Abstract
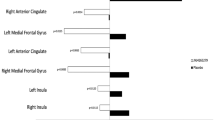
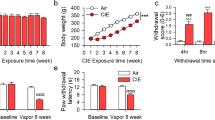
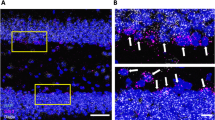
The occurrence of chronic stress, depression, and anxiety can increase nociception in humans and may facilitate the transition from localized to chronic widespread pain. The mechanisms underlying chronic widespread pain are still unknown, hindering the development of effective pharmacological therapies. Here, we exposed C57BL/6J mice to chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) to investigate how persistent stress affects nociception. Next, mice were treated with multiple intramuscular nerve growth factor (NGF) injections, which induced chronic widespread nociception. Thus, combination of CUS and NGF served as a model where psychophysiological impairment coexists with long-lasting hyperalgesia. We found that CUS increased anxiety- and depression-like behavior and enhanced basal nociception in mice. When co-applied with repeated NGF injections, CUS elicited a sustained long-lasting widespread hyperalgesia. In order to evaluate a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of chronic pain associated with stress, we hypothesized that the endocannabinoid system (ECS) may represent a target signaling system. We found that URB597, an inhibitor of the anandamide-degrading enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and JZL184, an inhibitor of the 2-arachidonoyl glycerol-degrading enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), increased eCB levels in the brain and periphery and were both effective in reducing CUS-induced anxiety measured by the light–dark test and CUS-induced thermal hyperalgesia. Remarkably, the long-lasting widespread hyperalgesia induced by combining CUS and NGF was effectively reduced by URB597, but not by JZL184. Simultaneous inhibition of FAAH and MAGL did not improve the overall therapeutic response. Therefore, our findings indicate that enhancement of anandamide signaling with URB597 is a promising pharmacological approach for the alleviation of chronic widespread nociception in stress-exposed mice, and thus, it could represent a potential treatment strategy for chronic pain associated with neuropsychiatric disorders in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bailey KM, Carleton RN, Vlaeyen JW, Asmundson GJ (2010). Treatments addressing pain-related fear and anxiety in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: a preliminary review. Cogn Behav Ther 39: 46–63.
Bortolato M, Mangieri RA, Fu J, Kim JH, Arguello O, Duranti A et al (2007). Antidepressant-like activity of the fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 in a rat model of chronic mild stress. Biol Psychiatry 62: 1103–1110.
Cantarella G, Scollo M, Lempereur L, Saccani-Jotti G, Basile F, Bernardini R (2011). Endocannabinoids inhibit release of nerve growth factor by inflammation-activated mast cells. Biochem Pharmacol 82: 380–388.
Cattaneo A (2010). Tanezumab, a recombinant humanized mAb against nerve growth factor for the treatment of acute and chronic pain. Curr Opin Mol Ther 12: 94–106.
Chang YW, Tan A, Saab C, Waxman S (2010). Unilateral focal burn injury is followed by long-lasting bilateral allodynia and neuronal hyperexcitability in spinal cord dorsal horn. J Pain 11: 119–130.
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994). Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53: 55–63.
Deising S, Weinkauf B, Blunk J, Obreja O, Schmelz M, Rukwied R (2012). NGF-evoked sensitization of muscle fascia nociceptors in humans. Pain 153: 1673–1679.
Denk F, McMahon SB, Tracey I (2014). Pain vulnerability: a neurobiological perspective. Nat Neurosci 17: 192–200.
Dubreucq S, Matias I, Cardinal P, Häring M, Lutz B, Marsicano G et al (2012). Genetic dissection of the role of cannabinoid type-1 receptors in the emotional consequences of repeated social stress in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 37: 1885–1900.
Farquhar-Smith WP, Rice AS (2003). A novel neuroimmune mechanism in cannabinoid-mediated attenuation of nerve growth factor-induced hyperalgesia. Anesthesiology 99: 1391–1401.
Ghosh S, Wise LE, Chen Y, Gujjar R, Mahadevan A, Cravatt BF et al (2013). The monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor JZL184 suppresses inflammatory pain in the mouse carrageenan model. Life Sci 92: 498–505.
Gorzalka BB, Hill MN, Hillard CJ (2008). Regulation of endocannabinoid signaling by stress: implications for stress-related affective disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32: 1152–1160.
Hayashi K, Ozaki N, Kawakita K, Itoh K, Mizumura K, Furukawa K et al (2011). Involvement of NGF in the rat model of persistent muscle pain associated with taut band. J Pain 12: 1059–1068.
Hayashi K, Shiozawa S, Ozaki N, Mizumura K, Graven-Nielsen T (2013). Repeated intramuscular injections of nerve growth factor induced progressive muscle hyperalgesia, facilitated temporal summation, and expanded pain areas. Pain 154: 2344–2352.
Herren-Gerber RK, Nie H, Arendt-Nielsen L, Curatolo M, Graven-Nielsen T (2011). Local pain and spreading hyperalgesia induced by intramuscular injection of nerve growth factor are not reduced by local anesthesia of the muscle. Clin J Pain 27: 240–247.
Hill MN, Kumar SA, Filipski SB, Iverson M, Stuhr KL, Keith JM et al (2013). Disruption of fatty acid amide hydrolase activity prevents the effects of chronic stress on anxiety and amygdalar microstructure. Mol Psychiatry 18: 1125–1135.
Hill MN, Patel S (2013). Translational evidence for the involvement of the endocannabinoid system in stress-related psychiatric illnesses. Biol Mood Anxiety Disord 3: 19.
Hill MN, Patel S, Carrier EJ, Rademacher DJ, Ormerod BK, Hillard CJ et al (2005). Downregulation of endocannabinoid signaling in the hippocampus following chronic unpredictable stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 30: 508–515.
Hoheisel U, Reuter R, de Freitas MF, Treede RD, Mense S (2013). Injection of nerve growth factor into a low back muscle induces long-lasting latent hypersensitivity in rat dorsal horn neurones. Pain 154: 1953–1960.
Hoheisel U, Unger T, Mense S (2005). Excitatory and modulatory effects of inflammatory cytokines and neurotrophins on mechanosensitive group IV muscle afferents in the rat. Pain 114: 168–176.
Hoheisel U, Unger T, Mense S (2007). Sensitization of rat dorsal horn neurons by NGF-induced subthreshold potentials and low-frequency activation. A study employing intracellular recordings in vivo. Brain Res 1169: 34–43.
Häring M, Grieb M, Monory K, Lutz B, Moreira FA (2013). Cannabinoid CB1 receptor in the modulation of stress coping behavior in mice: the role of serotonin and different forebrain neuronal subpopulations. Neuropharmacology 65: 83–89.
Jann MW, Slade JH (2007). Antidepressant agents for the treatment of chronic pain and depression. Pharmacotherapy 27: 1571–1587.
Jhaveri MD, Richardson D, Kendall DA, Barrett DA, Chapman V (2006). Analgesic effects of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 26: 13318–13327.
Kathuria S, Gaetani S, Fegley D, Valiño F, Duranti A, Tontini A et al (2003). Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Nat Med 9: 76–81.
Keimpema E, Tortoriello G, Alpár A, Capsoni S, Arisi I, Calvigioni D et al (2013). Nerve growth factor scales endocannabinoid signaling by regulating monoacylglycerol lipase turnover in developing cholinergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: 1935–1940.
Kinsey SG, Long JZ, Cravatt BF, Lichtman AH (2010). Fatty acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitors produce anti-allodynic effects in mice through distinct cannabinoid receptor mechanism. J Pain 11: 1420–1428.
Kinsey SG, Long JZ, O'Neal ST, Abdullah RA, Poklis JL, Boger DL et al (2009). Blockade of endocannabinoid-degrading enzymes attenuates neuropathic pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330: 902–910.
Kinsey SG, Wise LE, Ramesh D, Abdullah R, Selley DE, Cravatt BF et al (2013). Repeated low-dose administration of the monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor JZL184 retains cannabinoid receptor type 1-mediated antinociceptive and gastroprotective effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 345: 492–501.
Long JZ, Li W, Booker L, Burston JJ, Kinsey SG, Schlosburg JE et al (2009a). Selective blockade of 2-arachidonoylglycerol hydrolysis produces cannabinoid behavioral effects. Nat Chem Biol 5: 37–44.
Long JZ, Nomura DK, Vann RE, Walentiny DM, Booker L, Jin X et al (2009b). Dual blockade of FAAH and MAGL identifies behavioral processes regulated by endocannabinoid crosstalk in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 20270–20275.
Luongo L, Maione S, Di Marzo V (2014). Endocannabinoids and neuropathic pain: focus on neuron-glia and endocannabinoid-neurotrophin interactions. Eur J Neurosci 39: 401–408.
Lutz B (2009). Endocannabinoid signals in the control of emotion. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9: 46–52.
Maione S, Costa B, Di Marzo V (2013). Endocannabinoids: a unique opportunity to develop multitarget analgesics. Pain 154 (Suppl 1): S87–S93.
Mills CD, Nguyen T, Tanga FY, Zhong C, Gauvin DM, Mikusa J et al (2013). Characterisation of nerve growth factor-induced mechanical and hypersensitivity in rats. Eur J Pain 17: 469–479.
Mineur YS, Belzung C, Crusio WE (2006). Effects of unpredictable chronic mild stress on anxiety and depression-like behavior in mice. Behav Brain Res 175: 43–50.
Moreira FA, Kaiser N, Monory K, Lutz B (2008). Reduced anxiety-like behaviour induced by genetic and pharmacological inhibition of the endocannabinoid-degrading enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is mediated by CB1 receptors. Neuropharmacology 54: 141–150.
Nomura DK, Morrison BE, Blankman JL, Long JZ, Kinsey SG, Marcondes MC et al (2011). Endocannabinoid hydrolysis generates brain prostaglandins that promote neuroinflammation. Science 334: 809–813.
Pan B, Wang W, Long JZ, Sun D, Hillard CJ, Cravatt BF et al (2009). Blockade of 2-arachidonoylglycerol hydrolysis by selective monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor 4-nitrophenyl 4-(dibenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl(hydroxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (JZL184) Enhances retrograde endocannabinoid signaling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 331: 591–597.
Pfizer (2012). Tanezumab: Arthritis Advisory Committee Briefing Document http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryComittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/ArthritisAdvisoryCommittee/UCM295205.pdf.
Piomelli D, Sasso O (2014). Peripheral gating of pain signals by endogenous lipid mediators. Nat Neurosci 17: 164–174.
Piomelli D, Tarzia G, Duranti A, Tontini A, Mor M, Compton TR et al (2006). Pharmacological profile of the selective FAAH inhibitor KDS-4103 (URB597). CNS Drug Rev 12: 21–38.
Raquibul Hasan SM, Hossain MM, Akter R, Jamila M, Mazumder MEH, Alam MA et al (2010). Analgesic activity of the different fractions of the aerial parts of commelina benghalensis linn. Int J Pharmacol 6: 63–67.
Reich CG, Taylor ME, McCarthy MM (2009). Differential effects of chronic unpredictable stress on hippocampal CB1 receptors in male and female rats. Behav Brain Res 203: 264–269.
Rey AA, Purrio M, Viveros MP, Lutz B (2012). Biphasic effects of cannabinoids in anxiety responses: CB1 and GABA(B) receptors in the balance of GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission. Neuropsychopharmacology 37: 2624–2634.
Rossi S, De Chiara V, Musella A, Sacchetti L, Cantarella C, Castelli M et al (2010). Preservation of striatal cannabinoid CB1 receptor function correlates with the antianxiety effects of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition. Mol Pharmacol 78: 260–268.
Saab CY (2012). Pain-related changes in the brain: diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Trends Neurosci 35: 629–637.
Schlosburg JE, Blankman JL, Long JZ, Nomura DK, Pan B, Kinsey SG et al (2010). Chronic monoacylglycerol lipase blockade causes functional antagonism of the endocannabinoid system. Nat Neurosci 13: 1113–1119.
Sciolino NR, Zhou W, Hohmann AG (2011). Enhancement of endocannabinoid signaling with JZL184, an inhibitor of the 2-arachidonoylglycerol hydrolyzing enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase, produces anxiolytic effects under conditions of high environmental aversiveness in rats. Pharmacol Res 64: 226–234.
Sharif-Naeini R, Basbaum AI (2011). Targeting pain where it resides... In the brain. Sci Transl Med 3: 65ps1.
Shi M, Qi WJ, Gao G, Wang JY, Luo F (2010). Increased thermal and mechanical nociceptive thresholds in rats with depressive-like behaviors. Brain Res 1353: 225–233.
Sluka KA, Kalra A, Moore SA (2001). Unilateral intramuscular injections of acidic saline produce a bilateral, long-lasting hyperalgesia. Muscle Nerve 24: 37–46.
Sumislawski JJ, Ramikie TS, Patel S (2011). Reversible gating of endocannabinoid plasticity in the amygdala by chronic stress: a potential role for monoacylglycerol lipase inhibition in the prevention of stress-induced behavioral adaptation. Neuropsychopharmacology 36: 2750–2761.
Wang W, Sun D, Pan B, Roberts CJ, Sun X, Hillard CJ et al (2010). Deficiency in endocannabinoid signaling in the nucleus accumbens induced by chronic unpredictable stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 35: 2249–2261.
Wise LE, Long KA, Abdullah RA, Long JZ, Cravatt BF, Lichtman AH (2012). Dual fatty acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol lipase blockade produces THC-like Morris water maze deficits in mice. ACS Chem Neurosci 3: 369–378.
Zhong P, Wang W, Pan B, Liu X, Zhang Z, Long JZ et al (2014). Monoacylglycerol lipase inhibition blocks chronic stress-induced depressive-like behaviors via activation of mTOR signaling. Neuropsychopharmacology 39: 1763–1776.
Acknowledgements
We thank Michael Plenikowski for graphic arrangement of the figures and Dr Konstantin Radyushkin for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lomazzo, E., Bindila, L., Remmers, F. et al. Therapeutic Potential of Inhibitors of Endocannabinoid Degradation for the Treatment of Stress-Related Hyperalgesia in an Animal Model of Chronic Pain. Neuropsychopharmacol 40, 488–501 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.198
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.198
This article is cited by
-
A monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor showing therapeutic efficacy in mice without central side effects or dependence
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Persistent muscle hyperalgesia after adolescent stress is exacerbated by a mild-nociceptive input in adulthood and is associated with microglia activation
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
The antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of cannabinoids in chronic unpredictable stress: a preclinical systematic review and meta-analysis
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
mGluR5-Mediated eCB Signaling in the Nucleus Accumbens Controls Vulnerability to Depressive-Like Behaviors and Pain After Chronic Social Defeat Stress
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Activation of tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B in pyramidal neurons impairs endocannabinoid signaling by tyrosine receptor kinase trkB and causes schizophrenia-like behaviors in mice
Neuropsychopharmacology (2020)