Abstract
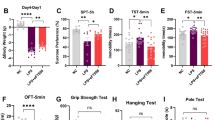
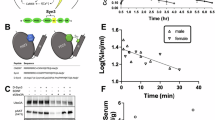
In mice lacking the central domain of the presynaptic scaffold Bassoon the occurrence of repeated cortical seizures induces cell-type-specific plasticity changes resulting in a general enhancement of the feedforward inhibition within the striatal microcircuit. Early antiepileptic treatment with valproic acid (VPA) reduces epileptic attacks, inhibits the emergence of pathological form of plasticity in fast-spiking (FS) interneurons and restores physiological striatal synaptic plasticity in medium spiny (MS) neurons. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a key factor for the induction and maintenance of synaptic plasticity and it is also implicated in the mechanisms underlying epilepsy-induced adaptive changes. In this study, we explore the possibility that the TrkB/BDNF system is involved in the striatal modifications associated with the Bassoon gene (Bsn) mutation. In epileptic mice abnormal striatum-dependent learning was paralleled by higher TrkB levels and an altered distribution of BDNF. Accordingly, subchronic intrastriatal administration of k252a, an inhibitor of TrkB receptor tyrosine kinase activity, reversed behavioral alterations in Bsn mutant mice. In addition, in vitro manipulations of the TrkB/BDNF complex by k252a, prevented the emergence of pathological plasticity in FS interneurons. Chronic treatment with VPA, by reducing seizures, was able to rebalance TrkB to control levels favoring a physiological redistribution of BDNF between MS neurons and FS interneurons with a concomitant recovery of striatal plasticity. Our results provide the first indication that BDNF is involved in determining the striatal alterations occurring in the early-onset epileptic syndrome associated with the absence of presynaptic protein Bassoon.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Altrock WD, tom Dieck S, Sokolov M, Meyer AC, Sigler A, Brakebusch C et al (2003). Functional inactivation of a fraction of excitatory synapses in mice deficient for the active zone protein bassoon. Neuron 37: 787–800.
Bartrup JT, Moorman JM, Newberry NR (1997). BDNF enhances neuronal growth and synaptic activity in hippocampal cell cultures. Neuroreport 8: 3791–3794.
Berghuis P, Dobszay MB, Sousa KM, Schulte G, Mager PP, Hartig W et al (2004). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor controls functional differentiation and microcircuit formation of selectively isolated fast-spiking GABAergic interneurons. Eur J Neurosci 20: 1290–1306.
Bolton MM, Pittman AJ, Lo DC (2000). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor differentially regulates excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission in hippocampal cultures. J Neurosci 20: 3221–3232.
Calabresi P, Pisani A, Mercuri NB, Bernardi G (1992). Long-term potentiation in the striatum is unmasked by removing the voltage-dependent magnesium block of NMDA receptor channels. Eur J Neurosci 4: 929–935.
Castren E, Voikar V, Rantamaki T (2007). Role of neurotrophic factors in depression. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7: 18–21.
Fumagalli F, Di Pasquale L, Caffino L, Racagni G, Riva MA (2007). Repeated exposure to cocaine differently modulates BDNF mRNA and protein levels in rat striatum and prefrontal cortex. Eur J Neurosci 26: 2756–2763.
Gabrieli JD (1995). A systematic view of human memory processes. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 1: 115–118.
Gall CM (1993). Seizure-induced changes in neurotrophin expression: implications for epilepsy. Exp Neurol 124: 150–166.
Ghiglieri V, Picconi B, Sgobio C, Bagetta V, Barone I, Paille V et al (2009). Epilepsy-induced abnormal striatal plasticity in Bassoon mutant mice. Eur J Neurosci 29: 1979–1993.
Humpel C, Wetmore C, Olson L (1993). Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger RNA and protein at the cellular level in pentylenetetrazol-induced epileptic seizures. Neuroscience 53: 909–918.
Isackson PJ, Huntsman MM, Murray KD, Gall CM (1991). BDNF mRNA expression is increased in adult rat forebrain after limbic seizures: temporal patterns of induction distinct from NGF. Neuron 6: 937–948.
Jankowsky JL, Patterson PH (2001). The role of cytokines and growth factors in seizures and their sequelae. Prog Neurobiol 63: 125–149.
Lu B (2003). BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation. Learn Mem 10: 86–98.
Marty S, Berninger B, Carroll P, Thoenen H (1996). GABAergic stimulation regulates the phenotype of hippocampal interneurons through the regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuron 16: 565–570.
McDonald RJ, White NM (1993). A triple dissociation of memory systems: hippocampus, amygdala, and dorsal striatum. Behav Neurosci 107: 3–22.
Merlio JP, Ernfors P, Kokaia Z, Middlemas DS, Bengzon J, Kokaia M et al (1993). Increased production of the TrkB protein tyrosine kinase receptor after brain insults. Neuron 10: 151–164.
Molteni R, Cattaneo A, Calabrese F, Macchi F, Olivier JD, Racagni G et al (2009). Reduced function of the serotonin transporter is associated with decreased expression of BDNF in rodents as well as in humans. Neurobiol Dis, print copy in press (originally published online 23 December 2009, at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.12.014 ).
Nagappan G, Lu B (2005). Activity-dependent modulation of the BDNF receptor TrkB: mechanisms and implications. Trends Neurosci 28: 464–471.
Packard MG, McGaugh JL (1996). Inactivation of hippocampus or caudate nucleus with lidocaine differentially affects expression of place and response learning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 65: 65–72.
Packard MG, White NM (1991). Dissociation of hippocampus and caudate nucleus memory systems by posttraining intracerebral injection of dopamine agonists. Behav Neurosci 105: 295–306.
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2007). The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates Second Edition. Academic Press: San Diego.
Poldrack RA, Packard MG (2003). Competition among multiple memory systems: converging evidence from animal and human brain studies. Neuropsychologia 41: 245–251.
Poo MM (2001). Neurotrophins as synaptic modulators. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 24–32.
Russo SJ, Mazel-Robinson MS, Ables JL, Nestler EJ (2009). Neurotrophic factors and structural plasticity in addiction. Neuropharmacology 56 (Suppl 1): 73–82.
Rutherford LC, Nelson SB, Turrigiano GG (1998). BDNF has opposite effects on the quantal amplitude of pyramidal neuron and interneuron excitatory synapses. Neuron 21: 521–530.
Salin T, Mudo G, Jiang XH, Timmusk T, Metsis M, Belluardo N (1995). Up-regulation of TrkB mRNA expression in the rat striatum after seizures. Neurosci Lett 194: 181–184.
Schmidt-Kastner R, Humpel C, Wetmore C, Olson L (1996). Cellular hybridization for BDNF, TrkB, and NGF mRNAs and BDNF-immunoreactivity in rat forebrain after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Exp Brain Res 107: 331–347.
Sgobio C, Ghiglieri V, Costa C, Bagetta V, Siliquini S, Barone I et al (2010). Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, memory, and epilepsy: effects of long-term valproic acid treatment. Biol Psychiatry, print copy in press (originally published online 13 January 2010, at http://journals.elsevierhealth.com/periodicals/bps/inpress).
Takahashi M, Hayashi S, Kakita A, Wakabayashi K, Fukuda M, Kameyama S et al (1999). Patients with temporal lobe epilepsy show an increase in brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein and its correlation with neuropeptide Y. Brain Res 818: 579–582.
White NM, McDonald RJ (2002). Multiple parallel memory systems in the brain of the rat. Neurobiol Learn Mem 77: 125–184.
Wyneken U, Marengo JJ, Villanueva S, Soto D, Sandoval R, Gundelfinger ED et al (2003). Epilepsy-induced changes in signaling systems of human and rat postsynaptic densities. Epilepsia 44: 243–246.
Wyneken U, Smalla KH, Marengo JJ, Soto D, de la Cerda A, Tischmeyer W et al (2001). Kainate-induced seizures alter protein composition and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function of rat forebrain postsynaptic densities. Neuroscience 102: 65–74.
Yamada MK, Nakanishi K, Ohba S, Nakamura T, Ikegaya Y, Nishiyama N et al (2002). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes the maturation of GABAergic mechanisms in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 22: 7580–7585.
Zuccato C, Cattaneo E (2009). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurol 5: 311–322.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Community Contract Number 222918 (REPLACES) FP7—Thematic priority HEALTH (PC, EG), Ministero della Salute Progetto Strategico 2007 (PC, BP), and Progetti Finalizzati e Ricerca Corrente IRCCS Ministero della Salute 2006–2008 (PC, BP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghiglieri, V., Sgobio, C., Patassini, S. et al. TrkB/BDNF-Dependent Striatal Plasticity and Behavior in a Genetic Model of Epilepsy: Modulation by Valproic Acid. Neuropsychopharmacol 35, 1531–1540 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.23
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.23
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Deletion of PLCγ1 in GABAergic neurons increases seizure susceptibility in aged mice
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Ablation of the presynaptic organizer Bassoon in excitatory neurons retards dentate gyrus maturation and enhances learning performance
Brain Structure and Function (2018)
-
The Role for Alterations in Neuronal Activity in the Pathogenesis of Polyglutamine Repeat Disorders
Neurotherapeutics (2014)
-
Hippocampal enlargement in Bassoon-mutant mice is associated with enhanced neurogenesis, reduced apoptosis, and abnormal BDNF levels
Cell and Tissue Research (2011)