Abstract
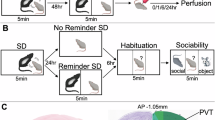
Peripheral cytokines affect central nervous system (CNS) function, manifesting in symptoms of anxiety and cognitive decline. Although the peripheral blockage of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α has been effective in alleviating depression and rheumatoid arthritis, it is yet unknown whether central blockade of TNF-α is beneficial for immune-challenged CNS function. This study investigated the effects of central etanercept administration following a peripheral immune challenge on anxiety-like and cognition-like behaviors and microglia and astrocyte numbers. Twelve-week-old C57BL/6 mice (n=40) were treated with either LPS or saline administered peripherally 24 h before being treated with either etanercept or artificial CSF (aCSF) by intracerebroventricular injection. Mice underwent behavioral analyses for locomotion, memory, and anxiety-like behavior 24 h post-etanercept/aCSF treatment, and tissue was collected to estimate the numbers of hippocampal microglia and astrocytes. Following peripheral immune challenge with LPS, mice showed increased anxiety-like behavior, which was significantly improved following treatment with etanercept (two-way ANOVA: Interaction: F(1,30)=0.60, P=0.44; Saline/LPS challenge: F(1,30)=23.92, P<0.0001, etanercept vs aCSF: F(1,30)=11.09, P=0.0023). For cognition, a significant interaction effect found by two-way ANOVA (Interaction: F(1,20)=4.96, P=0.037, Saline/LPS challenge: F(1,20)=4.966, P=0.31, aCSF/etanercept treatment: F(1,20)=0.06, P=0.80) and post-hoc analysis revealed a significant decrease in cognition in LPS-aCSF compared with Sal-aCSF mice (P=0.038), but no significant difference was noted between LPS-aCSF and LPS-Etan mice (P>0.9). A significant reduction in the number of microglia within the hippocampus of these mice was noted (two-way ANOVA: Interaction: F(1,15)=11.41, P=0.0041; Saline/LPS challenge: F(1,15)=50.13, P<0.0001, etanercept vs aCSF: F(1,15)=3.36, P=0.08). Centrally administered etanercept improved anxiety-like behavior but not spatial memory under a peripheral immune challenge and was associated with a decrease in the hippocampal microglia numbers. This suggests that etanercept recovers anxiety-like behavior possibly mediated by a reduction of TNF-α-related central inflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bai YM, Chiou WF, Su TP, Li CT, Chen MH (2013). Pro-inflammatory cytokine associated with somatic and pain symptoms in depression. J Affect Disord 155: 28–34.
Bassukas ID, Hyphantis T, Gamvroulia C, Gaitanis G, Mavreas V (2008). Infliximab for patients with plaque psoriasis and severe psychiatric comorbidity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 22: 257–258.
Baune BT, Camara M-l, Eyre H, Jawahar C, Anscomb H, Koerner H (2012). Tumour necrosis factor alpha mediated mechanisms of cognitive dysfunction. Trans Neurosci 3: 263–277.
Bayramgurler D, Karson A, Ozer C, Utkan T (2013). Effects of long-term etanercept treatment on anxiety- and depression-like neurobehaviors in rats. Physiol Behav 119: 145–148.
Bian Y, Zhao X, Li M, Zeng S, Zhao B (2013). Various roles of astrocytes during recovery from repeated exposure to different doses of lipopolysaccharide. Behav Brain Res 253: 253–261.
Boado RJ, Hui EK, Lu JZ, Zhou QH, Pardridge WM (2010). Selective targeting of a TNFR decoy receptor pharmaceutical to the primate brain as a receptor-specific IgG fusion protein. J Biotechnol 146: 84–91.
Bossu P, Cutuli D, Palladino I, Caporali P, Angelucci F, Laricchiuta D et al (2012). A single intraperitoneal injection of endotoxin in rats induces long-lasting modifications in behavior and brain protein levels of TNF-alpha and IL-18. J Neuroinflammation 9: 101.
Brown RE, Stanford L, Schellinck HM (2000). Developing standardized behavioral tests for knockout and mutant mice. ILAR J 41: 163–174.
Camara ML, Corrigan F, Jaehne EJ, Jawahar MC, Anscomb H, Koerner H et al (2013). TNF-alpha and its receptors modulate complex behaviours and neurotrophins in transgenic mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38: 3102–3114.
Cavailles A, Brinchault-Rabin G, Dixmier A, Goupil F, Gut-Gobert C, Marchand-Adam S et al (2013). Comorbidities of COPD. Eur Respir Rev 22: 454–475.
Chandarana PC, Eals M, Steingart AB, Bellamy N, Allen S (1987). The detection of psychiatric morbidity and associated factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Can J Psychiatry 32: 356–361.
Chen J, Song Y, Yang J, Zhang Y, Zhao P, Zhu XJ et al (2013). The contribution of TNF-alpha in the amygdala to anxiety in mice with persistent inflammatory pain. Neurosci Lett 541: 275–280.
Chen YM, Chen HH, Lan JL, Chen DY (2010). Improvement of cognition, a potential benefit of anti-TNF therapy in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 77: 366–367.
Chio CC, Chang CH, Wang CC, Cheong CU, Chao CM, Cheng BC et al (2013). Etanercept attenuates traumatic brain injury in rats by reducing early microglial expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. BMC Neurosci 14: 33.
Choy KH, de Visser Y, Nichols NR, van den Buuse M (2008). Combined neonatal stress and young-adult glucocorticoid stimulation in rats reduce BDNF expression in hippocampus: effects on learning and memory. Hippocampus 18: 655–667.
Couch Y, Anthony DC, Dolgov O, Revischin A, Festoff B, Santos AI et al (2013). Microglial activation, increased TNF and SERT expression in the prefrontal cortex define stress-altered behaviour in mice susceptible to anhedonia. Brain Behav Immun 29: 136–146.
Dantzer R, O’Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008). From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 9: 46–56.
Davidson RJ (2002). Anxiety and affective style: role of prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Biol Psychiatry 51: 68–80.
Dulawa SC, Grandy DK, Low MJ, Paulus MP, Geyer MA (1999). Dopamine D4 receptor-knock-out mice exhibit reduced exploration of novel stimuli. J Neurosci 19: 9550–9556.
Francis PT (2009). Altered glutamate neurotransmission and behaviour in dementia: evidence from studies of memantine. Curr Mol Pharmacol 2: 77–82.
Frenois F, Moreau M, O'Connor J, Lawson M, Micon C, Lestage J et al (2007) Psychoneuroendocrinology 32: 516–531.
Haji N, Mandolesi G, Gentile A, Sacchetti L, Fresegna D, Rossi S et al (2012). TNF-alpha-mediated anxiety in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Exp Neurol 237: 296–303.
Himmerich H, Binder EB, Kunzel HE, Schuld A, Lucae S, Uhr M et al (2006). Successful antidepressant therapy restores the disturbed interplay between TNF-alpha system and HPA axis. Biol Psychiatry 60: 882–888.
Hinwood M, Morandini J, Day TA, Walker FR (2012). Evidence that microglia mediate the neurobiological effects of chronic psychological stress on the medial prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 22: 1442–1454.
Hunt L, Emery P (2013). Etanercept in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 13: 1441–1450.
Jenkins TA, Harte MK, Stenson G, Reynolds GP (2009). Neonatal lipopolysaccharide induces pathological changes in parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of the rat. Behav Brain Res 205: 355–359.
Kaster MP, Gadotti VM, Calixto JB, Santos ARS, Rodrigues ALS (2012). Depressive-like behavior induced by tumor necrosis factor-α in mice. Neuropharmacology 62: 419–426.
Kekow J, Moots R, Khandker R, Melin J, Freundlich B, Singh A (2011). Improvements in patient-reported outcomes, symptoms of depression and anxiety, and their association with clinical remission among patients with moderate-to-severe active early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 50: 401–409.
Kerfoot SM, D'Mello C, Nguyen H, Ajuebor MN, Kubes P, Le T et al (2006). TNF-alpha-secreting monocytes are recruited into the brain of cholestatic mice. Hepatology 43: 154–162.
Kuhlmann AC, Guilarte TR (2000). Cellular and subcellular localization of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors after trimethyltin neurotoxicity. J Neurochem 74: 1694–1704.
Li Z, Ma L, Kulesskaya N, Võikar V, Tian L (2014). Microglia are polarized to M1 type in high-anxiety inbred mice in response to lipopolysaccharide challenge. Brain Behav Immun 38: 237–248.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25: 402–408.
Medeiros R, Prediger RD, Passos GF, Pandolfo P, Duarte FS, Franco JL et al (2007). Connecting TNF-alpha signaling pathways to iNOS expression in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: relevance for the behavioral and synaptic deficits induced by amyloid beta protein. J Neurosci 27: 5394–5404.
Menter A, Augustin M, Signorovitch J, Yu AP, Wu EQ, Gupta SR et al (2010). The effect of adalimumab on reducing depression symptoms in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: a randomized clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol 62: 812–818.
Miller EK, Cohen JD (2001). An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24: 167–202.
Mohler KM, Torrance DS, Smith CA, Goodwin RG, Stremler KE, Fung VP et al (1993). Soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors are effective therapeutic agents in lethal endotoxemia and function simultaneously as both TNF carriers and TNF antagonists. J Immunol 151: 1548–1561.
Nadeau S, Rivest S (2000). Role of microglial-derived tumor necrosis factor in mediating CD14 transcription and nuclear factor kappa B activity in the brain during endotoxemia. J Neurosci 20: 3456–3468.
Ni M, Li X, Yin Z, Jiang H, Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Milatovic D et al (2010). Methylmercury induces acute oxidative stress, altering Nrf2 protein level in primary microglial cells. Toxicol Sci 116: 590–603.
Nilsberth C, Elander L, Hamzic N, Norell M, Lonn J, Engstrom L et al (2009). The role of interleukin-6 in lipopolysaccharide-induced fever by mechanisms independent of prostaglandin E2. Endocrinology 150: 1850–1860.
Noble F, Rubira E, Boulanouar M, Palmier B, Plotkine M, Warnet JM et al (2007). Acute systemic inflammation induces central mitochondrial damage and mnesic deficit in adult Swiss mice. Neurosci Lett 424: 106–110.
Ortega A, Jadeja V, Zhou H (2011). Postnatal development of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in the brain. Inflamm Res 60: 175–185.
Qin L, Wu X, Block ML, Liu Y, Breese GR, Hong JS et al (2007). Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 55: 453–462.
Rivest S (2003). Molecular insights on the cerebral innate immune system. Brain Behav Immun 17: 13–19.
Salim S, Asghar M, Taneja M, Hovatta I, Chugh G, Vollert C et al (2011). Potential contribution of oxidative stress and inflammation to anxiety and hypertension. Brain Res 1404: 63–71.
Semmler A, Frisch C, Debeir T, Ramanathan M, Okulla T, Klockgether T et al (2007). Long-term cognitive impairment, neuronal loss and reduced cortical cholinergic innervation after recovery from sepsis in a rodent model. Exp Neurol 204: 733–740.
Shepherd JK, Grewal SS, Fletcher A, Bill DJ, Dourish CT (1994). Behavioural and pharmacological characterisation of the elevated ‘zero-maze’ as an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharmacology 116: 56–64.
Sweatt JD (2004). Hippocampal function in cognition. Psychopharmacology 174: 99–110.
Takeuchi H, Jin S, Wang J, Zhang G, Kawanokuchi J, Kuno R et al (2006). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces neurotoxicity via glutamate release from hemichannels of activated microglia in an autocrine manner. J Biol Chem 281: 21362–21368.
Tamminga CA (1998). Schizophrenia and glutamatergic transmission. Crit Rev Neurobiol 12: 21–36.
Tobinick E, Gross H, Weinberger A, Cohen H (2006). TNF-alpha modulation for treatment of Alzheimer's disease: a 6-month pilot study. Med Gen Med 8: 25.
Tobinick EL, Gross H (2008). Rapid cognitive improvement in Alzheimer’s disease following perispinal etanercept administration. J Neuroinflammation 5: 2.
Tyring S, Gordon KB, Poulin Y, Langley RG, Gottlieb AB, Dunn M et al (2007). Long-term safety and efficacy of 50 mg of etanercept twice weekly in patients with psoriasis. Arch Dermatol 143: 719–726.
Tyring S, Gottlieb A, Papp K, Gordon K, Leonardi C, Wang A et al (2006). Etanercept and clinical outcomes, fatigue, and depression in psoriasis: double-blind placebo-controlled randomised phase III trial. Lancet 367: 29–35.
Ubogu EE, Cossoy MB, Ransohoff RM (2006). The expression and function of chemokines involved in CNS inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27: 48–55.
Uguz F, Akman C, Kucuksarac S, Tufekci O (2009). Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy is associated with less frequent mood and anxiety disorders in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 63: 50–55.
Venters HD, Dantzer R, Kelley KW (2000). A new concept in neurodegeneration: TNFalpha is a silencer of survival signals. Trends Neurosci 23: 175–180.
Wohleb ES, Hanke ML, Corona AW, Powell ND, Stiner LM, Bailey MT et al (2011). beta-Adrenergic receptor antagonism prevents anxiety-like behavior and microglial reactivity induced by repeated social defeat. J Neurosci 31: 6277–6288.
Wohleb ES, Powell ND, Godbout JP, Sheridan JF (2013). Stress-induced recruitment of bone marrow-derived monocytes to the brain promotes anxiety-like behavior. J Neurosci 33: 13820–13833.
Yirmiya R, Pollak Y, Barak O, Avitsur R, Ovadia H, Bette M et al (2001). Effects of antidepressant drugs on the behavioral and physiological responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in rodents. Neuropsychopharmacology 24: 531–544.
Zhang X, Wang J, Qian W, Zhao J, Sun L, Qian Y et al (2014). Dexmedetomidine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 6 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated astrocytes by suppression of c-Jun N-terminal kinases. Inflammation 37: 942–949.
Zhu CB, Blakely RD, Hewlett WA (2006). The proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha activate serotonin transporters. Neuropsychopharmacology 31: 2121–2131.
Zhu F, Zhang L, Ding YQ, Zhao J, Zheng Y (2014). Neonatal intrahippocampal injection of lipopolysaccharide induces deficits in social behavior and prepulse inhibition and microglial activation in rats: Implication for a new schizophrenia animal model. Brain Behav Immun 38: 166–174.
Acknowledgements
We thank Jim Manavis and Gaurav Singhal for help with some histological aspects used in this study. We also thank Professor Amanda Page, head, Nerve-Gut Lab School of Medicine, for allowing us to use their ABI 7500 Fast real-time PCR machine and the lab space for conducting the RT-qPCR analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camara, M., Corrigan, F., Jaehne, E. et al. Effects of Centrally Administered Etanercept on Behavior, Microglia, and Astrocytes in Mice Following a Peripheral Immune Challenge. Neuropsychopharmacol 40, 502–512 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.199
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.199
This article is cited by
-
The Emerging Role of Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Neuroinflammatory Signals in Psychiatric Disorders and Acquired Epilepsy
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
Daytime Light Deficiency Leads to Sex- and Brain Region-Specific Neuroinflammatory Responses in a Diurnal Rodent
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Sustained TNF signaling is required for the synaptic and anxiety-like behavioral response to acute stress
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
Altered activity of pain processing brain regions in association with hip osteoarthritis
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
LncRNA HOXA-AS2 regulates microglial polarization via recruitment of PRC2 and epigenetic modification of PGC-1α expression
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2021)