Abstract
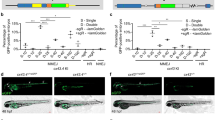
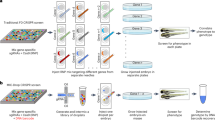
Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) are widely used in studies of vertebrate gene regulation and function because they often closely recapitulate the expression patterns of endogenous genes. Here we report a step-by-step protocol for efficient BAC transgenesis in zebrafish using the medaka Tol2 transposon. Using recombineering in Escherichia coli, we introduce the iTol2 cassette in the BAC plasmid backbone, which contains the inverted minimal cis-sequences required for Tol2 transposition, and a reporter gene to replace a target locus in the BAC. Microinjection of the Tol2-BAC and a codon-optimized transposase mRNA into fertilized eggs results in clean integrations in the genome and transmission to the germline at a rate of ∼15%. A single person can prepare a dozen constructs within 3 weeks, and obtain transgenic fish within approximately 3–4 months. Our protocol drastically reduces the labor involved in BAC transgenesis and will greatly facilitate biological and biomedical studies in model vertebrates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giraldo, P. & Montoliu, L. Size matters: use of YACs, BACs and PACs in transgenic animals. Transgenic. Res. 10, 83–103 (2001).
Nagy, A., Gertsenstein, M., Vintersten, K. & Behringer, R. Manipulating the Mouse Embryo: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd edn. (Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, USA, 2001).
Vintersten, K., Testa, G., Naumann, R., Anastassiadis, K. & Stewart, A.F. Bacterial artificial chromosome transgenesis through pronuclear injection of fertilized mouse oocytes. Methods Mol. Biol. 415, 83–100 (2008).
Copeland, N.G., Jenkins, N.A. & Court, D.L. Recombineering: a powerful new tool for mouse functional genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 769–779 (2001).
Heintz, N. BAC to the future: the use of bac transgenic mice for neuroscience research. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 861–870 (2001).
Jessen, J.R., Willett, C.E. & Lin, S. Artificial chromosome transgenesis reveals long-distance negative regulation of rag1 in zebrafish. Nat. Genet. 23, 15–16 (1999).
Yang, Z. et al. Modified bacterial artificial chromosomes for zebrafish transgenesis. Methods 39, 183–188 (2006).
Higashijima, S.-I. Transgenic zebrafish expressing fluorescent proteins in central nervous system neurons. Dev. Growth Diff. 50, 407–413 (2008).
Lieschke, G.J. & Currie, P.D. Animal models of human disease: zebrafish swim into view. Nat. Rev. Genet. 8, 353–367 (2007).
Asakawa, K. et al. Genetic dissection of neural circuits by Tol2 transposon-mediated Gal4 gene and enhancer trapping in zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 1255–1260 (2008).
Scott, E. et al. Targeting neural circuitry in zebrafish using Gal4 enhancer trapping. Nat. Methods 4, 323–326 (2007).
Emelyanov, A. & Parinov, S. Mifepristone-inducible LexPR system to drive and control gene expression in transgenic zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 320, 113–121 (2008).
Langenau, D.M. et al. Cre/lox-regulated zebrafish model with conditional myc-induced T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 6068–6073 (2005).
Knopf, F. et al. Dually inducible TetON systems for tissue-specific conditional gene expression in zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 19933–19938 (2010).
Chandler, K.J. et al. Relevance of BAC transgene copy number in mice: transgene copy number variation across multiple transgenic lines and correlations with transgene integrity and expression. Mamm. Genome 18, 693–708 (2007).
Garrick, D., Fiering, S., Martin, D.I. & Whitelaw, E. Repeat-induced gene silencing in mammals. Nat. Genet. 18, 56–59 (1998).
Dorer, D.R. Do transgene arrays form heterochromatin in vertebrates? Transgenic. Res. 6, 3–10 (1997).
Stuart, G.W., McMurray, J.V. & Westerfield, M. Replication, integration and stable germ-line transmission of foreign sequences injected into early zebrafish embryos. Development 103, 403–412 (1988).
Amsterdam, A., Lin, S. & Hopkins, N. The Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein can be used as a reporter in live zebrafish embryos. Dev. Biol. 171, 123–129 (1995).
Long, Q. et al. GATA-1 expression pattern can be recapitulated in living transgenic zebrafish using GFP reporter gene. Development 124, 4105–4111 (1997).
Higashijima, S., Okamoto, H., Ueno, N., Hotta, Y. & Eguchi, G. High-frequency generation of transgenic zebrafish which reliably express GFP in whole muscles or the whole body by using promoters of zebrafish origin. Dev. Biol. 192, 289–299 (1997).
Rembold, M., Lahiri, K., Foulkes, N.S. & Wittbrodt, J. Transgenesis in fish: efficient selection of transgenic fish by co-injection with a fluorescent reporter construct. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1133–1139 (2006).
Lin, S. et al. Integration and germ-line transmission of a pseudotyped retroviral vector in zebrafish. Science 265, 666–669 (1994).
Gaiano, N., Allende, M., Amsterdam, A., Kawakami, K. & Hopkins, N. Highly efficient germ-line transmission of proviral insertions in zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 7777–7782 (1996).
Ellingsen, S. et al. Large-scale enhancer detection in the zebrafish genome. Development 132, 3799–811 (2005).
Wang, D. et al. Efficient genome-wide mutagenesis of zebrafish genes by retroviral insertions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 12428–12433 (2007).
Thomas, C.E., Ehrhardt, A. & Kay, M.A. Progress and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 4, 346–358 (2003).
Fadool, J.M., Hartl, D.L. & Dowling, J.E. Transposition of the mariner element from Drosophila mauritiana in zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 5182–516 (1998).
Kawakami, K. et al. A transposon-mediated gene trap approach identifies developmentally regulated genes in zebrafish. Dev. Cell 7, 133–144 (2004).
Davidson, A.E. et al. Efficient gene delivery and gene expression in zebrafish using the Sleeping Beauty transposon. Dev. Biol. 263, 191–202 (2003).
Kawakami, K. Tol2: a versatile gene transfer vector in vertebrates. Genome Biol. 8 (Suppl 1): S7 (2007).
Korzh, V. Transposons as tools for enhancer trap screens in vertebrates. Genome Biol. 8 (Suppl 1): S8 (2007).
Suster, M.L., Sumiyama, K. & Kawakami, K. Transposon-mediated BAC transgenesis in zebrafish and mice. BMC Genomics 10, 477 (2009).
Kawakami, K. & Shima, A. Identification of the Tol2 transposase of the medaka fish Oryzias latipes that catalyzes excision of a nonautonomous Tol2 element in zebrafish Danio rerio. Gene 240, 239–244 (1999).
Balciunas, D. et al. Harnessing a high cargo-capacity transposon for genetic applications in vertebrates. PLoS Genet. 2, e169 (2006).
Urasaki, A., Morvan, G. & Kawakami, K. Functional dissection of the Tol2 transposable element identified the minimal cis-sequence and a highly repetitive sequence in the subterminal region essential for transposition. Genetics 174, 639–649 (2006).
Suster, M.L. et al. A novel conserved evx1 enhancer links spinal interneuron morphology and cis-regulation from fish to mammals. Dev. Biol. 325, 422–433 (2009).
Sharan, K., Thomason, L.C., Kuznetsov, S.G. & Court, D.L. Recombineering: a homologous recombination-based method of genetic engineering. Nat. Protoc. 4, 206–223 (2009).
Zhang, Z.D. et al. Statistical analysis of the genomic distribution and correlation of regulatory elements in the ENCODE regions. Genome Res. 17, 787–797 (2007).
Murphy, K.C. Use of bacteriophage l recombination functions to promote gene replacement in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 180, 2063–2071 (1998).
Murphy, K.C., Campellone, K.G. & Poteete, A.R. PCR-mediated gene replacement in Escherichia coli. Gene 246, 321–330 (2000).
Zhang, Y., Buchholz, F., Muyrers, J.P. & Stewart, A.F. A new logic for DNA engineering using recombination in Escherichia coli. Nat. Genet. 20, 123–128 (1998).
Zhang, Y., Muyrers, J.P., Testa, G. & Stewart, A.F. DNA cloning by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 1314–1317 (2000).
Yu, D. et al. An efficient recombination system for chromosome engineering in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 5978–5983 (2000).
Warming, S., Costantino, N., Court, D.L., Jenkins, N.A. & Copeland, N.G. Simple and highly efficient BAC recombineering using galK selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, e36 (2005).
Cassuto, E. & Radding, C.M. Mechanism for the action of l exonuclease in genetic recombination. Nat. New Biol. 229, 13–16 (1971).
Little, J.W. An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage l. II. Nature of the enzymatic reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 242, 679–686 (1967).
Carter, D.M. & Radding, C.M. The role of exonuclease and b protein of phage l in genetic recombination. II. Substrate specificity and the mode of action of lambda exonuclease. J. Biol. Chem. 246, 2502–2512 (1971).
Cassuto, E., Lash, T., Sriprakash, K.S. & Radding, C.M. Role of exonuclease and b protein of phage l in genetic recombination. V. Recombination of l DNA in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68, 1639–1643 (1971).
Sadowski, I., Ma, J., Triezenberg, S. & Ptashne, M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature 335, 563–564 (1988).
Köster, R.W. & Fraser, S.E. Tracing transgene expression in living zebrafish embryos. Dev. Biol. 233, 329–346 (2001).
Sternberg, N. & Hamilton, D. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination: I. Recombination between loxP sites. J. Mol. Biol. 150, 467–486 (1981).
Suster, M.L., Kikuta, H., Urasaki, A., Asakawa, K. & Kawakami, K. Transgenesis in zebrafish with the tol2 transposon system. Methods Mol. Biol. 561, 41–63 (2009).
Baier, H. & Scott, E.K. Genetic and optical targeting of neural circuits and behavior—zebrafish in the spotlight. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 19, 553–560.
Friedenreich, H. & Schartl, M. Transient expression directed by homologous and heterologous promoter and enhancer sequences in fish cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 3299–3305 (1990).
Datta, S., Costantino, N. & Court, D.L. A set of recombineering plasmids for Gram-negative bacteria. Gene 379, 109–115 (2006).
Lister, J.A., Robertson, C.P., Lepage, T., Johnson, S.L. & Raible, D.W. nacre encodes a zebrafish microphthalmia-related protein that regulates neural-crest-derived pigment cell fate. Development 126, 3757–3767 (1999).
Acknowledgements
For excellent fish care, we thank T. Kronstad, F. Silva and J. Xu at the Sars International Centre, and A. Ito, M. Suzuki, M. Mizushina, N. Mouri and T. Uematsu at the National Institute of Genetics. We thank A. Urasaki for initial characterization of zT2TP and K. Sumiyama for the pBSK-GFP-pA-FRT-kan-FRT plasmid. This work was supported by core funding from the Sars International Centre, a fellowship from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Takeda Science Foundation to M.L.S., and grants from the National BioResource Project of Japan and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technnology of Japan to K.K.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
M.L.S. wrote the manuscript, directed the work at the Sars Centre and generated data and reagents. A.S. contributed reagents and optimized extensively the protocol. G.A. contributed data. K.K directed the work and wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Data
Full sequence and graphic map of plasmids used. (PDF 550 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
(TIFF 28336 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suster, M., Abe, G., Schouw, A. et al. Transposon-mediated BAC transgenesis in zebrafish. Nat Protoc 6, 1998–2021 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.416
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.416
This article is cited by
-
Alcam-a and Pdgfr-α are essential for the development of sclerotome-derived stromal cells that support hematopoiesis
Nature Communications (2023)
-
A53T mutant α-synuclein fibrils formed in macrophage are spread to neurons
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
Bacterial Artificial Chromosome-based Protein Expression Platform Using the Tol2 Transposon System
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering (2022)
-
Rapid and Efficient BAC Recombineering: Gain & Loss Screening System
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering (2021)
-
Zebrafish Larvae Carrying a Splice Variant Mutation in cacna1d: A New Model for Schizophrenia-Like Behaviours?
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)