Abstract
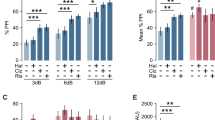
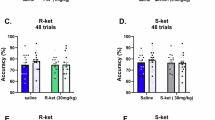
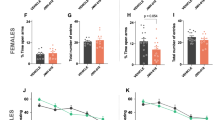
The endocannabinoid system has been widely involved in the pathophysiology of sensorimotor gating deficits. This study aimed to evaluate the pharmacological modulation of the sensorimotor gating impairment induced by cannabinoid CB1 receptor (CB1r) deletion. For this purpose, the prepulse inhibition (PPI) paradigm was used to evaluate the effect of two antipsychotics drugs (risperidone and haloperidol) and a psychostimulant (methylphenidate) on the preattentional deficit presented by CB1KO mice. Furthermore, the effects of the CB1r antagonist AM251 on PPI were evaluated in WT mice. Real-time PCR and immunohistochemical studies were carried out to analyze dopamine transporter (DAT) and α-2C adrenergic receptor (ADRA2C) gene expressions and the distribution of parvalbumin (PV) and cholecystokinin-8 (CCK) immunoreactive (ir) cortical neurons, respectively. Neither risperidone nor haloperidol significantly modified the PPI of WT and CB1KO mice, whereas methylphenidate improved the preattentional deficit of CB1KO mice. In addition, treatment with AM251 (3 mg/kg; i.p.) significantly decreased the PPI of WT animals. The administration of methylphenidate increased DAT and ADRA2C gene expressions in CB1KO mice without producing any effect in WT animals. Immunohistochemical studies revealed that there were no significant changes in CCK immunolabeling between WT and CB1KO mice, whereas the radial distribution of PV-ir neurons was abnormal in CB1KO mice. These data further support the important role of CB1r in sensorimotor gating regulation and the therapeutic usefulness of methylphenidate for the treatment of psychiatric disorders with associated preattentional deficits.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Andrews GD, Lavin A (2006). Methylphenidate increases cortical excitability via activation of alpha-2 noradrenergic receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 31: 594–601.
Berbel P, Auso E, Garcia-Velasco JV, Molina ML, Camacho M (2001). Role of thyroid hormones in the maturation and organisation of rat barrel cortex. Neuroscience 107: 383–394.
Berbel P, Marco P, Cerezo JR, DeFelipe J (1996). Distribution of parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the neocortex of hypothyroid adult rats. Neurosci Lett 204: 65–68.
Berbel P, Navarro D, Román G (2014). An evo-devo approach to thyroid hormones in cerebral and cerebellar cortical development: etiological implications for autism. Front Endocrinol 5: 146.
Berghuis P, Rajnicek AM, Morozov YM, Ross RA, Mulder J, Urban GM et al (2007). Hardwiring the brain: endocannabinoids shape neuronal connectivity. Science 316: 1212–1216.
Calipari ES, Ferris MJ, Salahpour A, Caron MG, Jones SR (2013). Methylphenidate amplifies the potency and reinforcing effects of amphetamines by increasing dopamine transporter expression. Nat Commun 4: 2720.
Cardin JA, Carlen M, Meletis K, Knoblich U, Zhang F, Deisseroth K et al (2009). Driving fast-spiking cells induces gamma rhythm and controls sensory responses. Nature 459: 663–667.
Castellanos FX, Fine EJ, Kaysen D, Marsh WL, Rapoport JL, Hallett M (1996). Sensorimotor gating in boys with Tourette's syndrome and ADHD: preliminary results. Biol Psychiatry 39: 33–41.
Conzelmann A, Pauli P, Mucha RF, Jacob CP, Gerdes AB, Romanos J et al (2010). Early attentional deficits in an attention-to-prepulse paradigm in ADHD adults. J Abnorm Psychol 119: 594–603.
Dawson ME, Hazlett EA, Filion DL, Nuechterlein KH, Schell AM (1993). Attention and schizophrenia: impaired modulation of the startle reflex. J Abnorm Psychol 102: 633–641.
DeFelipe J (2004). Cortical microanatomy and human brain disorders: epilepsy. Cortex 40: 232–233.
Feifel D, Minassian A, Perry W (2009). Prepulse inhibition of startle in adults with ADHD. J Psychiatr Res 43: 484–489.
Fernandez-Espejo E, Galan-Rodriguez B (2004). Sensorimotor gating in mice is disrupted after AM404, an anandamide reuptake and degradation inhibitor. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 175: 220–224.
Glausier JR, Fish KN, Lewis DA (2014). Altered parvalbumin basket cell inputs in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia subjects. Mol Psychiatry 19: 30–36.
Gomes FV, Issy AC, Ferreira FR, Viveros MP, Del Bel EA, Guimaraes FS (2014). Cannabidiol attenuates sensorimotor gating disruption and molecular changes induced by chronic antagonism of NMDA receptors in mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18.
Hajos M, Hoffmann WE, Kocsis B (2008). Activation of cannabinoid-1 receptors disrupts sensory gating and neuronal oscillation: relevance to schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 63: 1075–1083.
Hanlon MC, Karayanidis F, Schall U (2009). Intact sensorimotor gating in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12: 701–707.
Heekeren K, Meincke U, Geyer MA, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E (2004). Attentional modulation of prepulse inhibition: a new startle paradigm. Neuropsychobiology 49: 88–93.
Inda MC, DeFelipe J, Munoz A (2009). Morphology and distribution of chandelier cell axon terminals in the mouse cerebral cortex and claustroamygdaloid complex. Cereb Cortex 19: 41–54.
Kawaguchi Y, Kubota Y (1997). GABAergic cell subtypes and their synaptic connections in rat frontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 7: 476–486.
Kedzior KK, Martin-Iverson MT (2006). Chronic cannabis use is associated with attention-modulated reduction in prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex in healthy humans. J Psychopharmacol 20: 471–484.
Kohl S, Heekeren K, Klosterkotter J, Kuhn J (2013). Prepulse inhibition in psychiatric disorders—apart from schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 47: 445–452.
Leroy S, Griffon N, Bourdel MC, Olie JP, Poirier MF, Krebs MO (2001). Schizophrenia and the cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1): association study using a single-base polymorphism in coding exon 1. Am J Med Genet 105: 749–752.
Levin R, Peres FF, Almeida V, Calzavara MB, Zuardi AW, Hallak JE et al (2014). Effects of cannabinoid drugs on the deficit of prepulse inhibition of startle in an animal model of schizophrenia: the SHR strain. Front Pharmacol 5: 10.
Lewis DA (2014). Inhibitory neurons in human cortical circuits: substrate for cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Curr Opin Neurobiol 26: 22–26.
Lovett-Barron M, Losonczy A (2014). Behavioral consequences of GABAergic neuronal diversity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 26: 27–33.
Malone DT, Taylor DA (2006). The effect of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on sensorimotor gating in socially isolated rats. Behav Brain Res 166: 101–109.
Marongiu MF, Poddie D, Porcu S, Manchinu MF, Castelli MP, Sogos V et al (2012). Reversible disruption of pre-pulse inhibition in hypomorphic-inducible and reversible CB1−/− mice. PLoS One 7: e35013.
Martin RS, Secchi RL, Sung E, Lemaire M, Bonhaus DW, Hedley LR et al (2003). Effects of cannabinoid receptor ligands on psychosis-relevant behavior models in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 165: 128–135.
Mulder J, Aguado T, Keimpema E, Barabas K, Ballester Rosado CJ, Nguyen L et al (2008). Endocannabinoid signaling controls pyramidal cell specification and long-range axon patterning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 8760–8765.
Navarro D, Alvarado M, Navarrete F, Giner M, Obregon MJ, Manzanares J et al (2015). Gestational and early postnatal hypothyroidism alters VGluT1 and VGAT bouton distribution in the neocortex and hippocampus, and behavior in rats. Front Neuroanat 9: 9.
Ornitz EM, Hanna GL, de Traversay J (1992). Prestimulation-induced startle modulation in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and nocturnal enuresis. Psychophysiology 29: 437–451.
Ornitz EM, Russell AT, Hanna GL, Gabikian P, Gehricke JG, Song D et al (1999). Prepulse inhibition of startle and the neurobiology of primary nocturnal enuresis. Biol Psychiatry 45: 1455–1466.
Ortega-Alvaro A, Aracil-Fernandez A, Garcia-Gutierrez MS, Navarrete F, Manzanares J (2011). Deletion of CB2 cannabinoid receptor induces schizophrenia-related behaviors in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 36: 1489–1504.
Oudin MJ, Hobbs C, Doherty P (2011). DAGL-dependent endocannabinoid signalling: roles in axonal pathfinding, synaptic plasticity and adult neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 34: 1634–1646.
Pezze M, McGarrity S, Mason R, Fone KC, Bast T (2014). Too little and too much: hypoactivation and disinhibition of medial prefrontal cortex cause attentional deficits. J Neurosci 34: 7931–7946.
Rubino T, Parolaro D (2014). Cannabis abuse in adolescence and the risk of psychosis: a brief review of the preclinical evidence. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 52: 41–44.
Sallinen J, Haapalinna A, Viitamaa T, Kobilka BK, Scheinin M (1998). Adrenergic alpha2C-receptors modulate the acoustic startle reflex, prepulse inhibition, and aggression in mice. J Neurosci 18: 3035–3042.
Schneider M, Koch M (2002). The cannabinoid agonist WIN 55,212-2 reduces sensorimotor gating and recognition memory in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13: 29–37.
Schulz-Juergensen S, Thiemann A, Gebhardt J, Baumgarten-Walczak A, Eggert P (2014). Prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle and the influence of methylphenidate in children with ADHD. J Atten Disord 18: 117–122.
Somkuwar SS, Darna M, Kantak KM, Dwoskin LP (2013). Adolescence methylphenidate treatment in a rodent model of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: dopamine transporter function and cellular distribution in adulthood. Biochem Pharmacol 86: 309–316.
Somogyi P, Klausberger T (2005). Defined types of cortical interneurone structure space and spike timing in the hippocampus. J Physiol 562: 9–26.
Stoner R, Chow ML, Boyle MP, Sunkin SM, Mouton PR, Roy S et al (2014). Patches of disorganization in the neocortex of children with autism. N Engl J Med 370: 1209–1219.
Strauss ME (1993). Relations of symptoms to cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 19: 215–231.
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1993). Clozapine and haloperidol in an animal model of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44: 741–744.
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA, Braff DL (2001). Neural circuit regulation of prepulse inhibition of startle in the rat: current knowledge and future challenges. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 156: 194–215.
Uriguen L, Garcia-Fuster MJ, Callado LF, Morentin B, La Harpe R, Casado V et al (2009). Immunodensity and mRNA expression of A2A adenosine, D2 dopamine, and CB1 cannabinoid receptors in postmortem frontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia: effect of antipsychotic treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 206: 313–324.
Volk DW, Lewis DA (2014). Early developmental disturbances of cortical inhibitory neurons: contribution to cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 40: 952–957.
Wang LJ, Huang YS, Hsiao CC, Chen CK (2012). The trend in morning levels of salivary cortisol in children with ADHD during 6 months of methylphenidate treatment. J Atten Disord (in press).
Zavitsanou K, Garrick T, Huang XF (2004). Selective antagonist [3H]SR141716A binding to cannabinoid CB1 receptors is increased in the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28: 355–360.
Acknowledgements
We thank Raquel Poveda for the excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by the following research grants: Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación SAF2011–23420 to Jorge Manzanares and SAF2009–10689 to Pere Berbel; Foundation Alicia Koplowitz to Pere Berbel; and Instituto de Salud ‘Carlos III’ (FIS), RETICS, Red de Trastornos Adictivos (RD06/0001/1004, RD12/0028/0019) to Jorge Manzanares.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortega-Álvaro, A., Navarrete, F., Aracil-Fernández, A. et al. Differential Pharmacological Regulation of Sensorimotor Gating Deficit in CB1 Knockout Mice and Associated Neurochemical and Histological Alterations. Neuropsychopharmacol 40, 2639–2647 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.113
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.113
This article is cited by
-
Activation of tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B in pyramidal neurons impairs endocannabinoid signaling by tyrosine receptor kinase trkB and causes schizophrenia-like behaviors in mice
Neuropsychopharmacology (2020)
-
Abnormal wiring of CCK+ basket cells disrupts spatial information coding
Nature Neuroscience (2017)