Abstract
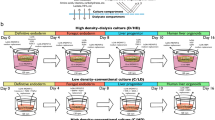
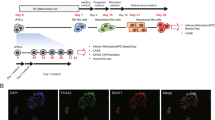
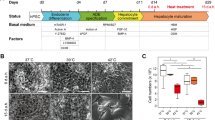
This protocol describes a co-culture system for the in vitro differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Differentiation involves four steps: (i) formation of embryoid bodies (EB), (ii) induction of definitive endoderm from 2-d-old EBs, (iii) induction of hepatic progenitor cells and (iv) maturation into hepatocyte-like cells. Differentiation is completed by 16 d of culture. EBs are formed, and cells can be induced to differentiate into definitive endoderm by culture in Activin A and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2). Hepatic differentiation and maturation of cells is accomplished by withdrawal of Activin A and FGF-2 and by exposure to liver nonparenchymal cell-derived growth factors, a deleted variant of hepatocyte growth factor (dHGF) and dexamethasone. Approximately 70% of differentiated embryonic stem (ES) cells express albumin and can be recovered by albumin promoter-based cell sorting. The sorted cells produce albumin in culture and metabolize ammonia, lidocaine and diazepam at approximately two-thirds the rate of primary mouse hepatocytes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamamoto, H. et al. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells into hepatocytes: biological functions and therapeutic application. Hepatology 37, 983–993 (2003).
Teratani, T. et al. Direct hepatic fate specification from mouse embryonic stem cells. Hepatology 41, 836–846 (2005).
Yamada, T. et al. In vitro differentiation of embryonic stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells identified by cellular uptake of indocyanine green. Stem Cells 20, 146–154 (2002).
Chinzei, R. et al. Embryoid-body cells derived from a mouse embryonic stem cell line show differentiation into functional hepatocytes. Hepatology 36, 22–29 (2002).
Kumashiro, Y. et al. Enrichment of hepatocytes differentiated from mouse embryonic stem cells as a transplantable source. Transplantation 79, 550–557 (2005).
Lavon, N., Yanuka, O. & Benvenisty, N. Differentiation and isolation of hepatic-like cells from human embryonic stem cells. Differentiation 72, 230–238 (2004).
Rambhatla, L., Chiu, C.P., Kundu, P., Peng, Y. & Carpenter, M.K. Generation of hepatocyte-like cells from human embryonic stem cells. Cell Transplant. 12, 1–11 (2003).
Kubo, A. et al. Development of definitive endoderm from embryonic stem cells in culture. Development 131, 1651–1662 (2004).
D'Amour, K.A. et al. Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nat. Biotechnol. 23, 1534–1541 (2005).
Yasunaga, M. et al. Induction and monitoring of definitive and visceral endoderm differentiation of mouse ES cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 23, 1542–1550 (2005).
Jang, Y.Y., Collector, M.I., Baylin, S.B., Diehl, A.M. & Sharkis, S.J. Hematopoietic stem cells convert into liver cells within days without fusion. Nat. Cell Biol. 6, 532–539 (2004).
Poll, D.V. et al. Elevated hepatocyte-specific functions in fetal rat hepatocytes co-cultured with adult rat hepatocytes. Tissue Eng. 12, 2965–2973 (2006).
Kang, Y.H., Berthiaume, F., Nath, B.D. & Yarmush, M.L. Growth factors and nonparenchymal cell conditioned media induce mitogenic responses in stable long-term adult rat hepatocyte cultures. Exp. Cell Res. 293, 239–247 (2004).
Matsumura, T. et al. Establishment of an immortalized human-liver endothelial cell line with SV40T and hTERT. Transplantation 77, 1357–1365 (2004).
Watanabe, T. et al. Establishment of immortalized human hepatic stellate scavenger cells to develop bioartificial livers. Transplantation 75, 1873–1880 (2003).
Maruyama, M. et al. Establishment of a highly differentiated immortalized human cholangiocyte cell line with SV40T and hTERT. Transplantation 77, 446–451 (2004).
Soto-Gutierrez, A. et al. Reversal of mouse hepatic failure using an implanted liver-assist device containing ES cell-derived hepatocytes. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 1412–1419 (2006).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to N.K. and NIH grant DK48794 to I.J.F.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Map of pALB-GFP (11231 bps, Amp+) (PDF 5910 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
The sequence of pALB-GFP (11231 bp) (PDF 63 kb)
Supplementary Note
Material Transfer Agreement (PDF 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soto-Gutiérrez, A., Navarro-Álvarez, N., Zhao, D. et al. Differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells to hepatocyte-like cells by co-culture with human liver nonparenchymal cell lines. Nat Protoc 2, 347–356 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.18
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.18
This article is cited by
-
Three Dimensional Bioprinting for Hepatic Tissue Engineering: From In Vitro Models to Clinical Applications
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2024)
-
Different approaches for transformation of mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2020)
-
HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis: the role of signalling pathways and innovative ex vivo research models
BMC Cancer (2019)
-
A Pathway to Personalizing Therapy for Metastases Using Liver-on-a-Chip Platforms
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2017)
-
An investigation into the stability of commercial versus MG63-derived hepatocyte growth factor under flow cultivation conditions
Biotechnology Letters (2015)