Key Points
-
The Gram-negative outer membrane protein (OMP) family includes proteins that are associated with basic physiological functions, virulence and multidrug resistance, and therefore plays a fundamental part in the maintenance of cellular viability.
-
Understanding how these proteins are targeted and folded into this membrane is crucial, as it could offer important medical benefits. Compounds that inhibit key stages of this process would block key stages of OMP biogenesis, thereby inhibiting essential physiological, pathogenic and drug resistance functions, and could prove useful in combating diverse pathogens, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria meningitidis and Salmonella enterica.
-
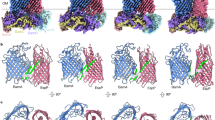
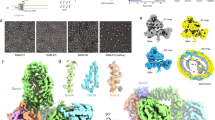
OMP biogenesis in Gram-negative bacteria has, until recently, remained a largely unknown mechanism. However, over the past 3 years, a complex of proteins has been discovered that is known as the β-barrel assembly machinery (BAM) and is responsible for folding and inserting OMPs into the membrane.
-
Recent advances in our understanding of the molecular basis of OMP biogenesis in Gram-negative bacteria are discussed.
-
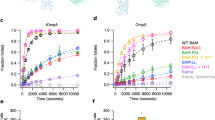
Emphasis is placed on analysis of the recently discovered component structures and accessory interactions, in particular with the periplasmic chaperones DegP, Skp and SurA, which are known to interact with OMPs.
-
The mechanisms that the BAM complex might use in the folding and insertion of OMPs into the membrane are also discussed.
Abstract
The folding of transmembrane proteins into the outer membrane presents formidable challenges to Gram-negative bacteria. These proteins must migrate from the cytoplasm, through the inner membrane and into the periplasm, before being recognized by the β-barrel assembly machinery, which mediates efficient insertion of folded β-barrels into the outer membrane. Recent discoveries of component structures and accessory interactions of this complex are yielding insights into how cells fold membrane proteins. Here, we discuss how these structures illuminate the mechanisms responsible for the biogenesis of outer membrane proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bos, M. P., Robert, V. & Tommassen, J. Biogenesis of the Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 61, 191–214 (2007).
Breyton, C., Haase, W., Rapoport, T. A., Kuhlbrandt, W. & Collinson, I. Three-dimensional structure of the bacterial protein-translocation complex SecYEG. Nature 418, 662–665 (2002).
Van den Berg, B. et al. X-ray structure of a protein-conducting channel. Nature 427, 36–44 (2004).
Driessen, A. J. & Nouwen, N. Protein translocation across the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 643–667 (2008).
Rapoport, T. A. Protein translocation across the eukaryotic endoplasmic reticulum and bacterial plasma membranes. Nature 450, 663–669 (2007).
Qi, H. Y., Hyndman, J. B. & Bernstein, H. D. DnaK promotes the selective export of outer membrane protein precursors in SecA-deficient Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 51077–51083 (2002).
Papanikou, E., Karamanou, S. & Economou, A. Bacterial protein secretion through the translocase nanomachine. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 5, 839–851 (2007).
Sklar, J. G., Wu, T., Kahne, D. & Silhavy, T. J. Defining the roles of the periplasmic chaperones SurA, Skp, and DegP in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 21, 2473–2484 (2007).
Onufryk, C., Crouch, M. L., Fang, F. C. & Gross, C. A. Characterization of six lipoproteins in the σE regulon. J. Bacteriol. 187, 4552–4561 (2005).
Rizzitello, A. E., Harper, J. R. & Silhavy, T. J. Genetic evidence for parallel pathways of chaperone activity in the periplasm of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 183, 6794–6800 (2001).
Werner, J. & Misra, R. YaeT (Omp85) affects the assembly of lipid-dependent and lipid-independent outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 57, 1450–1459 (2005).
Wu, T. et al. Identification of a multicomponent complex required for outer membrane biogenesis in Escherichia coli. Cell 121, 235–245 (2005). First documented evidence that BamA forms a heterooligomeric structure; the BamB–D lipoproteins were identified as accessory components of the complex.
Doerrler, W. T. & Raetz, C. R. Loss of outer membrane proteins without inhibition of lipid export in an Escherichia coli YaeT mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 27679–27687 (2005).
Malinverni, J. C. et al. YfiO stabilizes the YaeT complex and is essential for outer membrane protein assembly in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 61, 151–164 (2006).
Collin, S., Guilvout, I., Chami, M. & Pugsley, A. P. YaeT-independent multimerization and outer membrane association of secretin PulD. Mol. Microbiol. 64, 1350–1357 (2007).
Guilvout, I. et al. In vitro multimerization and membrane insertion of bacterial outer membrane secretin PulD. J. Mol. Biol. 382, 13–23 (2008).
Bolla, J. M., Lazdunski, C. & Pages, J. M. The assembly of the major outer membrane protein OmpF of Escherichia coli depends on lipid synthesis. EMBO J. 7, 3595–3599 (1988).
Sklar, J. G. et al. Lipoprotein SmpA is a component of the YaeT complex that assembles outer membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 6400–6405 (2007).
Vuong, P., Bennion, D., Mantei, J., Frost, D. & Misra, R. Analysis of YfgL and YaeT interactions through bioinformatics, mutagenesis, and biochemistry. J. Bacteriol. 190, 1507–1517 (2008).
Misra, R. First glimpse of the crystal structure of YaeT's POTRA domains. ACS Chem. Biol. 2, 649–651 (2007).
Gatsos, X. et al. Protein secretion and outer membrane assembly in Alphaproteobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 32, 995–1009 (2008).
Aoki, S. K. et al. Contact-dependent growth inhibition requires the essential outer membrane protein BamA (YaeT) as the receptor and the inner membrane transport protein AcrB. Mol. Microbiol. 70, 323–340 (2008).
Voulhoux, R., Bos, M. P., Geurtsen, J., Mols, M. & Tommassen, J. Role of a highly conserved bacterial protein in outer membrane protein assembly. Science 299, 262–265 (2003). The authors of this paper described, for the first time, the essential nature of BamA and its role in the biogenesis of membrane proteins.
Genevrois, S., Steeghs, L., Roholl, P., Letesson, J. J. & van der Ley, P. The Omp85 protein of Neisseria meningitidis is required for lipid export to the outer membrane. EMBO J. 22, 1780–1789 (2003).
Bos, M. P., Tefsen, B., Geurtsen, J. & Tommassen, J. Identification of an outer membrane protein required for the transport of lipopolysaccharide to the bacterial cell surface. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 9417–9422 (2004).
Sanchez-Pulido, L., Devos, D., Genevrois, S., Vicente, M. & Valencia, A. POTRA: a conserved domain in the FtsQ family and a class of β-barrel outer membrane proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28, 523–526 (2003). The POTRA domains were identified in a wide range of proteins through in silico predictions.
Schleiff, E. & Soll, J. Membrane protein insertion: mixing eukaryotic and prokaryotic concepts. EMBO Rep. 6, 1023–1027 (2005).
Gentle, I. E., Burri, L. & Lithgow, T. Molecular architecture and function of the Omp85 family of proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 58, 1216–1225 (2005).
Kim, S. et al. Structure and function of an essential component of the outer membrane protein assembly machine. Science 317, 961–964 (2007). First identification of the crystal structure of POTRA 1–4 from E. coli BamA, which revealed the first structure of a POTRA fold.
Knowles, T. J. et al. Fold and function of polypeptide transport-associated domains responsible for delivering unfolded proteins to membranes. Mol. Microbiol. 68, 1216–1227 (2008). A description of the NMR structures of POTRA 1–2 from E. coli BamA; this study detected interdomain flexibility and evidence for direct binding of nascent barrel proteins.
Gatzeva-Topalova, P. Z., Walton, T. A. & Sousa, M. C. Crystal structure of YaeT: conformational flexibility and substrate recognition. Structure 16, 1873–1881 (2008).
Clantin, B. et al. Structure of the membrane protein FhaC: a member of the Omp85–TpsB transporter superfamily. Science 317, 957–961 (2007). This paper documents the crystal structure of FhaC, a two-partner secretion system OMP that is related to BamA. The authors found a tandem POTRA domain fold that was associated with an integral outer membrane barrel domain.
Vanini, M. M., Spisni, A., Sforca, M. L., Pertinhez, T. A. & Benedetti, C. E. The solution structure of the outer membrane lipoprotein OmlA from Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri reveals a protein fold implicated in protein–protein interaction. Proteins 71, 2051–2064 (2008).
Reynolds, K. A. et al. Structural and computational characterization of the SHV-1 β-lactamase-β-lactamase inhibitor protein interface. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 26745–26753 (2006).
Williams, J. C. et al. Structural and thermodynamic characterization of a cytoplasmic dynein light chain-intermediate chain complex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 10028–10033 (2007).
van den Ent, F. et al. Structural and mutational analysis of the cell division protein FtsQ. Mol. Microbiol. 68, 110–123 (2008).
Robert, V. et al. Assembly factor Omp85 recognizes its outer membrane protein substrates by a species-specific C-terminal motif. PLoS Biol. 4, e377 (2006).
Struyve, M., Moons, M. & Tommassen, J. Carboxy-terminal phenylalanine is essential for the correct assembly of a bacterial outer membrane protein. J. Mol. Biol. 218, 141–148 (1991).
Habib, S. J. et al. The N-terminal domain of Tob55 has a receptor-like function in the biogenesis of mitochondrial β-barrel proteins. J. Cell Biol. 176, 77–88 (2007).
Bos, M. P., Robert, V. & Tommassen, J. Functioning of outer membrane protein assembly factor Omp85 requires a single POTRA domain. EMBO Rep. 8, 1149–1154 (2007).
Stenberg, F. et al. Protein complexes of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 34409–34419 (2005).
Surana, N. K. et al. Evidence for conservation of architecture and physical properties of Omp85-like proteins throughout evolution. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 14497–14502 (2004).
Li, H., Grass, S., Wang, T., Liu, T. & St Geme, J. W. 3rd. Structure of the Haemophilus influenzae HMW1B translocator protein: evidence for a twin pore. J. Bacteriol. 189, 7497–7502 (2007).
Fussenegger, M., Facius, D., Meier, J. & Meyer, T. F. A novel peptidoglycan-linked lipoprotein (ComL) that functions in natural transformation competence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol. Microbiol. 19, 1095–1105 (1996).
Blatch, G. L. & Lassle, M. The tetratricopeptide repeat: a structural motif mediating protein–protein interactions. Bioessays 21, 932–939 (1999).
D'Andrea, L. D. & Regan, L. TPR proteins: the versatile helix. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28, 655–662 (2003).
Chan, N. C., Likic, V. A., Waller, R. F., Mulhern, T. D. & Lithgow, T. The C-terminal TPR domain of Tom70 defines a family of mitochondrial protein import receptors found only in animals and fungi. J. Mol. Biol. 358, 1010–1022 (2006).
Wu, Y. & Sha, B. Crystal structure of yeast mitochondrial outer membrane translocon member Tom70p. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 589–593 (2006).
Ruiz, N., Falcone, B., Kahne, D. & Silhavy, T. J. Chemical conditionality: a genetic strategy to probe organelle assembly. Cell 121, 307–317 (2005).
Charlson, E. S., Werner, J. N. & Misra, R. Differential effects of yfgL mutation on Escherichia coli outer membrane proteins and lipopolysaccharide. J. Bacteriol. 188, 7186–7194 (2006).
Rolhion, N., Barnich, N., Claret, L. & Darfeuille-Michaud, A. Strong decrease in invasive ability and outer membrane vesicle release in Crohn's disease-associated adherent-invasive Escherichia coli strain LF82 with the yfgL gene deleted. J. Bacteriol. 187, 2286–2296 (2005).
Khairnar, N. P., Kamble, V. A., Mangoli, S. H., Apte, S. K. & Misra, H. S. Involvement of a periplasmic protein kinase in DNA strand break repair and homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 65, 294–304 (2007).
Ruiz, N., Kahne, D. & Silhavy, T. J. Advances in understanding bacterial outer-membrane biogenesis. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 4, 57–66 (2006).
Lipinska, B., Zylicz, M. & Georgopoulos, C. The HtrA (DegP) protein, essential for Escherichia coli survival at high temperatures, is an endopeptidase. J. Bacteriol. 172, 1791–1797 (1990).
Spiess, C., Beil, A. & Ehrmann, M. A temperature-dependent switch from chaperone to protease in a widely conserved heat shock protein. Cell 97, 339–347 (1999).
Behrens, S., Maier, R., de Cock, H., Schmid, F. X. & Gross, C. A. The SurA periplasmic PPIase lacking its parvulin domains functions in vivo and has chaperone activity. EMBO J. 20, 285–294 (2001).
Chen, R. & Henning, U. A periplasmic protein (Skp) of Escherichia coli selectively binds a class of outer membrane proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 19, 1287–1294 (1996).
Ureta, A. R., Endres, R. G., Wingreen, N. S. & Silhavy, T. J. Kinetic analysis of the assembly of the outer membrane protein LamB in Escherichia coli mutants each lacking a secretion or targeting factor in a different cellular compartment. J. Bacteriol. 189, 446–454 (2007).
Schafer, U., Beck, K. & Muller, M. Skp, a molecular chaperone of Gram-negative bacteria, is required for the formation of soluble periplasmic intermediates of outer membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 24567–24574 (1999).
Harms, N. et al. The early interaction of the outer membrane protein PhoE with the periplasmic chaperone Skp occurs at the cytoplasmic membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 18804–18811 (2001).
Typas, A. et al. High-throughput, quantitative analyses of genetic interactions in E. coli. Nature Methods 5, 781–787 (2008).
Arie, J. P., Sassoon, N. & Betton, J. M. Chaperone function of FkpA, a heat shock prolyl isomerase, in the periplasm of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 39, 199–210 (2001).
Meli, A. C. et al. Channel properties of TpsB transporter FhaC point to two functional domains with a C-terminal protein-conducting pore. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 158–166 (2006).
Ertel, F. et al. The evolutionarily related β-barrel polypeptide transporters from Pisum sativum and Nostoc PCC7120 contain two distinct functional domains. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 28281–28289 (2005).
Guedin, S. et al. Novel topological features of FhaC, the outer membrane transporter involved in the secretion of the Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 30202–30210 (2000).
Krojer, T. et al. Interplay of PDZ and protease domain of DegP ensures efficient elimination of misfolded proteins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 7702–7707 (2008).
Krojer, T. et al. Structural basis for the regulated protease and chaperone function of DegP. Nature 453, 885–890 (2008). This study indicated that DegP can form higher order homooligomers and is capable of interacting with folded outer membrane proteins and with lipid.
Jiang, J. et al. Activation of DegP chaperone-protease via formation of large cage-like oligomers upon binding to substrate proteins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 11939–11944 (2008).
Krojer, T., Garrido-Franco, M., Huber, R., Ehrmann, M. & Clausen, T. Crystal structure of DegP (HtrA) reveals a new protease-chaperone machine. Nature 416, 455–459 (2002).
Huber, D. & Bukau, B. DegP: a protein “death star”. Structure 16, 989–990 (2008).
Koronakis, V., Sharff, A., Koronakis, E., Luisi, B. & Hughes, C. Crystal structure of the bacterial membrane protein TolC central to multidrug efflux and protein export. Nature 405, 914–919 (2000).
Kozjak, V. et al. An essential role of Sam50 in the protein sorting and assembly machinery of the mitochondrial outer membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 48520–48523 (2003).
Inoue, K. & Potter, D. The chloroplastic protein translocation channel Toc75 and its paralog OEP80 represent two distinct protein families and are targeted to the chloroplastic outer envelope by different mechanisms. Plant J. 39, 354–365 (2004).
Henderson, I. R., Navarro-Garcia, F., Desvaux, M., Fernandez, R. C. & Ala'Aldeen, D. Type V protein secretion pathway: the autotransporter story. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 68, 692–744 (2004).
Wiedemann, N. et al. Biogenesis of the protein import channel Tom40 of the mitochondrial outer membrane: intermembrane space components are involved in an early stage of the assembly pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 18188–18194 (2004).
Pfanner, N., Wiedemann, N., Meisinger, C. & Lithgow, T. Assembling the mitochondrial outer membrane. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 11, 1044–1048 (2004).
Kutik, S. et al. Dissecting membrane insertion of mitochondrial β-barrel proteins. Cell 132, 1011–1024 (2008).
Meisinger, C. et al. The mitochondrial morphology protein Mdm10 functions in assembly of the preprotein translocase of the outer membrane. Dev. Cell 7, 61–71 (2004).
Meisinger, C. et al. The morphology proteins Mdm12/Mmm1 function in the major β-barrel assembly pathway of mitochondria. EMBO J. 26, 2229–2239 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Related links
Related links
DATABASES
Entrez Genome Project
Glossary
- Chaperone
-
A protein that facilitates the proper folding of other proteins.
- Amphipathic
-
A molecule with both polar and non-polar portions in its structure.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knowles, T., Scott-Tucker, A., Overduin, M. et al. Membrane protein architects: the role of the BAM complex in outer membrane protein assembly. Nat Rev Microbiol 7, 206–214 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2069
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2069
This article is cited by
-
Peptidoglycan endopeptidase MepM of uropathogenic Escherichia coli contributes to competitive fitness during urinary tract infections
BMC Microbiology (2024)
-
Aminolipids elicit functional trade-offs between competitiveness and bacteriophage attachment in Ruegeria pomeroyi
The ISME Journal (2023)
-
First report of whole genome sequence of septicemic Pasteurella multocida serovar B:2 ‘Soron’ strain isolated from swine
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2023)
-
Secretome analysis of an environmental isolate Enterobacter sp. S-33 identifies proteins related to pathogenicity
Archives of Microbiology (2022)
-
Affinity of Skp to OmpC revealed by single-molecule detection
Scientific Reports (2020)