Abstract
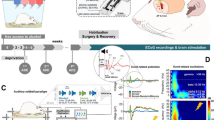
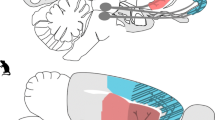
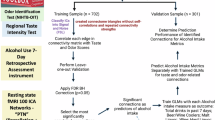
Critical development of the prefrontal cortex occurs during adolescence, a period of increased independence marked by decision making that often includes engagement in risky behaviors, such as substance use. Consumption of alcohol during adolescence has been associated with increased impulsivity that persists across the lifespan, an effect which may be caused by long-term disruptions in cortical processing of rewards. To determine if alcohol consumption alters cortical encoding of rewards of different sizes and probabilities, we gave rats limited access to alcohol in gelatin during adolescence only. In adulthood, we recorded the electrophysiological activity of individual neurons of the orbitofrontal cortex while rats performed a risk task that varied the level of risk from day-to-day. Rats that had consumed higher levels of alcohol showed increased risk preference in the task compared with control and low alcohol-consuming rats. Patterns of neuronal responses were identified using principal component analysis. Of the multiple patterns observed, only one was modulated by adolescent alcohol consumption and showed strongest modulation after reward receipt. This subpopulation of neurons showed blunted firing rates following rewards in alcohol-consuming rats, suggesting a mechanism through which adolescent alcohol exposure may have lasting effects on reward processing in the context of decision making. The differences in OFC responses between high alcohol consumers and control animals not given access to alcohol support the idea that, regardless of potential variability in innate alcohol preferences, voluntary consumption of alcohol during adolescence biases choice patterns longitudinally through alterations in cortical function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bava S, Tapert SF (2010). Adolescent brain development and the risk for alcohol and other drug problems. Neuropsychol Rev 20: 398–413.
Bell RL, Rodd ZA, Sable HJK, Schultz JA, Hsu CC, Lumeng L et al (2006). Daily patterns of ethanol drinking in peri-adolescent and adult alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 83: 35–46.
Bell RL, Rodd ZA, Smith RJ, Toalston JE, Franklin KM, McBride WJ (2011). Modeling binge-like ethanol drinking by peri-adolescent and adult P rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100: 90–97.
Clark JJ, Nasrallah NA, Hart AS, Collins AL, Bernstein IL, Phillips PEM (2012). Altered risk-based decision making following adolescent alcohol use results from an imbalance in reinforcement learning in rats. PLoS One 7: e37357.
Cocker PJ, Dinelle K, Kornelson R, Sossi V, Winstanley CA (2012). Irrational choice under uncertainty correlates with lower striatal D(2/3) receptor binding in rats. J Neurosci 32: 15450–15457.
Courtney K, Polich J (2009). Binge drinking in young adults: data, definitions, and determinants. Psychol Bull 135: 142–156.
Crews FT, He J, Hodge C (2007). Adolescent cortical development: a critical period of vulnerability for addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86: 189–199.
Crews FT, Mdzinarishvili A, Kim D, He J, Nixon K (2006). Neurogenesis in adolescent brain is potently inhibited by ethanol. Neuroscience 137: 437–445.
Doremus-Fitzwater TL, Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2010). Motivational systems in adolescence: possible implications for age differences in substance abuse and other risk-taking behaviors. Brain Cogn 72: 114–123.
Enoch M-A (2011). The role of early life stress as a predictor for alcohol and drug dependence. Psychopharmacology 214: 17–31.
Hsu M, Bhatt M, Adolphs R, Tranel D, Camerer CF (2005). Neural systems responding to degrees of uncertainty in human decision-making. Science 310: 1680–1683.
Johnson PM, Kenny PJ (2010). Dopamine D2 receptors in addiction-like reward dysfunction and compulsive eating in obese rats. Nat Neurosci 13: 635–641.
Kepecs A, Uchida N, Zariwala HA, Mainen ZF (2008). Neural correlates, computation and behavioural impact of decision confidence. Nature 455: 227–231.
Lovallo WR (2013). Early life adversity reduces stress reactivity and enhances impulsive behavior: implications for health behaviors. Int J Psychophysiol 90: 8–16.
Lovallo WR, Farag NH, Sorocco KH, Acheson A, Cohoon AJ, Vincent AS (2013). Early life adversity contributes to impaired cognition and impulsive behavior: studies from the Oklahoma Family Health Patterns Project. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37: 616–623.
McDannald MA, Esber GR, Wegener MA, Wied HM, Liu T-L, Stalnaker TA et al (2014). Orbitofrontal neurons acquire responses to “valueless” Pavlovian cues during unblocking. eLife 3: e02653.
McMurray MS, Amodeo LR, Roitman JD (2014). Effects of voluntary alcohol intake on risk preference and behavioral flexibility during rat adolescence. PLoS One 9: e100697.
Nasrallah NA, Clark JJ, Collins AL, Akers CA, Phillips PEM, Bernstein IL (2011). Risk preference following adolescent alcohol use is associated with corrupted encoding of costs but not rewards by mesolimbic dopamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 5466–5471.
Nasrallah NA, Yang TWH, Bernstein IL (2009). Long-term risk preference and suboptimal decision making following adolescent alcohol use. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 17600–17604.
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (2004). NIAAA council approves definition of binge drinking. NIAAA Newsl 3: 3.
Nixon K, Morris SA, Liput DJ, Kelso ML (2010). Roles of neural stem cells and adult neurogenesis in adolescent alcohol use disorders. Alcohol 44: 39–56.
Padoa-Schioppa C, Cai X (2011). The orbitofrontal cortex and the computation of subjective value: consolidated concepts and new perspectives. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1239: 130–137.
Peris J, Zharikova A, Li Z, Lingis M, MacNeill M, Wu MT et al (2006). Brain ethanol levels in rats after voluntary ethanol consumption using a sweetened gelatin vehicle. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85: 562–568.
Roitman JD, Roitman MF (2010). Risk-preference differentiates orbitofrontal cortex responses to freely chosen reward outcomes. Eur J Neurosci 31: 1492–1500.
Selemon LD (2013). A role for synaptic plasticity in the adolescent development of executive function. Transl Psychiatry 3: e238.
Stalnaker TA, Cooch NK, McDannald MA, Liu T-L, Wied H, Schoenbaum G (2014). Orbitofrontal neurons infer the value and identity of predicted outcomes. Nat Commun 5: 3926.
Stein JS, Renda CR, Barker SM, Liston KJ, Shahan TA, Madden GJ (2015). Impulsive choice predicts anxiety-like behavior, but not alcohol or sucrose consumption, in male Long-Evans rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 39: 932–940.
Tobler PN, Christopoulos GI, O’Doherty JP, Dolan RJ, Schultz W (2009). Risk-dependent reward value signal in human prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 7185–7190.
Volkow ND, Wang G-J, Tomasi D, Baler RD (2013). The addictive dimensionality of obesity. Biol Psychiatry 73: 811–818.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Christopher Sinon and Alyssa Secreto for their assistance with data collection, and Dr Darin Knapp for his assistance with blood ethanol level quantification.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McMurray, M., Amodeo, L. & Roitman, J. Consequences of Adolescent Ethanol Consumption on Risk Preference and Orbitofrontal Cortex Encoding of Reward. Neuropsychopharmacol 41, 1366–1375 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.288
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.288
This article is cited by
-
Effects of Acute Alcohol Exposure on Layer 5 Pyramidal Neurons of Juvenile Mice
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
-
Behavioral Inefficiency on a Risky Decision-Making Task in Adulthood after Adolescent Intermittent Ethanol Exposure in Rats
Scientific Reports (2017)