Abstract
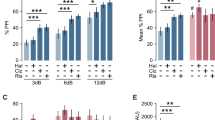
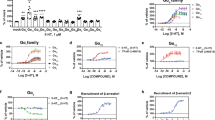
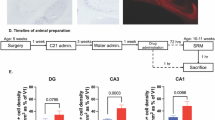
Clozapine, by virtue of its absence of extrapyramidal side effects and greater efficacy, revolutionized the treatment of schizophrenia, although the mechanisms underlying this exceptional activity remain controversial. Combining an unbiased cheminformatics and physical screening approach, we evaluated clozapine's activity at >2350 distinct molecular targets. Clozapine, and the closely related atypical antipsychotic drug olanzapine, interacted potently with a unique spectrum of molecular targets. This distinct pattern, which was not shared with the typical antipsychotic drug haloperidol, suggested that the serotonergic neuronal system was a key determinant of clozapine's actions. To test this hypothesis, we used pet1−/− mice, which are deficient in serotonergic presynaptic markers. We discovered that the antipsychotic-like properties of the atypical antipsychotic drugs clozapine and olanzapine were abolished in a pharmacological model that mimics NMDA-receptor hypofunction in pet1−/− mice, whereas haloperidol's efficacy was unaffected. These results show that clozapine's ability to normalize NMDA-receptor hypofunction, which is characteristic of schizophrenia, depends on an intact presynaptic serotonergic neuronal system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abbas AI, Yadav PN, Yao WD, Arbuckle MI, Grant SG, Caron MG et al (2009). PSD-95 is essential for hallucinogen and atypical antipsychotic drug actions at serotonin receptors. J Neurosci 29: 7124–7136.
Angst J, Jaenicke U, Padrutt A, Scharfetter C (1971). Ergebnisse eines Doppelblindversuches von HF 1854* (8-Chlor-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo (b, e) (1,4) diazepin) im Vergleich zu Levomepromazin. Pharmacopsychiatry 4: 192–200.
Armbruster BN, Roth BL (2005). Mining the receptorome. J Biol Chem 280: 5129–5132.
Bakshi VP, Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1994). Clozapine antagonizes phencyclidine-induced deficits in sensorimotor gating of the startle response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271: 787–794.
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2009). Akt/GSK3 signaling in the action of psychotropic drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49: 327–347.
Beaulieu JM, Marion S, Rodriguiz RM, Medvedev IO, Sotnikova TD, Ghisi V et al (2008). A beta-arrestin 2 signaling complex mediates lithium action on behavior. Cell 132: 125–136.
Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Marion S, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2005). An Akt/beta-arrestin 2/PP2A signaling complex mediates dopaminergic neurotransmission and behavior. Cell 122: 261–273.
Beck SG, Pan YZ, Akanwa AC, Kirby LG (2004). Median and dorsal raphe neurons are not electrophysiologically identical. J Neurophysiol 91: 994–1005.
Belforte JE, Zsiros V, Sklar ER, Jiang Z, Yu G, Li Y et al (2010). Postnatal NMDA receptor ablation in corticolimbic interneurons confers schizophrenia-like phenotypes. Nat Neurosci 13: 76.
Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E (1992). Antagonism by anitmuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharm Exp Ther 260: 576–580.
Bressan RA, Erlandsson K, Stone JM, Mulligan RS, Krystal JH, Ell PJ et al (2005). Impact of schizophrenia and chronic antipsychotic treatment on [123I]CNS-1261 binding to N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in vivo. Biol Psychiatry 58: 41–46.
Carlsson A, Waters N, Carlsson ML (1999). Neurotransmitter interactions in schizophrenia-therapeutic implications. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 249 (Suppl 4): 37–43.
Conn PJ, Roth BL (2008). Opportunities and challenges of psychiatric drug discovery: roles for scientists in academic, industry, and government settings. Neuropsychopharmacology 33: 2048–2060.
Creese I, Burt DR, Snyder SH (1976). Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science 192: 481–483.
Enna SJ, Bennett Jr JP, Burt DR, Creese I, Snyder SH (1976). Stereospecificity of interaction of neuroleptic drugs with neurotransmitters and correlation with clinical potency. Nature 263: 338–341.
Fink H, Morgenstern R, Oelssner W (1984). Clozapine—a serotonin antagonist? Phamacol Biochem Behav 20: 513–517.
Geyer MA, Braff DL (1987). Startle habituation and sensorimotor gating in schizophrenia and related animal models. Schizophr Bull 13: 643–668.
Gray JA, Roth BL (2007). The pipeline and future of drug development in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 12: 904.
Hendricks T, Francis N, Fyodorov D, Deneris ES (1999). The ETS domain factor Pet-1 is an early and precise marker of central serotonin neurons and interacts with a conserved element in serotonergic genes. J Neurosci 19: 10348–10356.
Hendricks TJ, Fyodorov DV, Wegman LJ, Lelutiu NB, Pehek EA, Yamamoto B et al (2003). Pet-1 ETS gene plays a critical role in 5-HT neuron development and is required for normal anxiety-like and aggressive behavior. Neuron 37: 233–247.
Hert J, Keiser MJ, Irwin JJ, Oprea TI, Shoichet BK (2008). Quantifying the relationships among drug classes. J Chem Inf Model 48: 755–765.
Hippius H (1999). A historical perspective of clozapine. J Clin Psychiatry 60 (Suppl 12): 22–23.
Hopkins AL, Groom CR (2002). The druggable genome. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1: 727–730.
James CA, Weininger D, Delaney J (1992). Daylight Theory Manual. Daylight Chemical Information Systems, Inc.: Mission Viejo, CA.
Javitt DC, Duncan L, Balla A, Sershen H (2005). Inhibition of system A-mediated glycine transport in cortical synaptosomes by therapeutic concentrations of clozapine: implications for mechanisms of action. Mol Psychiatry 10: 275–287.
Javitt DC, Zukin SR (1991). Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 148: 1301–1308.
Jensen P, Farago AF, Awatramani RB, Scott MM, Deneris ES, Dymecki SM (2008). Redefining the serotonergic system by genetic lineage. Nat Neurosci 11: 417–419.
Kane J, Honigfield G, Singer J, Meltzer HY (1988). Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45: 789–796.
Kapur S, Seeman P (2001). Does fast dissociation from the dopamine d(2) receptor explain the action of atypical antipsychotics?: A new hypothesis. Am J Psychiatry 158: 360–369.
Karam CS, Ballon JS, Bivens NM, Freyberg Z, Girgis RR, Lizardi-Ortiz JE et al (2010). Signaling pathways in schizophrenia: emerging targets and therapeutic strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 31: 381–390.
Keiser MJ, Roth BL, Armbruster BN, Ernsberger P, Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK (2007). Relating protein pharmacology by ligand chemistry. Nat Biotechnol 25: 197–206.
Keiser MJ, Setola V, Irwin JJ, Laggner C, Abbas AI, Hufeisen SJ et al (2009). Predicting new molecular targets for known drugs. Nature 462: 175–181.
Li Z, Prus AJ, Dai J, Meltzer HY (2009). Differential effects of M1 and 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptors on atypical antipsychotic drug-induced dopamine efflux in the medial prefrontal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330: 948–955.
Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO et al (2005). Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med 353: 1209–1223.
Linnet K (2002). Glucuronidation of olanzapine by cDNA-expressed human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and human liver microsomes. Hum Psychopharmacol 17: 233–238.
Magalhaes AC, Holmes KD, Dale LB, Comps-Agrar L, Lee D, Yadav PN et al (2010). CRF receptor 1 regulates anxiety behavior via sensitization of 5-HT2 receptor signaling. Nat Neurosci 13: 622–629.
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S (2002). The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 298: 1912–1934.
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1989). Effects of phencyclidine and phencyclidine biologs on sensorimotor gating in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2: 299–308.
Matsuoka S, Huang M, Elledge SJ (1998). Linkage of ATM to cell cycle regulation by the Chk2 protein kinase. Science 282: 1893–1897.
Meltzer HY, Alphs L, Green AI, Altamura AC, Anand R, Bertoldi A et al (2003). Clozapine treatment for suicidality in schizophrenia: International Suicide Prevention Trial (InterSePT). Arch Gen Psychiatry 60: 82–91.
Meltzer HY, Matsubara S, Lee J-C (1989). Classification of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on the basis of dopamine D-1, D-2 and serotonin2 pKi values. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251: 238–246.
Meltzer HY, Okayli G (1995). Reduction of suicidality during clozapine treatment of neuroleptic-resistant schizophrenia: impact on risk-benefit assessment. Am J Psychiatry 152: 183–190.
Miller RJ, Hiley CR (1974). Anti-muscarinic properties of neuroleptics and drug-induced parkinsonism. Nature (London) 248: 546–547.
Mohn AR, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG, Koller BH (1999). Mice with reduced NMDA receptor expression display behaviors related to schizophrenia. Cell 98: 427–436.
Nash JF, Meltzer HY, Gudelsky GA (1988). Antagonism of serotonin receptor mediated neuroendocrine and temperature responses by atypical neuroleptics in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 151: 463–469.
Newman-Tancredi A, Gavaudan S, Conte C, Chaput C, Touzard M, Verriele L et al (1998). Agonist and antagonist actions of antipsychotic agents at 5-HT1A receptors: a [35S]GTPgammaS binding study. Eur J Pharmacol 355: 245–256.
Olah M, Bologa C, Oprea TI (2004). An automated PLS search for biologically relevant QSAR descriptors. J Comput Aided Mol Des 18: 437–449.
Oprea TI, Tropsha A, Faulon JL, Rintoul MD (2007). Systems chemical biology. Nat Chem Biol 3: 447–450.
Peroutka SJ, Lebovitz RM, Snyder SH (1981). Two distinct serotonin receptors with distinct physiological functions. Science 212: 827–829.
Purcell SM, Wray NR, Stone JL, Visscher PM, O’Donovan MC, Sullivan PF et al (2009). Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature 460: 748–752.
Rollema H, Lu Y, Schmidt AW, Zorn SH (1997). Clozapine increases dopamine release in prefrontal cortex by 5-HT1A receptor activation. Eur J Pharmacol 338: R3–R5.
Roth BL, Ciaranello RD, Meltzer HY (1992). Binding of typical and atypical antipsychotic agents to transiently expressed 5-HT1C receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260: 1361–1365.
Roth BL, Craigo SC, Choudhary MS, Uluer A, Monsma Jr FJ, Shen Y et al (1994). Binding of typical and atypical antipsychotic agents to 5- hydroxytryptamine-6 and 5-hydroxytryptamine-7 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268: 1403–1410.
Roth BL, Sheffler DJ, Kroeze WK (2004). Magic shotguns versus magic bullets: selectively non-selective drugs for mood disorders and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3: 353–359.
Schoemaker H, Claustre Y, Fage D, Rouquier L, Chergui K, Curet O et al (1997). Neurochemical characteristics of amisulpride, an atypical dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist with both presynaptic and limbic selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280: 83–97.
Schwieler L, Linderholm KR, Nilsson-Todd LK, Erhardt S, Engberg G (2008). Clozapine interacts with the glycine site of the NMDA receptor: electrophysiological studies of dopamine neurons in the rat ventral tegmental area. Life Sci 83: 170–175.
Scott MM, Wylie CJ, Lerch JK, Murphy R, Lobur K, Herlitze S et al (2005). A genetic approach to access serotonin neurons for in vivo and in vitro studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 16472–16477.
Seeman P, Corbett R, Van Tol HH (1997). Atypical neuroleptics have low affinity for dopamine D2 receptors or are selective for D4 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 16: 93–110, discussion 111–135.
Senn HJ, Jungi WF, Kunz H, Poldinger W (1977). Clozapine and agranulocytosis. Lancet 1: 547.
Shi J, Levinson DF, Duan J, Sanders AR, Zheng Y, Pe′er I et al (2009). Common variants on chromosome 6p22.1 are associated with schizophrenia. Nature 460: 753–757.
Stefansson H, Ophoff RA, Steinberg S, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Rujescu D et al (2009). Common variants conferring risk of schizophrenia. Nature 460: 744–747.
Stefansson H, Rujescu D, Cichon S, Pietilainen OP, Ingason A, Steinberg S et al (2008). Large recurrent microdeletions associated with schizophrenia. Nature 455: 232–236.
Sur C, Mallorga PJ, Wittmann M, Jacobson MA, Pascarella D, Williams JB et al (2003). N-desmethylclozapine, an allosteric agonist at muscarinic 1 receptor, potentiates N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 13674–13679.
Van Tol HH, Bunzow JR, Guan HC, Sunahara RK, Seeman P, Niznik HB et al (1991). Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature 350: 610–614.
Wittmann M, Marino MJ, Henze DA, Seabrook GR, Conn PJ (2005). Clozapine potentiation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor currents in the nucleus accumbens: role of NR2B and protein kinase A/Src kinases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313: 594–603.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by U19MH82441, RO1MH61887, RO1MH075047, the NIMH Psychoactive Drug Screening Program Contract, and the Michael Hooker Distinguished Professorship to BLR. Additional support was from GM71896 (to JJI and BKS) MH075047 to SGB, MH082611 to LKC and the Rogers Family Foundation (to MJK, JJI, and BKS). BKS thanks Tudor Oprea for a gift of the WOMBAT database and John Overington for early access to ChEMBL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr Roth in the past 24 months has been a consultant for Bristol Myers Squibb, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Medivation, Galenea Pharmaceuticals, the National Institutes of Health, Invitrogen, and Albany Molecular Researech, and has received royalty payments from licensing of 5-HT receptor patents (which are owned by UNC and Case Western Reserve University) to Galena Pharmaceuticals. Drs Shoichet and Irwin are co-founders of SeaChange, and Dr Keiser is an employee of SeaChange. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, P., Abbas, A., Farrell, M. et al. The Presynaptic Component of the Serotonergic System is Required for Clozapine's Efficacy. Neuropsychopharmacol 36, 638–651 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.195
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.195
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Chemogenetics for cell-type-specific modulation of signalling and neuronal activity
Nature Reviews Methods Primers (2023)
-
TAAR1 dependent and independent actions of the potential antipsychotic and dual TAAR1/5-HT1A receptor agonist SEP-363856
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
Chronic Kappa opioid receptor activation modulates NR2B: Implication in treatment resistant depression
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Mice Lacking the Serotonin Htr2B Receptor Gene Present an Antipsychotic-Sensitive Schizophrenic-Like Phenotype
Neuropsychopharmacology (2015)
-
Serotonin–glutamate and serotonin–dopamine reciprocal interactions as putative molecular targets for novel antipsychotic treatments: from receptor heterodimers to postsynaptic scaffolding and effector proteins
Psychopharmacology (2013)