Abstract
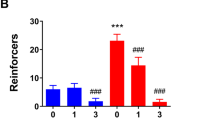
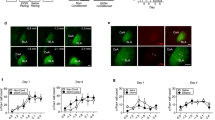
GABAergic signaling is involved in modulating the reinforcing properties of alcohol, and GABAB receptors have been proposed as a potential target for clinical treatment of alcoholism. The orthosteric GABAB receptor agonist baclofen has been shown to suppress operant self-administration of alcohol in animals and alcohol use in alcohol-dependent patients, but its utility is limited by a narrow therapeutic index. We tested the effects of ADX71441, a novel GABAB receptor positive allosteric modulator, on alcohol-related behaviors in rats. We first assessed the effects of ADX71441 (1, 3, 10 and 30 mg/kg, I.P.) on both non-dependent and dependent male Wistar rats trained to self-administer 20% alcohol. We then determined the effects of ADX71441 on stress-induced as well as cue-induced relapse-like behavior. Finally, we sought to identify the brain regions through which ADX71441 may act to prevent relapse-like behavior by mapping the neuronal activation induced by stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol-seeking using c-Fos immunohistochemistry. ADX71441 dose-dependently decreased alcohol self-administration of both dependent and non-dependent animals, but its potency was higher in alcohol-dependent rats. Furthermore, both cue- and stress-induced alcohol seeking were blocked by the GABAB receptor positive allosteric modulator. Finally, pretreatment with 3 mg/kg of ADX71441 before stress-induced reinstatement significantly decreased c-Fos expression in a network of brain regions implicated in stress-induced relapse, comprising the nucleus accumbens shell, the dorsal raphe nucleus and the medial prefrontal cortex. Our findings support a causal role of GABAB receptors in alcohol reinforcement and relapse to alcohol seeking. These effects are observed in the absence of significant sedative side effects. Jointly, these observations indicate that GABAB receptor positive allosteric modulators merit being tested clinically for the treatment of alcoholism. Our data also point to a potential biomarker of target engagement for early clinical studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Addolorato G, Caputo F, Capristo E, Domenicali M, Bernardi M, Janiri L et al (2002a). Baclofen efficacy in reducing alcohol craving and intake: a preliminary double-blind randomized controlled study. Alcohol Alcohol 37: 504–508.
Addolorato G, Caputo F, Capristo E, Janiri L, Bernardi M, Agabio R et al (2002b). Rapid suppression of alcohol withdrawal syndrome by baclofen. Am J Med 112: 226–229.
Addolorato G, Leggio L, Cardone S, Ferrulli A, Gasbarrini G (2009). Role of the GABA(B) receptor system in alcoholism and stress: focus on clinical studies and treatment perspectives. Alcohol 43: 559–563.
Addolorato G, Leggio L, Ferrulli A, Cardone S, Vonghia L, Mirijello A et al (2007). Effectiveness and safety of baclofen for maintenance of alcohol abstinence in alcohol-dependent patients with liver cirrhosis: randomised, double-blind controlled study. Lancet 370: 1915–1922.
Anstrom KK, Cromwell HC, Markowski T, Woodward DJ (2003). Effect of baclofen on alcohol and sucrose self-administration in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27: 900–908.
Augier E, Dulman RS, Rauffenbart C, Augier G, Cross AJ, Heilig M (2016). The mGluR2 positive allosteric modulator, AZD8529 and cue-induced relapse to alcohol seeking in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 41: 2932–2940.
Augier E, Dulman RS, Singley E, Heilig M (2017). A method for evaluating the reinforcing properties of ethanol in rats without water deprivation, saccharin fading or extended access training. J Vis Exp 119: e53305.
Augier E, Flanigan M, Dulman RS, Pincus A, Schank JR, Rice KC et al (2014). Wistar rats acquire and maintain self-administration of 20% ethanol without water deprivation, saccharin/sucrose fading, or extended access training. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231: 4561–4568.
Avena NM, Bocarsly ME, Murray S, Gold MS (2014). Effects of baclofen and naltrexone, alone and in combination, on the consumption of palatable food in male rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 22: 460–467..
Barbier E, Johnstone AL, Khomtchouk BB, Tapocik JD, Pitcairn C, Rehman F et al (2016). Dependence-induced increase of alcohol self-administration and compulsive drinking mediated by the histone methyltransferase PRDM2. Mol Psychiatry (doi:10.1038/mp.2016.131; e-pub ahead of print).
Besheer J, Lepoutre V, Hodge CW (2004). GABA(B) receptor agonists reduce operant ethanol self-administration and enhance ethanol sedation in C57BL/6 J mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174: 358–366.
Bormann J (2000). The 'ABC' of GABA receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 21: 16–19.
Bossert JM, Stern AL, Theberge FR, Marchant NJ, Wang HL, Morales M et al (2012). Role of projections from ventral medial prefrontal cortex to nucleus accumbens shell in context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. J Neurosci 32: 4982–4991.
Brebner K, Childress AR, Roberts DC (2002). A potential role for GABA(B) agonists in the treatment of psychostimulant addiction. Alcohol Alcohol 37: 478–484.
Colombo G, Serra S, Brunetti G, Atzori G, Pani M, Vacca G et al (2002). The GABA(B) receptor agonists baclofen and CGP 44532 prevent acquisition of alcohol drinking behaviour in alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Alcohol 37: 499–503.
Colombo G, Vacca G, Serra S, Brunetti G, Carai MA, Gessa GL (2003). Baclofen suppresses motivation to consume alcohol in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 167: 221–224.
Conn PJ, Christopoulos A, Lindsley CW (2009). Allosteric modulators of GPCRs: a novel approach for the treatment of CNS disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8: 41–54.
Cott J, Carlsson A, Engel J, Lindqvist M (1976). Suppression of ethanol-induced locomotor stimulation by GABA-like drugs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 295: 203–209.
Cousins MS, Roberts DC, de Wit H (2002). GABA(B) receptor agonists for the treatment of drug addiction: a review of recent findings. Drug Alcohol Depend 65: 209–220.
Daoust M, Saligaut C, Lhuintre JP, Moore N, Flipo JL, Boismare F (1987). GABA transmission, but not benzodiazepine receptor stimulation, modulates ethanol intake by rats. Alcohol 4: 469–472.
Dayas CV, Liu X, Simms JA, Weiss F (2007). Distinct patterns of neural activation associated with ethanol seeking: effects of naltrexone. Biol Psychiatry 61: 979–989.
Dutar P, Nicoll RA (1988). A physiological role for GABAB receptors in the central nervous system. Nature 332: 156–158.
Epstein DH, Preston KL, Stewart J, Shaham Y (2006). Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 189: 1–16.
Fadda P, Scherma M, Fresu A, Collu M, Fratta W (2003). Baclofen antagonizes nicotine-, cocaine-, and morphine-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of rat. Synapse 50: 1–6.
Figlewicz DP, Bennett-Jay JL, Kittleson S, Sipols AJ, Zavosh A (2011). Sucrose self-administration and CNS activation in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300: R876–884..
Funk D, Li Z, Le AD (2006). Effects of environmental and pharmacological stressors on c-fos and corticotropin-releasing factor mRNA in rat brain: Relationship to the reinstatement of alcohol seeking. Neuroscience 138: 235–243.
Garbutt JC, Kampov-Polevoy AB, Gallop R, Kalka-Juhl L, Flannery BA (2010). Efficacy and safety of baclofen for alcohol dependence: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34: 1849–1857.
Heilig M, Egli M (2006). Pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence: target symptoms and target mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 111: 855–876.
Heilig M, Egli M, Crabbe JC, Becker HC (2010). Acute withdrawal, protracted abstinence and negative affect in alcoholism: are they linked? Addict Biol 15: 169–184.
Heilig M, Sommer WH, Spanagel R (2016). The need for treatment responsive translational biomarkers in alcoholism research. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 28: 151–171.
Hodos W (1961). Progressive ratio as a measure of reward strength. Science 134: 943–944.
Hwa LS, Kalinichev M, Haddouk H, Poli S, Miczek KA (2014). Reduction of excessive alcohol drinking by a novel GABAB receptor positive allosteric modulator ADX71441 in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231: 333–343.
Janak PH, Michael Gill T (2003). Comparison of the effects of allopregnanolone with direct GABAergic agonists on ethanol self-administration with and without concurrently available sucrose. Alcohol 30: 1–7.
Kalinichev M, Palea S, Haddouk H, Royer-Urios I, Guilloteau V, Lluel P et al (2014). ADX71441, a novel, potent and selective positive allosteric modulator of the GABA(B) receptor, shows efficacy in rodent models of overactive bladder. Br J Pharmacol 171: 995–1006.
Kalivas PW, Volkow ND (2005). The neural basis of addiction: a pathology of motivation and choice. Am J Psychiatry 162: 1403–1413.
Leggio L, Garbutt JC, Addolorato G (2010). Effectiveness and safety of baclofen in the treatment of alcohol dependent patients. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 9: 33–44.
Liang JH, Chen F, Krstew E, Cowen MS, Carroll FY, Crawford D et al (2006). The GABA(B) receptor allosteric modulator CGP7930, like baclofen, reduces operant self-administration of ethanol in alcohol-preferring rats. Neuropharmacology 50: 632–639.
Ling W, Shoptaw S, Majewska D (1998). Baclofen as a cocaine anti-craving medication: a preliminary clinical study. Neuropsychopharmacology 18: 403–404.
Maccioni P, Serra S, Vacca G, Orru A, Pes D, Agabio R et al (2005). Baclofen-induced reduction of alcohol reinforcement in alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol 36: 161–168.
Macey DJ, Schulteis G, Heinrichs SC, Koob GF (1996). Time-dependent quantifiable withdrawal from ethanol in the rat: effect of method of dependence induction. Alcohol 13: 163–170.
May LT, Christopoulos A (2003). Allosteric modulators of G-protein-coupled receptors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 3: 551–556.
Meinhardt MW, Hansson AC, Perreau-Lenz S, Bauder-Wenz C, Stahlin O, Heilig M et al (2013). Rescue of infralimbic mGluR2 deficit restores control over drug-seeking behavior in alcohol dependence. J Neurosci 33: 2794–2806.
Meinhardt MW, Sommer WH (2015). Postdependent state in rats as a model for medication development in alcoholism. Addict Biol 20: 1–21.
Perdona E, Costantini VJ, Tessari M, Martinelli P, Carignani C, Valerio E et al (2011). In vitro and in vivo characterization of the novel GABAB receptor positive allosteric modulator, 2-{1-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl]-2-piperidinyl}eth anol (CMPPE). Neuropharmacology 61: 957–966.
Pin JP, Prezeau L (2007). Allosteric modulators of GABA(B) receptors: mechanism of action and therapeutic perspective. Curr Neuropharmacol 5: 195–201.
Rimondini R, Arlinde C, Sommer W, Heilig M (2002). Long-lasting increase in voluntary ethanol consumption and transcriptional regulation in the rat brain after intermittent exposure to alcohol. FASEB J 16: 27–35.
Roberts DC, Andrews MM (1997). Baclofen suppression of cocaine self-administration: demonstration using a discrete trials procedure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 131: 271–277.
Roberts DC, Andrews MM, Vickers GJ (1996). Baclofen attenuates the reinforcing effects of cocaine in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 15: 417–423.
Rogers J, Wiener SG, Bloom FE (1979). Long-term ethanol administration methods for rats: advantages of inhalation over intubation or liquid diets. Behav Neural Biol 27: 466–486.
Schank JR, Nelson BS, Damadzic R, Tapocik JD, Yao M, King CE et al (2015). Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonism attenuates neuronal activity triggered by stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking. Neuropharmacology 99: 106–114.
Sesack SR, Deutch AY, Roth RH, Bunney BS (1989). Topographical organization of the efferent projections of the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: an anterograde tract-tracing study with Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin. J Comp Neurol 290: 213–242.
Shirayama Y, Chaki S (2006). Neurochemistry of the nucleus accumbens and its relevance to depression and antidepressant action in rodents. Curr Neuropharmacol 4: 277–291.
Sivilotti L, Nistri A (1991). GABA receptor mechanisms in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 36: 35–92.
Urwyler S (2011). Allosteric modulation of family C G-protein-coupled receptors: from molecular insights to therapeutic perspectives. Pharmacol Rev 63: 59–126.
Walker BM, Koob GF (2007). The gamma-aminobutyric acid-B receptor agonist baclofen attenuates responding for ethanol in ethanol-dependent rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31: 11–18.
Zhao Y, Dayas CV, Aujla H, Baptista MA, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2006). Activation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors attenuates both stress and cue-induced ethanol-seeking and modulates c-fos expression in the hippocampus and amygdala. J Neurosci 26: 9967–9974.
Acknowledgements
We thank Gaëlle Augier for helpful comments on a previous draft of the manuscript and help with editing. We thank Addex Therapeutics for kindly providing ADX71441.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Augier, E., Dulman, R., Damadzic, R. et al. The GABAB Positive Allosteric Modulator ADX71441 Attenuates Alcohol Self-Administration and Relapse to Alcohol Seeking in Rats. Neuropsychopharmacol 42, 1789–1799 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.53
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.53
This article is cited by
-
Activation of GABAB receptors in central amygdala attenuates activity of PKCδ + neurons and suppresses punishment-resistant alcohol self-administration in rats
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Novel Agents for the Pharmacological Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorder
Drugs (2022)
-
Reducing effect of the novel positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, COR659, on binge-like alcohol drinking in male mice and rats
Psychopharmacology (2022)
-
Reduced motor cortex GABABR function following chronic alcohol exposure
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
A deeper insight into how GABA-B receptor agonism via baclofen may affect alcohol seeking and consumption: lessons learned from a human laboratory investigation
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)