Abstract
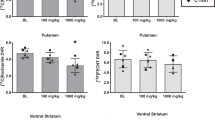
Psychopharmacological studies have implicated the mesolimbic dopamine (DA) system in the mediation of cost/benefit evaluations about delay or effort-related costs associated with larger rewards. However, the role of DA in risk-based decision making remains relatively unexplored. The present study investigated the effects of systemic manipulations of DA transmission on risky choice using a probabilistic discounting task. Over discrete trials, rats chose between two levers; a press on the ‘small/certain’ lever always delivered one reward pellet, whereas a press on the other, ‘large/risky’ lever delivered four pellets, but the probability of receiving reward decreased across the four trial blocks (100, 50, 25, 12.5%). In separate groups of well-trained rats we assessed the effects of the DA releaser amphetamine, as well as receptor selective agonists and antagonists. Amphetamine consistently increased preference for the large/risky lever; an effect that was blocked or attenuated by co-administration of either D1 (SCH23390) or D2 (eticlopride) receptor antagonists. Blockade of either of these receptors alone induced risk aversion. Conversely, stimulation of D1 (SKF81297) or D2 (bromocriptine) receptors also increased risky choice. In contrast, activation of D3 receptors with PD128,907 reduced choice of the large/risky lever. Likewise, D3 antagonism with nafadotride potentiated the amphetamine-induced increase in risky choice. Blockade or stimulation of D4 receptors did not reliably alter behavior. These findings indicate that DA has a critical role in mediating risk-based decision making, with increased activation of D1 and D2 receptors biasing choice toward larger, probabilistic rewards, whereas D3 receptors appear to exert opposing effects on this form of decision making.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adriani W, Laviola G (2006). Delay aversion but preference for large and rare rewards in two choice tasks: implications for the measurement of self-control parameters. BMC Neurosci 7: 52, doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-52.
Arnsten AF (1997). Catecholamine regulation of the prefrontal cortex. J Psychopharmacol 11: 151–162.
Bechara A, Damasio AR, Damasio H, Anderson SW (1994). Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition 50: 7–15.
Bechara A, Damasio H, Damasio AR, Lee GP (1999). Different contributions of the human amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex to decision-making. J Neurosci 19: 5473–5481.
Bechara A, Dolan S, Denburg N, Hindes A, Anderson SW, Nathan PE (2001). Decision-making deficits, linked to a dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in alcohol and stimulant abusers. Neuropsychologia 39: 376–389.
Benjamin J, Li L, Patterson C, Greenberg BD, Murphy DL, Hamer DH (1996). Population and familial association between the D4 dopamine receptor gene and measures of novelty seeking. Nat Genet 12: 81–84.
Bergh C, Eklund T, Södersten P, Nordin C (1997). Altered dopamine function in pathological gambling. Psychol Med 27: 473–475.
Bickel W, Odum A, Madden G (1999). Impulsivity and cigarette smoking: delay discounting in current, never, and ex-smokers. Psychopharmacology 146: 447–454.
Bitner RS, Nikkel AL, Otte S, Martino B, Barlow EH, Bhatia P et al (2006). Dopamine D4 receptor signaling in the rat paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus: evidence of natural coupling involving immediate early gene induction and mitogen activated protein kinase phosphorylation. Neuropharmacology 50: 521–531.
Bristow LJ, Cook GP, Gay JC, Kulagowski JJ, Landon L, Murray F et al (1996). The behavioural and neurochemical profile of the putative dopamine D3 receptor agonist, (+)-PD128907, in the rat. Neuropharmacology 35: 285–294.
Browman KE, Curzon P, Pan JB, Molesky AL, Komater VA, Decker MW et al (2005). A-412997, a selective dopamine D4 agonist, improves cognitive performance in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82: 148–155.
Cardinal RN, Howes NJ (2005). Effects of lesions of the nucleus accumbens core on choice between small certain rewards and large uncertain rewards in rats. BMC Neurosci 6: 37 (originally published online 28 May 2005, doi:10.1186/1471-2202-6-37).
Cardinal RN, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2000). The effects of d-amphetamine, chlordiazepoxide, alpha-flupenthixol and behavioral manipulations on choice of signaled and unsignalled delayed reinforcement in rats. Psychopharmacology 152: 362–375.
Chudasama Y, Robbins TW (2004). Dopaminergic modulation of visual attention and working memory in the rodent prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 29: 1628–1636.
Clark L, Bechara A, Damasio H, Aitken MR, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (2008). Differential effects of insular and ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions on risky decision making. Brain 131: 1311–1322.
Collins GT, Witkin JM, Newman AH, Svensson KA, Grundt P, Cao J et al (2005). Dopamine agonist-induced yawning in rats: a dopamine D3 receptor-mediated behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314: 310–319.
Comings DE, Gade R, Wu S, Chiu C, Dietz G, Muhleman D et al (1997). Studies of the potential role of the dopamine D1 receptor gene in addictive behaviors. Mol Psychiatry 2: 44–56.
Comings DE, Gade-Andavolu R, Gonzalez N, Wu S, Muhleman D, Chen C et al (2001). The additive effect of neurotransmitter genes in pathological gambling. Clin Genet 60: 107–116.
Comings DE, Rosenthal RJ, Lesieur HR, Rugle LJ, Muhleman D, Chiu C et al (1996). A study of the dopamine D2 receptor gene in pathological gambling. Pharmacogenetics 6: 223–234.
Cools R, Barker RA, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (2003). Dopa medication remediates cognitive inflexibility, but increases impulsivity in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neuropsychologia 41: 1431–1441.
Deakin J, Aitken M, Robbins T, Sahakian BJ (2004). Risk taking during decision-making in normal volunteers changes with age. JINS 10: 590–598.
Denk F, Walton ME, Jennings KA, Sharp T, Rushworth MFS, Bannerman DM (2005). Differential involvement of serotonin and dopamine systems in cost-benefit decisions about delay or effort. Psychopharmacology 179: 587–596.
Dodd ML, Klos KJ, Bower JH, Geda YE, Josephs KA, Ahlskog JE (2005). Pathological gambling caused by drugs used to treat Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 62: 1377–1381.
Evenden JL, Robbins TW (1985). The effects of d-amphetamine, chlordiazepoxide and alpha-flupenthixol on food-reinforced tracking of a visual stimulus by rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 85: 361–366.
Evenden JL, Ryan CN (1996). The pharmacology of impulsive behaviour in rats: the effects of drugs on response choice with varying delays of reinforcement. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 128: 161–170.
Fiorillo CD, Tobler PN, Schultz W (2003). Discrete coding of reward probability and uncertainty by dopamine neurons. Science 299: 1898–1902.
Floresco SB, Magyar O (2006). Mesocortical dopamine modulation of executive functions: beyond working memory. Psychopharmacology 188: 567–585.
Floresco SB, Phillips AG (2001). Delay-dependent modulation of memory retrieval by infusion of a dopamine D1 agonist into the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Behav Neurosci 115: 934–939.
Floresco SB, Tse MTL, Ghods-Sharifi S (2008). Dopaminergic and glutamatergic regulation of effort-and delay-based decision making. Neuropsychopharmacology 33: 1966–1979.
Frank MJ, Samanta J, Moustafa AA, Sherman SJ (2007). Hold your horses: impulsivity, deep brain stimulation, and medication in parkinsonism. Science 318: 1309–1312.
Gallagher DA, O’Sullivan SS, Evans AH, Lees AJ, Schrag AS (2007). Pathological gambling in Parkinson's disease: risk factors and differences from dopamine dysregulation an analysis of published case series. Mov Disord 22: 1757–1763.
Garcia RF, Ordacgi L, Mendlowicz MV, de Freitas GR, Rosso AZ, Nazar BP et al (2007). Treatment of juvenile Parkinson disease and the recurrent emergence of pathologic gambling. Cogn Behav Neurol 20: 11–14.
Gleason SD, Witkin JM (2006). Effects of dopamine D1 receptor agonists in rats trained to discriminate dihydrexidine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 186: 25–31.
Gobert A, Lejeune F, Rivet JM, Cistarelli L, Millan MJ (1996). Dopamine D3 (auto) receptors inhibit dopamine release in the frontal cortex of freely moving rats in vivo. J Neurochem 66: 2209–2212.
Green L, Myerson J (2004). A discounting framework for choice with delayed and probabilistic rewards. Psychol Bull 130: 769–792.
Griffon N, Diaz J, Levesque D, Soutel F, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P et al (1995). Localization, regulation and role of the dopamine D3 receptor are distinct from those of the D2 receptor. Clin Neuropharmacol 18 (Suppl 1): S130–S142.
Holt DD, Green L, Myerson J (2003). Is discounting impulsive? Evidence from temporal and probability discounting in gambling and non-gambling college students. Behav Processes 31: 355–367.
Hotte M, Naudon L, Jay TM (2005). Modulation of recognition and temporal order memory retrieval by dopamine D1 receptor in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 84: 85–92.
Imamura A, Uitti RJ, Wszolek ZK (2006). Dopamine agonist therapy for Parkinson disease and pathological gambling. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 12: 506–508.
Kaminski BJ, Ator NA (2001). Behavioral and pharmacological variables affecting risky choice in rats. J Exp Anal Behav 75: 275–297.
Kelsey JE, Carlezon Jr WA (2002). Prior experience with bromocriptine in the home cage attenuates locomotor sensitization in rats. Behav Brain Res 134: 1–8.
Levant B, Vansell NR (1997). In vivo occupancy of D2 dopamine receptors by nafadotride. Neuropsychopharmacology 17: 67–71.
Li D, Sham PC, Owen MJ, He L (2006). Meta-analysis shows significant association between dopamine system genes and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Hum Mol Genet 15: 2276–2284.
Lu C, Bharmal A, Suchowersky O (2006). Gambling and Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 63: 298.
Martin-Iverson MT, Wilkie D, Fibiger HC (1987). Effects of haloperidol and d-amphetamine on perceived quantity of food and tones. Psychopharmacology 93: 374–381.
Mazur JE (1988). Choice between small certain and large uncertain reinforcers. Anim Learn Behav 16: 199–205.
Mazur JE (1997). Choice, delay, probability, and conditioned reinforcement. Anim Learn Behav 25: 131–147.
Millan MJ, Gobert A, Newman-Tancredi A, Lejeune F, Cussac D, Rivet JM et al (2000). S33084, a novel, potent, selective, and competitive antagonist at dopamine D(3)-receptors: I. Receptorial, electrophysiological and neurochemical profile compared with GR218,231 and L741,626. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293: 1048–1062.
Millan MJ, Seguin L, Gobert A, Cussac D, Brocco M (2004). The role of dopamine D3 compared with D2 receptors in the control of locomotor activity: a combined behavioural and neurochemical analysis with novel, selective antagonists in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174: 341–357.
Mimura M, Oeda R, Kawamura M (2006). Impaired decision-making in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 12: 169–175.
Mobini S, Body S, Ho MY, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E, Deakin JF et al (2002). Effects of lesions of the orbitofrontal cortex on sensitivity to delayed and probabilistic reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 160: 290–298.
Mobini S, Chiang TJ, Ho MY, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E (2000). Effects of central 5-hydroxytryptamine depletion on sensitivity to delayed and probabilistic reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 152: 390–397.
Ostaszewski P, Karzel K (2002). Discounting of delayed and probabilistic losses of different amounts. Eur Psychol 7: 295–301.
Pais-Vieira M, Lima D, Galhardo V (2007). Orbitofrontal cortex lesions disrupt risk assessment in a novel serial decision-making task for rats. Neuroscience 145: 224–231.
Perachon S, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P (1999). Functional potencies of new antiparkinsonian drugs at recombinant human dopamine D1, D2 and D3 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 366: 293–300.
Pérez de Castro I, Ibáñez A, Sáiz-Ruiz J, Fernández-Piqueras J (1997). Genetic association study between pathological gambling and a functional DNA polymorphism at the D4 receptor. Pharmacogenetics 7: 345–348.
Phillips AG, Vacca G, Ahn S (2007). A top-down perspective on dopamine, motivation and memory. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90: 236–249 (originally published online 26 Nov 2007, doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2007.10.014).
Quickfall J, Suchowersky O (2007). Pathological gambling associated with dopamine agonist use in restless legs syndrome. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 13: 535–536.
Rachlin H, Raineri A, Cross D (1991). Subjective probability and delay. J Exp Anal of Behav 55: 233–244.
Richards JB, Zhang L, Mitchell SH, de Wit H (1999). Delay or probability discounting in a model of impulsive behavior: effect of alcohol. J Exp Anal Behav 71: 121–143.
Rogers RD, Everitt BJ, Baldacchino A, Blackshaw AJ, Swainson R, Wynne K et al (1999). Dissociable deficits in the decision-making cognition of chronic amphetamine abusers, opiate abusers, patients with focal damage to prefrontal cortex, and tryptophan-depleted normal volunteers: evidence for monoaminergic mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 20: 322–329.
Salamone JD, Wisniecki A, Carlson BB, Correa M (2001). Nucleus accumbens dopamine depletions make animals highly sensitive to high fixed ratio requirements but do not impair primary food reinforcement. Neuroscience 105: 863–870.
Schultz W (2006). Behavioral theories and the neurophysiology of reward. Annu Rev Psychol 57: 87–115.
Schultz W, Dickinson A (2000). Neuronal coding of prediction errors. Annu Rev Neurosci 23: 473–500.
Seedat S, Kesler S, Niehaus DJ, Stein DJ (2000). Pathological gambling behaviour: emergence secondary to treatment of Parkinson's disease with dopaminergic agents. Depress Anxiety 11: 185–186.
Seeman P, Van Tol HH (1993). Dopamine receptor pharmacology. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg 6: 602–608.
Sevy S, Hassoun Y, Bechara A, Yechiam E, Napolitano B, Burdick K et al (2006). Emotion-based decision making in healthy subjects: short-term effects of reducing dopamine levels. Psychopharmacology 188: 228–235.
Shah AA, Sjovold T, Treit D (2004). Selective antagonism of medial prefrontal cortex D4 receptors decreases fear-related behaviour in rats. Eur J Neurosci 19: 3393–3397.
Sigala S, Missale C, Spano P (1997). Opposite effects of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors on learning and memory in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 336: 107–112.
Szarfman A, Doraiswamy PM, Tonning JM, Levine JG (2006). Association between pathologic gambling and parkinsonian therapy as detected in the food and drug administration adverse event database. Arch Neurol 63: 299–300.
van den Bergh FS, Bloemarts E, Groenink L, Olivier B, Oosting RS (2006). Delay aversion: effects of 7-OH-DPAT, 5-HT1A/1B-receptor stimulation and D-cycloserine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85: 736–743.
van Gaalen MM, van Koten R, Schoffelmeer ANM, Vanderschuren LJMJ (2006). Critical involvement of dopaminergic neurotransmission in impulsive decision making. Biol Psychiatry 60: 66–73.
Vuchinich RE, Calamas ML (1997). Does the repeated gambles procedure measure impulsivity in social drinkers? Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 5: 157–162.
Wade TR, de Wit H, Richards JB (2000). Effects of dopaminergic drugs on delayed reward as a measure of impulsive behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 150: 90–101.
Weiner I (1990). Neural substrates of latent inhibition: the switching model. Psychol Bull 108: 443–461.
Williams GV, Castner SA (2006). Under the curve: critical issues for elucidating D1 receptor function in working memory. Neuroscience 139: 263–276.
Winstanley CA, Theobald DE, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2005). Interactions between serotonin and dopamine in the control of impulsive choice in rats: therapeutic implications for impulse control disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 30: 669–682.
Zack M, Poulos CS (2004). Amphetamine primes motivation to gamble and gambling-related semantic networks in problem gamblers. Neuropsychopharmacology 29: 195–207.
Zahrt J, Taylor JR, Mathew RG, Arnsten AF (1997). Supranormal stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors in the rodent prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance. J Neurosci 17: 8528–8535.
Zhang K, Grady CJ, Tsapakis EM, Andersen SL, Tarazi FI, Baldessarini RJ (2004). Regulation of working memory by dopamine D4 receptor in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 29: 1648–1655.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an operating grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and a Pilot Project Grant from Parkinson's Society Canada to SBF. JRSO is the recipient of scholarships from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research. SBF is a CIHR New Investigator, a Michael Smith Senior Scholar, and a recipient of a National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression Young Investigator Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
DISCLOSURE/CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
None.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website (http://www.nature.com/npp)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
St Onge, J., Floresco, S. Dopaminergic Modulation of Risk-Based Decision Making. Neuropsychopharmacol 34, 681–697 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2008.121
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2008.121
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dopamine facilitates the translation of physical exertion into assessments of effort
npj Parkinson's Disease (2023)
-
Dopamine D2 receptors in nucleus accumbens cholinergic interneurons increase impulsive choice
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Impulsivity and risk-seeking as Bayesian inference under dopaminergic control
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 antagonists alter aspects of risk/reward decision making independent of toluene-mediated effects
Psychopharmacology (2022)
-
Regulation of risky decision making by gonadal hormones in males and females
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)