Abstract
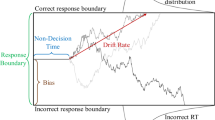
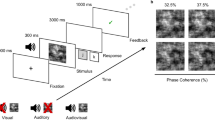
The compulsive behaviour underlying obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) may be related to abnormalities in decision-making. The inability to commit to ultimate decisions, for example, patients unable to decide whether their hands are sufficiently clean, may reflect failures in accumulating sufficient evidence before a decision. Here we investigate the process of evidence accumulation in OCD in perceptual discrimination, hypothesizing enhanced evidence accumulation relative to healthy volunteers. Twenty-eight OCD patients and thirty-five controls were tested with a low-level visual perceptual task (random-dot-motion task, RDMT) and two response conflict control tasks. Regression analysis across different motion coherence levels and Hierarchical Drift Diffusion Modelling (HDDM) were used to characterize response strategies between groups in the RDMT. Patients required more evidence under high uncertainty perceptual contexts, as indexed by longer response time and higher decision boundaries. HDDM, which defines a decision when accumulated noisy evidence reaches a decision boundary, further showed slower drift rate towards the decision boundary reflecting poorer quality of evidence entering the decision process in patients under low uncertainty. With monetary incentives emphasizing speed and penalty for slower responses, patients decreased the decision thresholds relative to controls, accumulating less evidence in low uncertainty. These findings were unrelated to visual perceptual deficits and response conflict. This study provides evidence for impaired decision-formation processes in OCD, with a differential influence of high and low uncertainty contexts on evidence accumulation (decision threshold) and on the quality of evidence gathered (drift rates). It further emphasizes that OCD patients are sensitive to monetary incentives heightening speed in the speed-accuracy tradeoff, improving evidence accumulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Association AP (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV-TR. American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC.
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J (1961). An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4: 561–571.
Chamberlain SR, Fineberg NA, Blackwell AD, Clark L, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2007). A neuropsychological comparison of obsessive-compulsive disorder and trichotillomania. Neuropsychologia 45: 654–662.
Clark L, Robbins TW, Ersche KD, Sahakian BJ (2006). Reflection impulsivity in current and former substance users. Biol Psychiatry 60: 515–522.
Dar R (2004). Elucidating the mechanism of uncertainty and doubt in obsessive-compulsive checkers. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 35: 153–163.
Djamshidian A, O'Sullivan SS, Tomassini A, Foltynie T, Limousin P, Aviles-Olmos I et al (2014). In a rush to decide: deep brain stimulation and dopamine agonist therapy in Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis 4: 579–583.
Endrass T, Klawohn J, Schuster F, Kathmann N (2008). Overactive performance monitoring in obsessive-compulsive disorder: ERP evidence from correct and erroneous reactions. Neuropsychologia 46: 1877–1887.
Eriksen BA, Eriksen CW (1974). Effects of noise letters upon identification of a target letter in a non-search task. Percept Psychophys 16: 143–149.
Fear CF, Healy D (1997). Probabilistic reasoning in obsessive-compulsive and delusional disorders. Psychol Med 27: 199–208.
Fine C, Gardner M, Craigie J, Gold I (2007). Hopping, skipping or jumping to conclusions? Clarifying the role of the JTC bias in delusions. Cogn Neuropsychiatry 12: 46–77.
Fitzgerald KD, Welsh RC, Gehring WJ, Abelson JL, Himle JA, Liberzon I et al (2005). Error-related hyperactivity of the anterior cingulate cortex in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 57: 287–294.
Forstmann BU, Anwander A, Schafer A, Neumann J, Brown S, Wagenmakers EJ et al (2010). Cortico-striatal connections predict control over speed and accuracy in perceptual decision making. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 15916–15920.
Frank MJ, Samanta J, Moustafa AA, Sherman SJ (2007). Hold your horses: impulsivity, deep brain stimulation, and medication in parkinsonism. Science 318: 1309–1312.
Frank MJ, Seeberger LC, O'Reilly RC (2004). By carrot or by stick: cognitive reinforcement learning in parkinsonism. Science 306: 1940–1943.
Gehring WJ, Himle J, Nisenson LG (2000). Action-monitoring dysfunction in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychol Sci 11: 1–6.
Gold JI, Shadlen MN (2007). The neural basis of decision making. Annu Rev Neurosci 30: 535–574.
Goodman WK, Price LH, Rasmussen SA, Mazure C, Fleischmann RL, Hill CL et al (1989). The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46: 1006–1011.
Green N, Bogacz R, Huebl J, Beyer AK, Kuhn AA, Heekeren HR (2013). Reduction of influence of task difficulty on perceptual decision making by STN deep brain stimulation. Curr Biol 23: 1681–1684.
Heekeren HR, Marrett S, Ungerleider LG (2008). The neural systems that mediate human perceptual decision making. Nat Rev Neurosci 9: 467–479.
Hermans D, Engelen U, Grouwels L, Joos E, Lemmens J, Pieters G (2008). Cognitive confidence in obsessive-compulsive disorder: distrusting perception, attention and memory. Behav Res Ther 46: 98–113.
Huddy VC, Clark L, Harrison I, Ron MA, Moutoussis M, Barnes TR et al (2013). Reflection impulsivity and response inhibition in first-episode psychosis: relationship to cannabis use. Psychol Med 43: 2097–2107.
Jaafari N, Aouizerate B, Tignol J, El-Hage W, Wassouf I, Guehl D et al (2011). The relationship between insight and uncertainty in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychopathology 44: 272–276.
Jacobsen P, Freeman D, Salkovskis P (2012). Reasoning bias and belief conviction in obsessive-compulsive disorder and delusions: jumping to conclusions across disorders? Br J Clin Psychol 51: 84–99.
Johannes S, Wieringa BM, Nager W, Rada D, Dengler R, Emrich HM et al (2001). Discrepant target detection and action monitoring in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res 108: 101–110.
Kaiser J, Lennert T, Lutzenberger W (2007). Dynamics of oscillatory activity during auditory decision making. Cereb Cortex 17: 2258–2267.
Kiehl KA, Liddle PF, Hopfinger JB (2000). Error processing and the rostral anterior cingulate: an event-related fMRI study. Psychophysiology 37: 216–223.
Kim J, Blake R, Park S, Shin YW, Kang DH, Kwon JS (2008). Selective impairment in visual perception of biological motion in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Depress Anxiety 25: E15–E25.
Lambrecq V, Rotge JY, Jaafari N, Aouizerate B, Langbour N, Bioulac B et al (2013). Differential role of visuospatial working memory in the propensity toward uncertainty in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder and in healthy subjects. Psychol Med 1–12.
Marchand S, Phillips McEnany G (2012). Hoarding's place in the DSM-5: another symptom, or a newly listed disorder? Issues Ment Health Nurs 33: 591–597.
Marsh R, Horga G, Parashar N, Wang Z, Peterson BS, Simpson HB (2013). Altered activation in fronto-striatal circuits during sequential processing of conflict in unmedicated adults with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 75: 615–625.
Menzies L, Achard S, Chamberlain SR, Fineberg N, Chen CH, del Campo N et al (2007). Neurocognitive endophenotypes of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Brain 130 (Pt 12): 3223–3236.
Morein-Zamir S, Craig KJ, Ersche KD, Abbott S, Muller U, Fineberg NA et al (2010). Impaired visuospatial associative memory and attention in obsessive compulsive disorder but no evidence for differential dopaminergic modulation. Psychopharmacology 212: 357–367.
Moutoussis M, Bentall RP, El-Deredy W, Dayan P (2011). Bayesian modelling of Jumping-to-Conclusions bias in delusional patients. Cogn Neuropsychiatry 16: 422–447.
Nelson HE (1982). National Adult Reading Test (NART): Test Manual NFER-Nelson: Windsor. UK.
Newsome WT, Britten KH, Movshon JA (1989). Neuronal correlates of a perceptual decision. Nature 341: 52–54.
Pelissier MC, O'Connor KP (2002). Deductive and inductive reasoning in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Br J Clin Psychol 41 (Pt 1): 15–27.
Ratcliff R, McKoon G (2008). The diffusion decision model: theory and data for two-choice decision tasks. Neural Comput 20: 873–922.
Romo R, Salinas E (2003). Flutter discrimination: neural codes, perception, memory and decision making. Nat Rev Neurosci 4: 203–218.
Rotge JY, Clair AH, Jaafari N, Hantouche EG, Pelissolo A, Goillandeau M et al (2008). A challenging task for assessment of checking behaviors in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand 117: 465–473.
Rotge JY, Langbour N, Dilharreguy B, Bordessoulles M, Guehl D, Bioulac B et al (2012). Contextual and behavioral influences on uncertainty in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Cortex 23: 00346–2.
Sachdev PS, Malhi GS (2005). Obsessive-compulsive behaviour: a disorder of decision-making. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 39: 757–763.
Sarig S, Dar R, Liberman N (2012). Obsessive-compulsive tendencies are related to indecisiveness and reliance on feedback in a neutral color judgment task. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 43: 692–697.
Savage CR, Baer L, Keuthen NJ, Brown HD, Rauch SL, Jenike MA (1999). Organizational strategies mediate nonverbal memory impairment in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 45: 905–916.
Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E et al (1998). The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychiatry 59 (Suppl 20): 22–33.
Shin NY, Jang JH, Kim HS, Shim G, Hwang JY, Kim SN et al (2013). Impaired body but not face perception in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Neuropsychol 7: 58–71.
Spielberger CD (1985). Assessment of state and trait anxiety: Conceptual and methodological issues. South Psychologist 2: 6–16.
Stern ER, Welsh RC, Gonzalez R, Fitzgerald KD, Abelson JL, Taylor SF (2012). Subjective uncertainty and limbic hyperactivation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Hum Brain Mapp 34: 1956–1970.
Stern ER, Welsh RC, Gonzalez R, Fitzgerald KD, Abelson JL, Taylor SF (2013). Subjective uncertainty and limbic hyperactivation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Hum Brain Mapp 34: 1956–1970.
Toffolo MBJ, Van den Hout MA, Hooge ITC, Engelhard IM, Cath DC (2013). Mild uncertainty promotes checking behavior in subclinical obsessive–compulsive disorder. Clin Psychol Sci 1: 103–109.
Uchida N, Kepecs A, Mainen ZF (2006). Seeing at a glance, smelling in a whiff: rapid forms of perceptual decision making. Nat Rev Neurosci 7: 485–491.
Ursu S, Stenger VA, Shear MK, Jones MR, Carter CS (2003). Overactive action monitoring in obsessive-compulsive disorder: evidence from functional magnetic resonance imaging. Psychol Sci 14: 347–353.
van den Hout M, Kindt M (2003a). Phenomenological validity of an OCD-memory model and the remember/know distinction. Behav Res Ther 41: 369–378.
van den Hout M, Kindt M (2003b). Repeated checking causes memory distrust. Behav Res Ther 41: 301–316.
van den Hout MA, Engelhard IM, de Boer C, du Bois A, Dek E (2008). Perseverative and compulsive-like staring causes uncertainty about perception. Behav Res Ther 46: 1300–1304.
van den Hout MA, Engelhard IM, Smeets M, Dek EC, Turksma K, Saric R (2009). Uncertainty about perception and dissociation after compulsive-like staring: time course of effects. Behav Res Ther 47: 535–539.
Volans PJ (1976). Styles of decision-making and probability appraisal in selected obsessional and phobic patients. Br J Soc Clin Psychol 15: 305–317.
Wiecki TV, Sofer I, Frank MJ (2013). HDDM: hierarchical bayesian estimation of the drift-diffusion model in python. Front Neuroinformatics 7: 14.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge all the participants for their participation in this study. We would also like to thank Michael J Frank for helpful discussions on the HDDM data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banca, P., Vestergaard, M., Rankov, V. et al. Evidence Accumulation in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: the Role of Uncertainty and Monetary Reward on Perceptual Decision-Making Thresholds. Neuropsychopharmacol 40, 1192–1202 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.303
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.303
This article is cited by
-
Functional connectivity abnormalities of brain networks in obsessive–compulsive disorder: a systematic review
Current Psychology (2024)
-
The prefrontal cortex and OCD
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
Joint contributions of metacognition and self-beliefs to uncertainty-guided checking behavior
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Thalamocortical excitability modulation guides human perception under uncertainty
Nature Communications (2021)
-
A cross-species assessment of behavioral flexibility in compulsive disorders
Communications Biology (2021)