Abstract
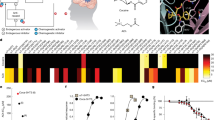
The current study uses an extended access rat model of cocaine self-administration (5-h session per day, 14 days), which elicits several features manifested during the transition to human addiction, to study the neural adaptations associated with cocaine withdrawal. Given that the hippocampus is thought to have an important role in maintaining addictive behavior and appears to be especially relevant to mechanisms associated with withdrawal, this study attempted to understand how extended access to cocaine impacts the hippocampus at the cellular and molecular levels, and how these alterations change over the course of withdrawal (1, 14, and 28 days). Therefore, at the cellular level, we examined the effects of cocaine withdrawal on cell proliferation (Ki-67+ and NeuroD+ cells) in the DG. At the molecular level, we employed a ‘discovery’ approach with gene expression profiling in the DG to uncover novel molecules possibly implicated in the neural adaptations that take place during cocaine withdrawal. Our results suggest that decreased hippocampal cell proliferation might participate in the adaptations associated with drug removal and identifies 14 days as a critical time-point of cocaine withdrawal. At the 14-day time-point, gene expression profiling of the DG revealed the dysregulation of several genes associated with cell fate regulation, highlighting two new neurobiological correlates (Ascl-1 and Dnmt3b) that accompany cessation of drug exposure. Moreover, the results point to Fas-Associated protein with Death Domain (FADD), a molecular marker previously associated with the propensity to substance abuse and cocaine sensitization, as a key cell fate regulator during cocaine withdrawal. Identifying molecules that may have a role in the restructuring of the hippocampus following substance abuse provides a better understanding of the adaptations associated with cocaine withdrawal and identifies novel targets for therapeutic intervention.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ahmed SH, Koob GF (1998). Transition from moderate to excessive drug intake: change in hedonic set point. Science 282: 298–300.
Altman J, Das GD (1965). Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol 124: 319–335.
Alvaro-Bartolome M, Esteban S, García-Gutiérrez MS, Manzanares J, Valverde O, García-Sevilla JA (2010). Regulation of Fas receptor/Fas-associated protein with death domain apoptotic complex and associated signalling systems by cannabinoid receptors in the mouse brain. Br J Pharmacol 160: 643–656.
Arguello AA, Harburg GC, Schonborn JR, Mandyam CD, Yamaguchi M, Eisch AJ (2008). Time course of morphine's effects on adult hippocampal subgranular zone reveals preferential inhibition of cell in S phase of the cell cycle and a subpopulation of immature neurons. Neuroscience 157: 70–79.
Banasr M, Soumier A, Hery M, Mocaër E, Daszuta A (2006). Agomelatine, a new antidepressant, induces regional changes in hippocampal neruogenesis. Biol Psychiatry 59: 1087–1096.
Bannerman DM, Rawlins JN, McHugh SB, Deacon RM, Yee BK, Bast T et al (2004). Regional dissociations within the hippocampus –memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28: 273–283.
Barros HM, Miczek KA (1996). Withdrawal from oral cocaine in rate: ultrasonic vocalizations and tactile startle. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 125: 379–384.
Bernard R, Kerman IA, Thompson RC, Jones EG, Bunney WE, Barchas JD et al (2010). Altered expression of glutamate signaling, growth factor, and glia genes in the locus coeruleus of patients with major depression. Mol Psychiatry 16: 634–646.
Bozarth MA, Wise RA (1985). Toxicity associated with long-term intravenous heroin and cocaine self-administration in the rat. JAMA 254: 81–83.
Briand LA, Flagel SB, Garcia-Fuster MJ, Watson SJ, Akil H, Sarter M et al (2008). Persistent alterations in cognitive function and prefrontal dopamine D2 receptors following extended, but not limited, access to self-administered cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 33: 2969–2980.
Cagnol S, Van Obberghen-Schilling E, Chambard JC (2006). Prolonged activation of ERK1,2 induces FADD-independent caspase 8 activation and cell death. Apoptosis 11: 337–346.
Cameron HA, McKay RD (2001). Adult neurogenesis produces a large pool of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol 435: 406–417.
Czéh B, Müller-Keuker JI, Rygula R, Abumaria N, Hiemke C, Domenici E et al (2007). Chronic social stress inhibits cell proliferation in the adult medial prefrontal cortex: hemispheric asymmetry and reversal by fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 32: 1490–1503.
Dietz DM, Dietz KC, Nestler EJ, Russo SJ (2009). Molecular mechanisms of psychostimulant-induced structural plasticity. Pharmacopsychiatry 42 (Suppl 1): S69–S78.
Domínguez-Escribà L, Hernández-Rabaza V, Soriano-Navarro M, Barcia JA, Romero FJ, García-Verdugo JM et al (2006). Chronic cocaine exposure impairs progenitor proliferation but spares survival and maturation of neural precursors in adult rat dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci 24: 586–594.
Eisch AJ, Harburg GC (2006). Opiates, psychostimulants, and adult hippocampal neurogenesis: insights for addiction and stem cell biology. Hippocampus 16: 271–286.
Eisch AJ, Nestler EJ (2002). To be or not to be: adult neurogenesis and psyquiatry. Clin Neurosci Res 2: 93–108.
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Björk-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA et al (1998). Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 4: 1313–1317.
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2005). Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nat Neurosci 8: 1481–1489.
Feng J, Chang H, Li E, Fan G (2005). Dynamic expression of de novo DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b in the central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 79: 734–746.
Ferrario CR, Gorny G, Crombag HS, Li Y, Kolb B, Robinson TE (2005). Neural and behavioral plasticity associated with the transition from controlled to escalated cocaine use. Biol Psychiatry 58: 751–759.
García-Fuster MJ, Clinton SM, Watson SJ, Akil H (2009). Effect of cocaine on Fas-associated protein with death domain in the rat brain: individual differences in a model of differential vulnerability to drug abuse. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 1123–1134.
García-Fuster MJ, Ferrer-Alcón M, Miralles A, García-Sevilla JA (2003). Modulation of Fas receptor proteins and dynamin during opiate addiction and induction of opiate withdrawal in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 368: 421–431.
García-Fuster MJ, Miralles A, García-Sevilla JA (2007). Effects of opiate drugs on Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) and effector caspases in the rat brain: regulation by the ERK1/2 MAP kinase pathway. Neuropsychopharmacology 32: 399–411.
García-Fuster MJ, Perez JA, Clinton SM, Watson SJ, Akil H (2010). Impact of cocaine on adult hippocampal neurogenesis in an animal model of differential propensity to drug abuse. Eur J Neurosci 31: 79–89.
Gao Z, Ure K, Ables JL, Lagace DC, Nave KA, Goebbels S et al (2009). Neurod1 is essential for the survival and maturation of adult-born neurons. Nat Neurosci 12: 1090–1092.
Gold LH, Hubner CB, Koob GF (1989). A role for the mesolimbic dopamine system in the psychostimulant actions of MDMA. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 99: 40–47.
Guzmán-Marín R, Suntsova N, Stewart DR, Gong H, Szymusiak R, McGinty D (2003). Sleep deprivation reduces proliferation of cells in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus in rats. J Physiol (Lond) 549: 563–571.
Hevner RF, Hodge RD, Daza RA, Englund C (2006). Transcription factors in glutamatergic neurogenesis: conserved programs in neocortex, cerebellum, and adult hippocampus. Neurosci Res 55: 223–233.
Hsieh J, Eisch AJ (2010). Epigenetics, hippocampal neurogenesis, and neuropsychiatric disorders: unraveling the genome to understand the mind. Neurobiol Dis 39: 73–84.
Jacobs BL, van Praag H, Gage FH (2000). Adult brain neurogenesis and psychiatry: a novel theory of depression. Mol Psychiatry 5: 262–269.
Jessberger S, Toni N, Clemenson Jr GD, Ray J, Gage FH (2008). Directed differentiation of hippocampal stem/progenitor cells in the adult brain. Nat Neurosci 11: 888–893.
Johnson JE, Birren SJ, Anderson DJ (1990). Two rat homologues of Drosophila achaete-scute specifically expressed in neuronal precursors. Nature 346: 858–861.
Kee N, Sivalingam S, Boonstra R, Wojtowicz JM (2002). The utility of Ki-67 and BrdU as proliferative markers of adult neurogenesis. J Neurosci Methods 115: 97–105.
Kerman IA, Buck BJ, Evans SJ, Akil H, Watson SJ (2006). Combining laser capture microdissection with quantitative real-time PCR: effects of tissue manipulation on RNA quality and gene expression. J Neurosci Methods 153: 71–85.
Kim SJ, Lee KJ, Shin YC, Choi SH, Do E, Kim S et al (2005). Stress-induced decrease of granule cell proliferation in adult rat hippocampus: assessment of granule cell proliferation using high doses of bromodeoxyuridine before and after restraint stress. Mol Cells 19: 74–80.
Lagace DC, Donovan MH, DeCarolis NA, Farnbauch LA, Malhotra S, Berton O et al (2010). Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is functionally important for stress-induced social avoidance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 4436–4441.
Lagace DC, Yee JK, Bolaños CA, Eisch AJ (2006). Juvenile administration of methylphenidate attenuates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Biol Psychiatry 60: 1121–1130.
Larsen MH, Rosenbrock H, Sams-Dodd F, Mikkelsen JD (2007). Expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor, activity-regulated cytoskeleton protein mRNA, and enhancement of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in rats after sub-chronic and chronic treatment with the triple monoamine re-uptake inhibitor tesofensine. Eur J Pharmacol 555: 115–121.
Lee JE (1997). Basic helix-loop-helix genes in neural development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 7: 13–20.
Levenson JM, Roth TL, Lubin FD, Miller CA, Huang IC, Desai P et al (2006). Evidence that DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferase regulates synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. J Biol Chem 281: 15763–15773.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25: 402–408.
Lodge DJ, Grace AA (2008). Amphetamine activation of hippocampal drive of mesolimbic dopamine neurons: a mechanism of behavioral sensitization. J Neurosci 28: 7876–7882.
Malberg JE, Duman RS (2003). Cell proliferation in adult hippocampus is decreased by inescapable stress: reversal by fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 28: 1562–1571.
Malberg JE, Eisch AJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS (2000). Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 20: 9104–9110.
Mandyam CD, Wee S, Crawford EF, Eisch AJ, Richardson HN, Koob GF (2008). Varied access to intravenous methamphetamine self-administration differentially alters adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Biol Psychiatry 64: 958–965.
Ming GL, Song H (2005). Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 28: 223–250.
Miyata T, Maeda T, Lee JE (1999). NeuroD is required for differentiation of the granule cells in the cerebellum and hippocampus. Genes Dev 13: 1647–1652.
Mutschler NH, Miczek KA (1998). Withdrawal from a self-administered or non-contingent cocaine binge: differences in ultrasonic distress vocalizations in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 136: 402–408.
Noonan MA, Bulin SE, Fuller DC, Eisch AJ (2010). Reduction of adult hippocampal neurogenesis confers vulnerability in an animal model of cocaine addiction. J Neurosci 30: 304–315.
Noonan MA, Choi KH, Self DW, Eisch AJ (2008). Withdrawal from cocaine self-administration normalizes deficits in proliferation and enhances maturity of adult-generated hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 28: 2516–2526.
Paterson NE, Markou A (2003). Increased motivation for self-administered cocaine after escalated cocaine intake. Neuroreport 14: 2229–2232.
Paxinos GT, Watson C (1997). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Compact edn. Academic: New York.
Perez JA, Clinton SM, Turner CA, Watson SJ, Akil H (2009). A new role for FGF2 as an endogenous inhibitor of anxiety. J Neurosci 29: 6379–6387.
Ramos-Miguel A, Esteban S, García-Sevilla JA (2010). The time course of unconditioned morphine-induced psicomotor sensitization mirrors the phosphorylation of FADD and MEK/ERK in rat striatum: role of PEA-15 as a FADD/ERK binding partner in striatal plasticity. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 20: 49–64.
Sahay A, Hen R (2007). Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in depression. Nat Neurosci 10: 1110–1115.
Schmidt HD, Duman RS (2007). The role of neurotrophic factors in adult hippocampal neurogenesis, antidepressant treatments and animal models of depressive-like behavior. Behav Pharmacol 18: 391–418.
Scholzen T, Gerdes J (2000). The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 182: 311–322.
Shen F, Meredith GE, Napier TC (2006). Amphetamine-induced place preference and conditioned motor sensitization requires activation of tyrosine kinase receptors in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 26: 11041–11051.
Stansberg C, Vik-Mo AO, Holdhus R, Breilid H, Srebro B, Petersen K et al (2007). Gene expression profiles in rat brain disclose CNS signature genes and regional patterns of functional specialization. BMC Genomics 8: 94.
Steiner B, Klempin F, Wang L, Kott M, Kettenmann H, Kempermann G (2006). Type-2 cells as link between glial and neuronal lineage in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Glia 54: 805–814.
Stevenson JR, Schroeder JP, Nixon K, Besheer J, Crews FT, Hodge CW (2009). Abstinence following alcohol drinking produces depression-like behavior and reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 1209–1222.
Tourneur L, Chiocchia G (2010). FADD: a regulator of life and death. Trends Immunol 31: 260–269.
von Bohlen Und Halbach O (2007). Immunohistological markers for staging neurogenesis in adult hippocampus. Cell Tissue Res 329: 409–420.
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH (2002). Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 415: 1030–1034.
Wojtowicz JM, Kee N (2006). BrdU assay for neurogenesis in rodents. Nat Protoc 1: 1399–1405.
Yamaguchi M, Suzuki T, Seki T, Namba T, Juan R, Arai H et al (2004). Repetitive cocaine administration decreases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. Ann NY Acad Sci 1025: 351–362.
Yamaguchi M, Suzuki T, Seki T, Namba T, Liu J, Arai H et al (2005). Decreased cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of rats after repeated administration of cocaine. Synapse 58: 63–71.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by NIDA 5P01DA021633-02; NIMH Conte Center Grant #L99MH60398; Office of Naval Research (ONR) N00014-09-1-0598 to HA and SJW; and The Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Research Foundation. The authors would like to thank Sharon Burke, Jennifer Fitzpatrick, James Beals, and Tracy Simmons for excellent technical assistance. Moreover, the authors would like to thank Suzanne Smith for her help in the microarray analysis as well as Stephanie Cooke and Ellen Pedersen for their help in performing the TaqMan Arrays. MJGF is a ‘Ramón y Cajal’ Researcher (MICINN-UIB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Fuster, M., Flagel, S., Mahmood, S. et al. Decreased Proliferation of Adult Hippocampal Stem Cells During Cocaine Withdrawal: Possible Role of the Cell Fate Regulator FADD. Neuropsychopharmacol 36, 2303–2317 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.119
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.119
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comparing the antidepressant-like effects of electroconvulsive seizures in adolescent and adult female rats: an intensity dose–response study
Biology of Sex Differences (2023)
-
Evaluating signs of hippocampal neurotoxicity induced by a revisited paradigm of voluntary ethanol consumption in adult male and female Sprague-Dawley rats
Pharmacological Reports (2023)
-
Revisiting the antidepressant-like effects of desipramine in male and female adult rats: sex disparities in neurochemical correlates
Pharmacological Reports (2022)
-
Adolescent cocaine induced persistent negative affect in female rats exposed to early-life stress
Psychopharmacology (2021)
-
Exploring the antidepressant-like potential of the selective I2-imidazoline receptor ligand LSL 60101 in adult male rats
Pharmacological Reports (2021)