Abstract
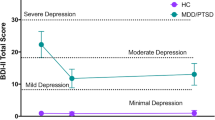
The antidepressant effects of ketamine are thought to depend on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) genotype and dose. The purpose of this study was to characterize the dose-related antidepressant effects of ketamine in patients with treatment-resistant depression drawn from a Chinese population predominately possessing lower activity BDNF genotypes (Val/Met, Met/Met). We conducted a double-blind, randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial of a single ketamine infusion (saline, 0.2 mg/kg, 0.5 mg/kg). Patients (N=71; BDNF genotype: Val/Val (N=12, 17%), Val/Met (N=40, 56.3%), and Met/Met (N=19, 26.8%)) received mood ratings before infusion, after infusion, and for the subsequent 14 days. Plasma ketamine levels and BDNF genotypes were assessed. This study found a significant dose-related ketamine effect on scores on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD). The responder analysis (>50% reduction from baseline HAMD on at least 2 days between days 2 and 5) also revealed a significant dose-related effect (saline: 12.5%, 0.2 mg/kg: 39.1%; 0.5 mg/kg: 45.8%). This is the first report to our knowledge to demonstrate the dose-related efficacy of R/S-ketamine for treatment-resistant depression and the first to characterize ketamine effects in a genotyped Chinese population in which most (83%) patients possessed at least one copy of the lower functioning Met allele of the BDNF gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aan Het Rot M, Zarate CA Jr, Charney DS, Mathew SJ (2012). Ketamine for depression: where do we go from here? Biol Psychiatry 72: 537–547.
Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS et al (2000). Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47: 351–354.
Chekroud AM, Gueorguieva R, Krumholz HM, Trivedi MH, Krystal JH, McCarthy G (2017). Reevaluating the efficacy and predictability of antidepressant treatments: a symptom clustering approach. JAMA Psychiatry 74: 370–378.
Chen ZY, Patel PD, Sant G, Meng CX, Teng KK, Hempstead BL et al (2004). Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Met66) alters the intracellular trafficking and activity-dependent secretion of wild-type BDNF in neurosecretory cells and cortical neurons. J Neurosci 24: 4401–4411.
Choi MJ, Kang RH, Lim SW, Oh KS, Lee MS (2006). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene polymorphism (Val66Met) and citalopram response in major depressive disorder. Brain Res 1118: 176–182.
Feinberg I, Campbell IG (1993). Ketamine administration during waking increases delta EEG intensity in rat sleep. Neuropsychopharmacology 9: 41–48.
Feinberg I, Campbell IG (1995). Stimulation of NREM delta EEG by ketamine administration during waking: demonstration of dose dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 12: 89–90.
Gaynes BN, Warden D, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Fava M, Rush AJ (2009). What did STAR*D teach us? Results from a large-scale, practical, clinical trial for patients with depression. Psychiatr Serv 60: 1439–1445.
Hamilton M (1960). A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23: 56–62.
Hedlund JL, Vieweg BW (1980). The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS): a comprehensive review. J Operational Psychiatry 11: 48–64.
Hu YD, Xiang YT, Fang JX, Zu S, Sha S, Shi H et al (2016). Single i.v. ketamine augmentation of newly initiated escitalopram for major depression: results from a randomized, placebo-controlled 4-week study. Psychol Med 46: 623–635.
Hustveit O, Maurset A, Oye I (1995). Interaction of the chiral forms of ketamine with opioid, phencyclidine, sigma and muscarinic receptors. Pharmacol Toxicol 77: 355–359.
Itoh K, Hashimoto K, Kumakiri C, Shimizu E, Iyo M (2004). Association between brain-derived neurotrophic factor 196 G/A polymorphism and personality traits in healthy subjects. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 124B: 61–63.
Kirsch I, Deacon BJ, Huedo-Medina TB, Scoboria A, Moore TJ, Johnson BT (2008). Initial severity and antidepressant benefits: a meta-analysis of data submitted to the Food and Drug Administration. PLoS Med 5: e45.
Kishimoto T, Chawla JM, Hagi K, Zarate CA, Kane JM, Bauer M et al (2016). Single-dose infusion ketamine and non-ketamine N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists for unipolar and bipolar depression: a meta-analysis of efficacy, safety and time trajectories. Psychol Med 46: 1459–1472.
Krystal JH, Karper LP, Seibyl JP, Freeman GK, Delaney R, Bremner JD et al (1994). Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, ketamine, in humans. Psychotomimetic, perceptual, cognitive, and neuroendocrine responses. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51: 199–214.
Krystal JH, Perry EB Jr, Gueorguieva R, Belger A, Madonick SH, Abi-Dargham A et al (2005). Comparative and interactive human psychopharmacologic effects of ketamine and amphetamine: implications for glutamatergic and dopaminergic model psychoses and cognitive function. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62: 985–994.
Krystal JH, Sanacora G, Duman RS (2013). Rapid-acting glutamatergic antidepressants: the path to ketamine and beyond. Biol Psychiatry 73: 1133–1141.
Laje G, Lally N, Mathews D, Brutsche N, Chemerinski A, Akula N et al (2012). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism and antidepressant efficacy of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 72: e27–e28.
Li CT, Chen MH, Lin WC, Hong CJ, Yang BH, Liu RS et al (2016). The effects of low-dose ketamine on the prefrontal cortex and amygdala in treatment-resistant depression: A randomized controlled study. Hum Brain Mapp 37: 1080–1090.
Liu RJ, Lee FS, Li XY, Bambico F, Duman RS, Aghajanian GK (2012). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met allele impairs basal and ketamine-stimulated synaptogenesis in prefrontalcortex. Biol Psychiatry 71: 996–1005.
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962). The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep 10: 799–812.
Pennybaker SJ, Niciu MJ, Luckenbaugh DA, Zarate CA (2017). Symptomatology and predictors of antidepressant efficacy in extended responders to a single ketamine infusion. J Affect Disord 208: 560–566.
Rush AJ, Fava M, Wisniewski SR, Lavori PW, Trivedi MH, Sackeim HA et al (2004). Sequenced treatment alternatives to relieve depression (STAR*D): rationale and design. Control Clin Trials 25: 119–142.
Saligan LN, Luckenbaugh DA, Slonena EE, Machado-Vieira R, Zarate CA Jr (2016). An assessment of the anti-fatigue effects of ketamine from a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study in bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 194: 115–119.
Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E et al (1998). The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychiatry 59 (Suppl 20): 22–33 quiz 34-57.
Simon GE, Revicki D, VonKorff M (1993). Telephone assessment of depression severity. J Psychiatr Res 27: 247–252.
Singh JB, Fedgchin M, Daly E, Xi L, Melman C, De Bruecker G et al (2015). Intravenous esketamine in adult treatment-resistant depression: a double-blind, double-randomization, placebo-controlled study. Biol Psychiatry 80: 424–431.
Vande Voort JL, Ballard ED, Luckenbaugh DA, Bernert RA, Richards EM, Niciu MJ et al (2016). Antisuicidal response following ketamine infusion is associated with decreased nighttime wakefulness in major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry (doi:10.4088/JCP.15m10440; e-pub ahead of print).
Xu G, Lin K, Rao D, Dang Y, Ouyang H, Mai G et al (2012). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene polymorphism (Val66Met) and the early response to antidepressant in Chinese Han population. Psychiatr Genet 22: 214–215.
Xu Y, Hackett M, Carter G, Loo C, Galvez V, Glozier N et al (2016). Effects of low-dose and very low-dose ketamine among patients with major depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol (doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyv124; e-pub ahead of print).
Zanos P, Moaddel R, Morris PJ, Georgiou P, Fischell J, Elmer GI et al (2016). NMDAR inhibition-independent antidepressant actions of ketamine metabolites. Nature 533: 481–486.
Zarate CA Jr, Brutsche N, Laje G, Luckenbaugh DA, Venkata SL, Ramamoorthy A et al (2012). Relationship of ketamine's plasma metabolites with response, diagnosis, and side effects in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 72: 331–338.
Zhao X, Venkata SL, Moaddel R, Luckenbaugh DA, Brutsche NE, Ibrahim L et al (2012). Simultaneous population pharmacokinetic modelling of ketamine and three major metabolites in patients with treatment-resistant bipolar depression. Br J Clin Pharmacol 74: 304–314.
Acknowledgements
We thank Jennifer Vessicchio for her assistance with the preparation of this manuscript. We express our gratitude to all patients who kindly participated in this study. We thank all research assistants, physicians, pharmacists, and nursing staffs at D020 Unit of Taipei Veterans General Hospital for their assistance during the study process, without whom this work could not have been possible. We also very much appreciate Dr Guang Cheng for providing excellent opinions on our work. The study was sponsored by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (101-2314-B-010-060, 102-2314-B-010-060) and the Kun-Po Soo Medical Foundation. The participation of Dr Krystal was supported by the US Department of Veterans Affairs via its support for the VA National Center for PTSD, the US National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (P50AA12870, M01RR00125), and the US National Center for Advancing Translational Science (UL1 RR024139). None of the aforementioned funding organizations had any role in the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation of result, writing of the report, and the ultimate decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, TP., Chen, MH., Li, CT. et al. Dose-Related Effects of Adjunctive Ketamine in Taiwanese Patients with Treatment-Resistant Depression. Neuropsychopharmacol. 42, 2482–2492 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.94
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.94
This article is cited by
-
Adjunctive ketamine vs. buprenorphine in co-occurring major depressive disorder and opioid use disorder: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial assessing anxiety symptom severity and craving intensity
Trials (2025)
-
Chronic, combinatorial targeting of NMDARs and 5-HT4Rs exerts extended behavioral effects against stress-induced perseverative behavior and hyponeophagia
Neuropsychopharmacology (2025)
-
Thalamocortical functional connectivity and rapid antidepressant and antisuicidal effects of low-dose ketamine infusion among patients with treatment-resistant depression
Molecular Psychiatry (2025)
-
Ketamine and its enantiomers for depression: a bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2023
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2025)
-
Esketamine in depression: putative biomarkers from clinical research
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2025)