Abstract
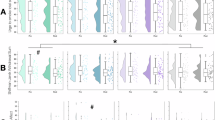
The glutamatergic neurotransmission system and the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) have been implicated in smoking and alcohol consumption behavior. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that nicotine and ethanol influence NMDAR functionality, which may have a role in tendencies to consume these substances. Nonetheless, little is known about concentrations of NMDAR coagonists in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma of individuals who smoke or consume alcohol. Glycine and L- and D-stereoisomers of alanine, serine, and proline were therefore measured using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in 403 healthy subjects. Nicotine and alcohol consumption were quantified using questionnaires. Possible differences in NMDAR coagonist concentrations in plasma and CSF were investigated using ANCOVA with age, body mass index, and storage duration as covariates. The significance threshold was Bonferroni corrected (α=0.00625). Compared with non-smokers, smokers displayed lower levels of D-proline in plasma (p=0.0027, Cohen’s d=−0.41) and D-proline in CSF (p=0.0026, Cohen’s d=−0.43). D-Serine in CSF was higher in smokers than in non-smokers (p=0.0052, Cohen’s d=0.41). After subdividing participants based on smoking quantity, dose-dependent decreases were demonstrated in smokers for D-proline in plasma (F=5.65, p=0.0039) and D-proline in CSF (F=5.20, p=0.0060). No differences in NMDAR coagonist levels between alcohol consumption groups were detected. To our knowledge, this is the first report to implicate D-amino acids in smoking behavior of humans. Whether such concentration differences lie at the root of or result from smoking habits may be addressed in prospective studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Buchanan T, Smith JL (1999). Using the Internet for psychological research: personality testing on the World Wide Web. Br J Psychol 90: 125–144.
Clelland CL, Read LL, Baraldi AN, Bart CP, Pappas CA, Panek LJ et al (2011). Evidence for association of hyperprolinemia with schizophrenia and a measure of clinical outcome. Schizophr Res 131: 139–145.
Eisenberg MJ, Filion KB, Yavin D, Belisle P, Mottillo S, Joseph L et al (2008). Pharmacotherapies for smoking cessation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cmaj 179: 135–144.
Ekman A, Dickman PW, Klint A, Weiderpass E, Litton JE (2006). Feasibility of using web-based questionnaires in large population-based epidemiological studies. Eur J Epidemiol 21: 103–111.
Fu Y, Matta SG, Gao W, Brower VG, Sharp BM (2000). Systemic nicotine stimulates dopamine release in nucleus accumbens: re-evaluation of the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the ventral tegmental area. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294: 458–465.
Gosling SD, Vazire S, Srivastava S, John OP (2004). Should we trust web-based studies? A comparative analysis of six preconceptions about internet questionnaires. Am Psychol 59: 93–104.
Grant KA, Valverius P, Hudspith M, Tabakoff B (1990). Ethanol withdrawal seizures and the NMDA receptor complex. Eur J Pharmacol 176: 289–296.
Grillner P, Svensson TH (2000). Nicotine-induced excitation of midbrain dopamine neurons in vitro involves ionotropic glutamate receptor activation. Synapse 38: 1–9.
Gulya K, Grant KA, Valverius P, Hoffman PL, Tabakoff B (1991). Brain regional specificity and time-course of changes in the NMDA receptor-ionophore complex during ethanol withdrawal. Brain Res 547: 129–134.
Henneberger C, Papouin T, Oliet SH, Rusakov DA (2010). Long-term potentiation depends on release of D-serine from astrocytes. Nature 463: 232–236.
Henzi V, Reichling DB, Helm SW, MacDermott AB (1992). L-Proline activates glutamate and glycine receptors in cultured rat dorsal horn neurons. Mol Pharmacol 41: 793–801.
Hoffman PL, Rabe CS, Moses F, Tabakoff B (1989). N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors and ethanol: inhibition of calcium flux and cyclic GMP production. J Neurochem 52: 1937–1940.
Hundt W, Danysz W, Holter SM, Spanagel R (1998). Ethanol and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex interactions: a detailed drug discrimination study in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 135: 44–51.
Jauniaux E, Gulbis B, Acharya G, Gerlo E (1999). Fetal amino acid and enzyme levels with maternal smoking. Obstet Gynecol 93: 680–683.
Joinson A (1999). Social desirability, anonymity, and Internet-based questionnaires. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 31: 433–438.
Kamboj SK, Joye A, Das RK, Gibson AJ, Morgan CJ, Curran HV (2012). Cue exposure and response prevention with heavy smokers: a laboratory-based randomised placebo-controlled trial examining the effects of D-cycloserine on cue reactivity and attentional bias. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 221: 273–284.
Kenny PJ, Chartoff E, Roberto M, Carlezon WA Jr, Markou A (2009). NMDA receptors regulate nicotine-enhanced brain reward function and intravenous nicotine self-administration: role of the ventral tegmental area and central nucleus of the amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 266–281.
Kleckner NW, Dingledine R (1988). Requirement for glycine in activation of NMDA-receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Science 241: 835–837.
Kotlinska J, Liljequist S (1997). The NMDA/glycine receptor antagonist, L-701,324, produces discriminative stimuli similar to those of ethanol. Eur J Pharmacol 332: 1–8.
Krystal JH, Petrakis IL, Webb E, Cooney NL, Karper LP, Namanworth S et al (1998). Dose-related ethanol-like effects of the NMDA antagonist, ketamine, in recently detoxified alcoholics. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55: 354–360.
Liechti ME, Markou A (2008). Role of the glutamatergic system in nicotine dependence: implications for the discovery and development of new pharmacological smoking cessation therapies. CNS Drugs 22: 705–724.
Little HJ (1991). Mechanisms that may underlie the behavioural effects of ethanol. Prog Neurobiol 36: 171–194.
Liu JZ, Tozzi F, Waterworth DM, Pillai SG, Muglia P, Middleton L et al (2010). Meta-analysis and imputation refines the association of 15q25 with smoking quantity. Nat Genet 42: 436–440.
Lovinger DM, White G, Weight FF (1989). Ethanol inhibits NMDA-activated ion current in hippocampal neurons. Science 243: 1721–1724.
Luykx JJ, Bakker SC, Lentjes E, Neeleman M, Strengman E, Mentink L et al (2013). Genome-wide association study of monoamine metabolite levels in human cerebrospinal fluid. Mol Psychiatry e-pub ahead of print 15 January 2013. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.183.
Luykx JJ, Vinkers CH, Bakker SC, Visser WF, van Boxmeer L, Strengman E et al (2012). A Common variant in ERBB4 regulates GABA concentrations in human cerebrospinal fluid. Neuropsychopharmacology 37: 2088–2092.
Mansvelder HD, McGehee DS (2000). Long-term potentiation of excitatory inputs to brain reward areas by nicotine. Neuron 27: 349–357.
Mansvelder HD, McGehee DS (2002). Cellular and synaptic mechanisms of nicotine addiction. J Neurobiol 53: 606–617.
Martin D, Ault B, Nadler JV (1992). NMDA receptor-mediated depolarizing action of proline on CA1 pyramidal cells. Eur J Pharmacol 219: 59–66.
Matsui T, Sekiguchi M, Hashimoto A, Tomita U, Nishikawa T, Wada K (1995). Functional comparison of D-serine and glycine in rodents: the effect on cloned NMDA receptors and the extracellular concentration. J Neurochem 65: 454–458.
McBain CJ, Kleckner NW, Wyrick S, Dingledine R (1989). Structural requirements for activation of the glycine coagonist site of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol 36: 556–565.
Mothet JP, Parent AT, Wolosker H, Brady RO Jr, Linden DJ, Ferris CD et al (2000). D-Serine is an endogenous ligand for the glycine site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 4926–4931.
Nesic J, Duka T, Rusted JM, Jackson A (2011). A role for glutamate in subjective response to smoking and its action on inhibitory control. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 216: 29–42.
Nong Y, Huang YQ, Ju W, Kalia LV, Ahmadian G, Wang YT et al (2003). Glycine binding primes NMDA receptor internalization. Nature 422: 302–307.
Panatier A, Theodosis DT, Mothet JP, Touquet B, Pollegioni L, Poulain DA et al (2006). Glia-derived D-serine controls NMDA receptor activity and synaptic memory. Cell 125: 775–784.
Papouin T, Ladepeche L, Ruel J, Sacchi S, Labasque M, Hanini M et al (2012). Synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors are gated by different endogenous coagonists. Cell 150: 633–646.
Rosner S, Leucht S, Lehert P, Soyka M (2008). Acamprosate supports abstinence, naltrexone prevents excessive drinking: evidence from a meta-analysis with unreported outcomes. J Psychopharmacol 22: 11–23.
Sakata K, Fukushima T, Minje L, Ogurusu T, Taira H, Mishina M et al (1999). Modulation by L- and D-isoforms of amino acids of the L-glutamate response of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Biochemistry 38: 10099–10106.
Santa Ana EJ, Rounsaville BJ, Frankforter TL, Nich C, Babuscio T, Poling J et al (2009). D-Cycloserine attenuates reactivity to smoking cues in nicotine dependent smokers: a pilot investigation. Drug Alcohol Depend 104: 220–227.
Schilstrom B, Fagerquist MV, Zhang X, Hertel P, Panagis G, Nomikos GG et al (2000). Putative role of presynaptic alpha7* nicotinic receptors in nicotine stimulated increases of extracellular levels of glutamate and aspartate in the ventral tegmental area. Synapse 38: 375–383.
Schilstrom B, Nomikos GG, Nisell M, Hertel P, Svensson TH (1998). N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonism in the ventral tegmental area diminishes the systemic nicotine-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Neuroscience 82: 781–789.
Shoaib M, Benwell ME, Akbar MT, Stolerman IP, Balfour DJ (1994). Behavioural and neurochemical adaptations to nicotine in rats: influence of NMDA antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 111: 1073–1080.
Shoaib M, Stolerman IP (1992). MK801 attenuates behavioural adaptation to chronic nicotine administration in rats. Br J Pharmacol 105: 514–515.
Snyder SH, Kim PM (2000). D-Amino acids as putative neurotransmitters: focus on D-serine. Neurochem Res 25: 553–560.
Tobacco and Genetics Consortium (2010). Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nat Genet 42: 441–447.
Townsend J, Roderick P, Cooper J (1994). Cigarette smoking by socioeconomic group, sex, and age: effects of price, income, and health publicity. BMJ 309: 923–927.
Visser WF, Verhoeven-Duif NM, Ophoff R, Bakker S, Klomp LW, Berger R et al (2011). A sensitive and simple ultra-high-performance-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based method for the quantification of D-amino acids in body fluids. J Chromatogr A 1218: 7130–7136.
Walter H, Schlaff WB, Lesch OM, Vitek L, Zima T, Hartl D et al (2008). Breath alcohol level and plasma amino acids: a comparison between older and younger chronic alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol Alcohol 43: 653–657.
Weight FF, Lovinger DM, White G, Peoples RW (1991). Alcohol and anesthetic actions on excitatory amino acid-activated ion channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci 625: 97–107.
WHO (2007) WHO Tobacco Control Report. World Health Organisation: Copenhaven, Denmark.
WHO (2009) WHO Global Health Risk. World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switserland.
WHO (2012) WHO World Health Statistics. World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland.
Yoon JH, Newton TF, Haile CN, Bordnick PS, Fintzy RE, Culbertson C et al (2013). Effects of D-cycloserine on cue-induced craving and cigarette smoking among concurrent cocaine- and nicotine-dependent volunteers. Addict Behav 38: 1518–1526.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luykx, J., Bakker, S., van Boxmeer, L. et al. D-Amino Acid Aberrations in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma of Smokers. Neuropsychopharmacol 38, 2019–2026 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.103
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Chiral capillary electrophoresis with UV-excited fluorescence detection for the enantioselective analysis of 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-derivatized amino acids
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2018)
-
Determining the presence of asthma-related molecules and salivary contamination in exhaled breath condensate
Respiratory Research (2017)
-
Metabolomic similarities between bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and plasma in humans and mice
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Evidence that COMT genotype and proline interact on negative-symptom outcomes in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
Translational Psychiatry (2016)
-
Genome-wide association study of NMDA receptor coagonists in human cerebrospinal fluid and plasma
Molecular Psychiatry (2015)