Abstract
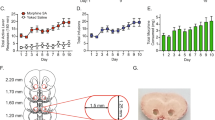
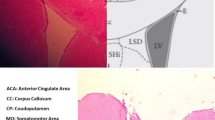
Regulator of G protein signalling 9-2 (Rgs9-2) modulates the actions of a wide range of CNS-acting drugs by controlling signal transduction of several GPCRs in the striatum. RGS9-2 acts via a complex mechanism that involves interactions with Gα subunits, the Gβ5 protein, and the adaptor protein R7BP. Our recent work identified Rgs9-2 complexes in the striatum associated with acute or chronic exposures to mu opioid receptor (MOR) agonists. In this study we use several new genetic tools that allow manipulations of Rgs9-2 activity in particular brain regions of adult mice in order to better understand the mechanism via which this protein modulates opiate addiction and analgesia. We used adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) to express forms of Rgs9-2 in the dorsal and ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens, NAc) in order to examine the influence of this protein in morphine actions. Consistent with earlier behavioural findings from constitutive Rgs9 knockout mice, we show that Rgs9-2 actions in the NAc modulate morphine reward and dependence. Notably, Rgs9-2 in the NAc affects the analgesic actions of morphine as well as the development of analgesic tolerance. Using optogenetics we demonstrate that activation of Channelrhodopsin2 in Rgs9-2-expressing neurons, or in D1 dopamine receptor (Drd1)-enriched medium spiny neurons, accelerates the development of morphine tolerance, whereas activation of D2 dopamine receptor (Drd2)-enriched neurons does not significantly affect the development of tolerance. Together, these data provide new information on the signal transduction mechanisms underlying opiate actions in the NAc.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Alexander GE, DeLong MR, Strick PL (1986). Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci 9: 357–381.
Anderson GR, Semenov A, Song JH, Martemyanov KA (2007). The membrane anchor R7BP controls the proteolytic stability of the striatal specific RGS protein, RGS9-2. J Biol Chem 282: 4772–4781.
Bailey CD, Connor M (2005). Opioids: cellular mechanisms of tolerance and physical actions of Spinophilin Regulate mu opioid receptor function. Neuron 58: 238- dependence. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5: 60–68.
Baliki MN, Geha PY, Fields HL, Apkarian AV (2010). Predicting value of pain and analgesia: nucleus accumbens response to noxious stimuli changes in the presence of chronic pain. Neuron 66: 149–160.
Baliki MN, Petre B, Torbey S, Herrmann KM, Huang L, Schnitzer TJ et al (2012). Corticostriatal functional connectivity predicts transition to chronic back pain. Nat Neurosci 15: 1117–1119.
Ballon DR, Flanary PL, Gladue DP, Konopka JB, Dohlman HG, Thorner J (2006). DEP-domain-mediated regulation of GPCR signaling responses. Cell 126: 1079–1093.
Charlton JJ, Allen PB, Psifogeorgou K, Chakravarty S, Gomes I, Neve R et al (2008). Multiple actions of spinophilin regulate mu opioid receptor function. Neuron 8: 238–247.
Chandra R, Lenz JD, Gancarz AM, Chaudhury D, Schroeder GL, Han MH et al (2013). Optogenetic inhibition of D1R containing nucleus accumbens neurons alters cocaine-mediated regulation of Tiam1. Front Mol Neurosci 24: 13.
Chaudhury D, Walsh JJ, Friedman AK, Juarez B, Ku SM, Koo JW et al (2013). Rapid regulation of depression-related behaviours by control of midbrain dopamine neurons. Nature 493: 532–536.
Contet C, Kieffer BL, Befort K. (2004). Mu opioid receptor, a gateway to drug addiction. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14: 370–378.
Dang MT, Yokoi F, Yin HH, Lovinger DM, Wang Y, Li Y (2006). Disrupted motor learning and long-term synaptic plasticity in mice lacking NMDAR1 in the striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 15254–15259.
Gold SJ, Hoang CV, Potts BW, Porras G, Pioli E, Kim KW et al (2007). RGS9-2 negatively modulates L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine-induced dyskinesia in experimental Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci 27: 14338–14348.
Gold SJ, Ni Y, Dohlman H, Nestler E (1997). Regulators of G-protein signaling (RGS) proteins: region-specific expression of nine subtypes in rat brain. J Neurosci 17: 8024–8037.
Graybiel AM (1990). Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci 13: 244–254.
Han M, Renthal W, Ring RH., Rahman Z, Psifogeorgou K, Howland D et al (2010). Brain region specific actions of RGS4 oppose morphine reward and dependence but promote analgesia. Biol Psychiatry 67: 761–769.
Hommel JD, Sears RM, Georgescou D, Simmons D.L, DiLeone RJ (2003). Local gene knockdown in the brain using viral mediated RNA interference. Nat Med 9: 1539–1544.
Kimple AJ, Bosch DE, Giguère PM, Siderovski DP (2011). Regulators of G-protein signaling and their Gα substrates: promises and challenges in their use as drug discovery targets. Pharmacol Rev 63: 728–749.
Koo JW, Mazei-Robison MS, Chaudhury D, Juarez B, LaPlant Q, Ferguson D et al (2012). BDNF is a negative modulator of morphine action. Science 338: 124–128.
Kovoor A, Seyffarth P, Ebert J, Barghshoon S, Chen CK, Schwarz S et al (2005). D2 dopamine receptors colocalize regulator of G protein signalling 9-2 via the RGS9 DEP domain, and RGS9 knockout mice develop dyskinesias associated with dopamine pathways. J Neurosci 280: 5133–5136.
Lim BK, Huang KW, Grueter B, Rothwell P, Malenka R (2012). Anhedonia requires MC4R-mediated synaptic adaptations in nucleus accumbens. Nature 487: 183–189.
Ling W, Mooney L, Hillhouse M (2011). Prescription opioid abuse, pain and addiction: clinical issues and implications. Drug Alcohol Rev 30: 300–305.
Lobo MK, Karsten SL, Gray M, Geschwind DH, Yang XW. (2006). FACS-array profiling of striatal projection neuron subtypes in juvenile and adult mouse brains. Nat Neurosci 9: 443–452.
Lobo MK, Covington HE 3rd, Chaudhury D, Friedman AK, Sun H et al (2010). Cell type-specific loss of BDNF signaling mimics optogenetic control of cocaine reward. Science 330: 385–390.
Masuho I, Wakasugi-Masuho H, Posokhova EN, Patton JR, Martemyanov KA (2011). Type 5G protein beta subunit (Gbeta5) controls the interaction of regulator of G protein signaling 9 (RGS9) with membrane anchors. J Biol Chem 286: 21806–21813.
Psifogeorgou K, Papakosta P, Russo SJ, Kardassis D, Gold SJ, Zachariou V (2007). RGS9-2 is a negative modulator of mu opioid receptor function. J Neurochem 103: 617–625.
Psifogeorgou K, Terzi D, Papachatzaki MM, Varidaki A, Gold SJ, Zachariou V (2011). A unique role of RGS9-2 in the striatum as a positive or negative regulator of opiate analgesia. J Neurosci 31: 5617–5624.
Quillinan N, Lau EK, Virk M, Von Zastrow M, Williams JT (2011). Recovery from mu-opioid receptor desensitization after chronic treatment with morphine and methadone. J Neurosci 31: 4434–4443.
Raehal KM, Bohn LM (2011). The role of beta-arrestin2 in the severity of antinociceptive tolerance and physical dependence induced by different opioid pain therapeutics. Neuropharmacology 60: 58–65.
Rahman Z, Schwarz J, Gold SJ, Zachariou V, Wein MN, Choi KH et al (2003). RGS9 modulates dopamine signaling in the basal ganglia. Neuron 38: 941–952.
Shuen JA, Chen M, Gloss B, Calakos N (2008). Drd1a-tdTomato BAC transgenic mice for simultaneous visualization of medium spiny neurons in the direct and indirect pathways of the basal ganglia. J Neurosci 28: 2681–2685.
Smith RJ, Lobo MK, Spencer S, Kalivas PW (2013). Cocaine-induced adaptations in D1 and D2 accumbens projection neurons (a dichotomy not necessarily synonymus with direct and indirect pathways). Curr Opin Neurobiol S0959-4388: 00045–00047.
Sun H, Maze I, Dietz DM, Scobie KN, Kennedy PJ, Damez-Werno D et al (2012). Morphine epigenomically regulates behavior through alterations in histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 32: 17454–17464.
Terzi D, Cao Y, Agrimaki I, Martemyanov KA, Zachariou V (2012). R7BP modulates opiate analgesia and tolerance but not withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology 37: 1005–1012.
Terzi D, Stergiou E, King SL, Zachariou V (2009). Regulators of G protein signaling in neuropsychiatric disorders. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 86: 299–333.
Traynor JR, Terzi D, Caldarone B, Zachariou V (2009). RGS9-2: probing an intracellular modulator of behavior as a drug target. Trends Pharmacol Sci 37: 1005–1012.
Tye KM, Mirzabekov JJ, Warden MR, Ferenczi EA, Tsai HC, Finkelstein J et al (2013). Dopamine neurons modulate neural encoding and expression of depression-related behaviour. Nature 493: 537–541.
Wanigasekera V, Lee MC, Rogers R, Kong Y, Leknes S, Andersson J et al (2012). Baseline reward circuitry activity and trait reward responsiveness predict expression of opioid analgesia in healthy subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109: 17705–17710.
Xie K, Masuho I, Brand C, Dessauer CW, Martemyanov KA (2012). The complex of G protein regulator RGS9-2 and Gβ(5) controls sensitization and signaling kinetics of type 5 adenylyl cyclase in the striatum. Sci Signal 5: ra63.
Xie W, Samoriski GM, McLaughlin JP, Romoser VA, Smrcka A, Hinkle PM et al (1999). Genetic alteration of phospholipase C beta3 expression modulates behavioral and cellular responses to mu opioids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 10385–10390.
Yizhar O, Fenno LE, Davidson TJ, Mogri M, Deisseroth K (2011). Optogenetics in neural systems. Neuron 71: 9–34.
Zachariou V, Bolanos CA, Selley DE, Theobald D, Cassidy M, Kelz M et al (2006). An essential role for ΔFosB in the nucleus accumbens in morphine action. Nat Neurosci 9: 205–211.
Zachariou V, Georgescu GD, Sanchez N, Rahman Z, DiLeone RJ, Berton O et al (2003). Essential role for RGS9 in opiate action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 13656–13661.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr E.J. Nestler for providing the Cre mouse lines and for reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaspari, S., Papachatzaki, M., Koo, J. et al. Nucleus Accumbens-Specific Interventions in RGS9-2 Activity Modulate Responses to Morphine. Neuropsychopharmacol 39, 1968–1977 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.45
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.45
This article is cited by
-
Tianeptine promotes lasting antiallodynic effects in a mouse model of neuropathic pain
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Single nucleus transcriptomic analysis of rat nucleus accumbens reveals cell type-specific patterns of gene expression associated with volitional morphine intake
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Opioid use disorder
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2020)
-
RGS9-2 Modulates Responses to Oxycodone in Pain-Free and Chronic Pain States
Neuropsychopharmacology (2017)