 (2001).
Loss, D., DiVincenzo, D. P. & Grinstein, G. Suppression of tunneling by interference in half-integer-spin particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 3232–3235 (1992).
von Delft, J. & Henley, C. L. Destructive quantum interference in spin tunneling problems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 3236–3239 (1992).
Garg, A. Topologically quenched tunnel splitting in spin systems without Kramers’ degeneracy. Europhys. Lett. 22, 205–210 (1993).
Leuenberger, M. N. & Loss, D. Spin tunneling and topological selection rules for integer spins. Phys. Rev. B 63, 054414 (2001).
Sjöqvist, E. Geometric phase for entangled spin pairs. Phys. Rev. A 62, 022109 (2000).
Rumberger, E., Zakharov, L., Rheingold, A. & Hendrickson, D. N. Synthesis and magnetic properties of wheel shaped [Mn12] and [Fe6] complexes. Inorg. Chem. 43, 6531–6533 (2004).
Rumberger, E. et al. Wheel shaped [Mn12] single molecule magnets. Inorg. Chem. 44, 2742–2752 (2005).
Foguet-Albiol, D. et al. DFT computational rationalization of an unusual spin ground state in an Mn-12 single-molecule magnet with a low-symmetry loop structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn 44, 897–901 (2005).
Dugan, D. M. & Hendrickson, D. N. Magnetic exchange interactions in transition-metal dimers 3: Nickel (II) di-μ-cyanato, di-μ-thiocyanato, and di-μ-selenocyanato complexes and related outer-sphere copper (II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 13, 2929–2940 (1974).
Bonesteel, N. E. Theory of anisotropic superexchange in insulating cuprates. Phys. Rev. B 47, 11302–11313 (1993).
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge fruitful discussions with Eduardo Mucciolo and Michael Leuenberger. E.d.B., S.H. and D.N.H. acknowledge support from the US National Science Foundation (DMR0706183 and DMR0747587), (DMR0506946 and DMR0239481) and (CHE0350615), respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.M.R. and E.d.B. planned and carried out the experiments. S.H. helped in the interpretation of the results. S.J.S., C.C.B. and D.N.H. synthesized the compound. All authors discussed the results and contributed to their interpretation.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramsey, C., del Barco, E., Hill, S. et al. Quantum interference of tunnel trajectories between states of different spin length in a dimeric molecular nanomagnet. Nature Phys 4, 277–281 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys886
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys886
This article is cited by
-
Measuring molecular magnets for quantum technologies
Nature Reviews Physics (2021)
-
Mono-nuclear and Hexa-nuclear Iron(III) Compounds Based on Phenol-Pyrazole Ligand: Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties
Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials (2015)