Abstract
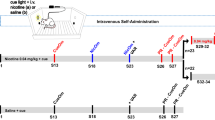
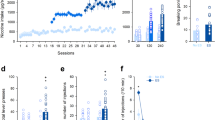
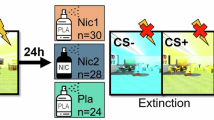
Tobacco addiction involves a transition from occasional, voluntary smoking towards habitual behavior that becomes increasingly resistant to quitting. The development of smoking habits may reflect a loss of behavioral control that can be modeled in rats. This study investigated the behavioral and neural substrates of habit formation in rats exposed to either brief (10 days) or extended (47 days) intravenous (IV) nicotine self-administration training. Following training, the first cohort of rats were exposed to a nicotine devaluation treatment, which involved repeated pairings of IV nicotine with lithium injection. They were then tested for sensitivity of responding to nicotine devaluation under extinction and reinstatement conditions. The second cohort of rats received equivalent self-administration training followed by processing of brain tissue for c-Fos immunohistochemistry. After brief training, devaluation suppressed nicotine-seeking during tests of extinction and reinstatement, confirming that responding is initially sensitive to current nicotine value, and therefore, goal directed. In contrast, after extended training, devaluation had no effect on extinction or reinstatement of responding, indicating that responding had become habitual. Complementary neuroanalysis revealed that extended nicotine self-administration was associated with increased c-Fos expression in brain regions implicated in habitual control of reward seeking, including activation of the dorsolateral striatum and substantia nigra pars compacta. These findings provide evidence of direct devaluation of an IV drug reward, that nicotine self-administration is initially goal-directed but becomes habitual with extended training, and that this behavioral transition involves activation of brain areas associated with the nigrostriatal system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adams CD, Dickinson A (1981). Instrumental responding following reinforcer devaluation. Q J Exp Psychol-B 33: 109–121.
Balleine BW, Dickinson A (1998). Goal-directed instrumental action: contingency and incentive learning and their cortical substrates. Neuropharmacology 37: 407–419.
Balleine BW, Killcross S (2006). Parallel incentive processing: an integrated view of amygdala function. Trends Neurosci 29: 272–279.
Belin-Rauscent A, Everitt BJ, Belin D (2012). Intrastriatal shifts mediate the transition from drug-seeking actions to habits. Biol Psychiatry 72: 343–345.
Belin D, Everitt BJ (2008). Cocaine seeking habits depend upon dopamine-dependent serial connectivity linking the ventral with the dorsal striatum. Neuron 57: 432–441.
Bird KD (2004) Analysis of Variance via Confidence Intervals. SAGE Publications: London. Thousand Oaks, Calif., xi 226.
Caggiula AR, Donny EC, Palmatier MI, Liu X, Chaudhri N, Sved AF (2009). The role of nicotine in smoking: a dual-reinforcement model. Nebr Symp Motiv 55: 91–109.
Charntikov S, Tracy ME, Zhao C, Li M, Bevins RA (2012). Conditioned response evoked by nicotine conditioned stimulus preferentially induces c-Fos expression in medial regions of caudate-putamen. Neuropsychopharmacology 37: 876–884.
Chen BT, Bowers MS, Martin M, Hopf FW, Guillory AM, Carelli RM et al (2008). Cocaine but not natural reward self-administration nor passive cocaine infusion produces persistent LTP in the VTA. Neuron 59: 288–297.
Clemens KJ, Caille S, Cador M (2010). The effects of response operandum and prior food training on intravenous nicotine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 211: 43–54.
Clemens KJ, Caille S, Stinus L, Cador M (2009). The addition of five minor tobacco alkaloids increases nicotine-induced hyperactivity, sensitization and intravenous self-administration in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12: 1355–1366.
Corbit LH, Janak PH (2010). Posterior dorsomedial striatum is critical for both selective instrumental and Pavlovian reward learning. Eur J Neurosci 31: 1312–1321.
Corbit LH, Nie H, Janak PH (2012). Habitual alcohol seeking: time course and the contribution of subregions of the dorsal striatum. Biol Psychiatry 72: 389–395.
Dar R, Rosen-Korakin N, Shapira O, Gottlieb Y, Frenk H (2010). The craving to smoke in flight attendants: relations with smoking deprivation, anticipation of smoking, and actual smoking. J Abnormal Psychol 119: 248–253.
Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV (2004). Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science 305: 1014–1017.
Dickinson A, Wood N, Smith JW (2002). Alcohol seeking by rats: action or habit? Q J Exp Psychl B 55: 331–348.
Faure A, Haberland U, Conde F, El Massioui N (2005). Lesion to the nigrostriatal dopamine system disrupts stimulus-response habit formation. J Neurosci 25: 2771–2780.
Hogarth L, Chase HW (2011). Parallel goal-directed and habitual control of human drug-seeking: implications for dependence vulnerability. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 37: 261–276.
Ikemoto S, Qin M, Liu ZH (2006). Primary reinforcing effects of nicotine are triggered from multiple regions both inside and outside the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 26: 723–730.
Jonkman S, Kosaki Y, Everitt BJ, Dickinson A (2010). The role of contextual conditioning in the effect of reinforcer devaluation on instrumental performance by rats. Behav Processes 83: 276–281.
Jonkman S, Pelloux Y, Everitt BJ (2012). Differential roles of the dorsolateral and midlateral striatum in punished cocaine seeking. J Neurosci 32: 4645–4650.
Keath JR, Iacoviello MP, Barrett LE, Mansvelder HD, McGehee DS (2007). Differential modulation by nicotine of substantia nigra versus ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. J Neurophysiol 98: 3388–3396.
Kenny PJ, Markou A (2006). Nicotine self-administration acutely activates brain reward systems and induces a long-lasting increase in reward sensitivity. Neuropsychopharmacology 31: 1203–1211.
Killcross S, Coutureau E (2003). Coordination of actions and habits in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats. Cereb Cortex 13: 400–408.
Leblanc KH, Maidment NT, Ostlund SB (2013). Impact of repeated intravenous cocaine administration on incentive motivation depends on mode of drug delivery. Addict Biol (advance online publication 3 May 2013).
Markou A (2008). Review. Neurobiology of nicotine dependence. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363: 3159–3168.
Marks MJ, Pauly JR, Gross SD, Deneris ES, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Heinemann SF et al (1992). Nicotine binding and nicotinic receptor subunit RNA after chronic nicotine treatment. J Neurosci 12: 2765–2784.
Miles FJ, Everitt BJ, Dickinson A (2003). Oral cocaine seeking by rats: action or habit? Behav Neurosci 117: 927–938.
Motbey CP, Clemens KJ, Apetz N, Winstock AR, Ramsey J, Li KM et al (2013). High levels of intravenous mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone) self-administration in rats: Neural consequences and comparison with methamphetamine. J Psychopharmacol 27: 823–836.
Nelson A, Killcross S (2006). Amphetamine exposure enhances habit formation. J Neurosci 26: 3805–3812.
Olmstead MC, Lafond MV, Everitt BJ, Dickinson A (2001). Cocaine seeking by rats is a goal-directed action. Behav Neurosci 115: 394–402.
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, IV Edition. Academic Press: San Diego.
Pelloux Y, Murray JE, Everitt BJ (2013). Differential roles of the prefrontal cortical subregions and basolateral amygdala in compulsive cocaine seeking and relapse after voluntary abstinence in rats. Eur J Neurosci 38: 3018–3026.
Pittenger ST, Bevins RA (2013). Interoceptive conditioning with a nicotine stimulus is susceptible to reinforcer devaluation. Behav Neurosci 127: 465–473.
Sellings LH, Baharnouri G, McQuade LE, Clarke PB (2008). Rewarding and aversive effects of nicotine are segregated within the nucleus accumbens. Eur J Neurosci 28: 342–352.
Stefanski R, Ladenheim B, Lee SH, Cadet JL, Goldberg SR (1999). Neuroadaptations in the dopaminergic system after active self-administration but not after passive administration of methamphetamine. Eur J Pharmacol 371: 123–135.
Vanderschuren LJ, Everitt BJ (2004). Drug seeking becomes compulsive after prolonged cocaine self-administration. Science 305: 1017–1019.
Wooltorton JR, Pidoplichko VI, Broide RS, Dani JA (2003). Differential desensitization and distribution of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in midbrain dopamine areas. J Neurosci 23: 3176–3185.
World Health Organisation (2011) Warning About the Dangers of Tobacco. WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic. WHO: Geneva, Switzerland.
Yin HH, Knowlton BJ, Balleine BW (2005). Blockade of NMDA receptors in the dorsomedial striatum prevents action-outcome learning in instrumental conditioning. Eur J Neurosci 22: 505–512.
Zapata A, Minney VL, Shippenberg TS (2010). Shift from goal-directed to habitual cocaine seeking after prolonged experience in rats. J Neurosci 30: 15457–15463.
Acknowledgements
We thank Christine Sutter and Wayne McTegg for animal care and Sophie Fletcher for technical assistance. This research was supported by a Macquarie University Research Fellowship (MURF) and an Australian Research Council (ARC) Discovery Early Career Researcher Award (DECRA) to Dr Clemens. Mr Castino is the recipient of an Australian Postgraduate Award (APA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clemens, K., Castino, M., Cornish, J. et al. Behavioral and Neural Substrates of Habit Formation in Rats Intravenously Self-Administering Nicotine. Neuropsychopharmacol 39, 2584–2593 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.111
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.111
This article is cited by
-
Subregion specific neuroadaptations in the female rat striatum during acute and protracted withdrawal from nicotine
Journal of Neural Transmission (2024)
-
On the interrelation between alcohol addiction–like behaviors in rats
Psychopharmacology (2022)
-
Nicotine Pretreatment Increases Sensitivity to Reward Devaluation in Extinction
The Psychological Record (2021)
-
Addiction is driven by excessive goal-directed drug choice under negative affect: translational critique of habit and compulsion theory
Neuropsychopharmacology (2020)
-
Inflexible habitual decision-making during choice between cocaine and a nondrug alternative
Translational Psychiatry (2019)