Abstract
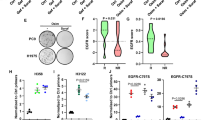
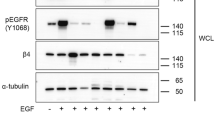
EGFRvIII, a frequent genetic alteration of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), has been shown to increase the migratory potential of tumor cells and normal fibroblasts. Previously, we showed that signal regulatory protein α1 (SIRPα1) receptors interact with SHP-2 to inhibit wild-type (wt) EGFR-mediated tumor migration, survival and cell transformation. However, the effects of SIRPα1 inhibitory receptors on EGFRvIII-mediated phenotypes are unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of SIRPα1 receptor on the EGFRvIII signalosome and phenotypes. Overexpression of SIRPα1 in U87MG.EGFRvIII cells inhibited transformation and migration in a MAPK-dependent manner, and is independent of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K)/Akt pathway. We observed reduced EGFRvIII/SHP-2/Gab1/Grb2/Sos-1 interaction and enhanced SIRP/SHP-2 association in U87MG.EGFRvIII/SIRPα1 cells when compared with empty vector control cells. Interestingly, SIRPα1 overexpression differentially modulated SHP-2 phosphorylation at tyrosyl 542 and 580 residues, which may regulate Erk1/2 activity and the EGFRvIII phenotype. In addition, SIRPα1-expressing cells exhibited reduced focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation and its recruitment to the EGFRvIII/Grb2/Sos-1/Gab1/SHP-2 complex. Collectively, our data indicate that SIRPα1 specifically affects the SHP-2/FAK/Grb2/Sos-1/MAPK activation loop to downmodulate EGFRvIII-mediated migration and transformation. Further understanding of the molecular interactions between the SIRPα1 inhibitory receptor and the EGFRvIII signalosome may facilitate the identification of novel targets to inhibit the EGFRvIII glioblastoma phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
01 June 2023
An Editorial Expression of Concern to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-023-02740-4
References
Aponte M, Jiang W, Lakkis M, Li MJ, Edwards D, Albitar L et al. (2008). Activation of platelet-activating factor receptor and pleiotropic effects on tyrosine phospho-EGFR/Src/FAK/paxillin in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 68: 5839–5848.
Araki T, Nawa H, Neel BG . (2003). Tyrosyl phosphorylation of Shp2 is required for normal ERK activation in response to some, but not all, growth factors. J Biol Chem 278: 41677–41684.
Benlimame N, He Q, Jie S, Xiao D, Xu YJ, Loignon M et al. (2005). FAK signaling is critical for ErbB-2/ErbB-3 receptor cooperation for oncogenic transformation and invasion. J Cell Biol 171: 505–516.
Bennett AM, Tang TL, Sugimoto S, Walsh CT, Neel BG . (1994). Protein-tyrosine-phosphatase SHPTP2 couples platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta to Ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 7335–7339.
Boockvar JA, Kapitonov D, Kapoor G, Schouten J, Counelis GJ, Bogler O et al. (2003). Constitutive EGFR signaling confers a motile phenotype to neural stem cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 24: 1116–1130.
Boockvar JA, Schouten J, Royo N, Millard M, Spangler Z, Castelbuono D et al. (2005). Experimental traumatic brain injury modulates the survival, migration, and terminal phenotype of transplanted epidermal growth factor receptor-activated neural stem cells. Neurosurgery 56: 163–171, discussion 171.
Boudot C, Kadri Z, Petitfrere E, Lambert E, Chretien S, Mayeux P et al. (2002). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulates glycosylphosphatidylinositol hydrolysis through PLC-gamma(2) activation in erythropoietin-stimulated cells. Cell Signal 14: 869–878.
Cetin S, Leaphart CL, Li J, Ischenko I, Hayman M, Upperman J et al. (2007). Nitric oxide inhibits enterocyte migration through activation of RhoA-GTPase in a SHP-2-dependent manner. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292: G1347–G1358.
Cui J, Han SY, Wang C, Su W, Harshyne L, Holgado-Madruga M et al. (2006). c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 2alpha2 promotes the tumorigenicity of human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 66: 10024–10031.
Dai HY, Hong CC, Liang SC, Yan MD, Lai GM, Cheng AL et al. (2008). Carbonic anhydrase III promotes transformation and invasion capability in hepatoma cells through FAK signaling pathway. Mol Carcinog 47: 956–963.
Dance M, Montagner A, Salles JP, Yart A, Raynal P . (2008). The molecular functions of Shp2 in the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK1/2) pathway. Cell Signal 20: 453–459.
Dong LW, Kong XN, Yan HX, Yu LX, Chen L, Yang W et al. (2008). Signal regulatory protein alpha negatively regulates both TLR3 and cytoplasmic pathways in type I interferon induction. Mol Immunol 45: 3025–3035.
Eminaga S, Bennett AM . (2008). Noonan syndrome-associated SHP-2/Ptpn11 mutants enhance SIRPalpha and PZR tyrosyl phosphorylation and promote adhesion-mediated ERK activation. J Biol Chem 283: 15328–15338.
Feng GS . (1999). Shp-2 tyrosine phosphatase: signaling one cell or many. Exp Cell Res 253: 47–54.
Garcia de Palazzo IE, Adams GP, Sundareshan P, Wong AJ, Testa JR, Bigner DD et al. (1993). Expression of mutated epidermal growth factor receptor by non-small cell lung carcinomas. Cancer Res 53: 3217–3220.
Guan JL . (1997). Role of focal adhesion kinase in integrin signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29: 1085–1096.
Guo HB, Randolph M, Pierce M . (2007). Inhibition of a specific N-glycosylation activity results in attenuation of breast carcinoma cell invasiveness-related phenotypes: inhibition of epidermal growth factor-induced dephosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem 282: 22150–22162.
Hanks SK, Polte TR . (1997). Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Bioessays 19: 137–145.
Heimberger AB, Hlatky R, Suki D, Yang D, Weinberg J, Gilbert M et al. (2005). Prognostic effect of epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma multiforme patients. Clin Cancer Res 11: 1462–1466.
Huang HS, Nagane M, Klingbeil CK, Lin H, Nishikawa R, Ji XD et al. (1997). The enhanced tumorigenic activity of a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor common in human cancers is mediated by threshold levels of constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation and unattenuated signaling. J Biol Chem 272: 2927–2935.
Kapoor GS, Christie A, O'Rourke DM . (2007). EGFR inhibition in glioblastoma cells induces G2/M arrest and is independent of p53. Cancer Biol Ther 6: 571–579.
Kapoor GS, Kapitonov D, O'Rourke DM . (2004a). Transcriptional regulation of signal regulatory protein alpha1 inhibitory receptors by epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Cancer Res 64: 6444–6452.
Kapoor GS, O'Rourke DM . (2003). Mitogenic signaling cascades in glial tumors. Neurosurgery 52: 1425–1434, discussion 1434–1435.
Kapoor GS, Zhan Y, Johnson GR, O'Rourke DM . (2004b). Distinct domains in the SHP-2 phosphatase differentially regulate epidermal growth factor receptor/NF-kappaB activation through Gab1 in glioblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 24: 823–836.
Keegan K, Cooper JA . (1996). Distinct domains in the SHP-2 phosphatase differentially regulate epidermal growth factor receptor/NF-kappaB activation through Gab1 in glioblastoma cells. Oncogene 12: 1537–1544.
Kharitonenkov A, Chen Z, Sures I, Wang H, Schilling J, Ullrich A . (1997). A family of proteins that inhibit signalling through tyrosine kinase receptors. Nature 386: 181–186.
Kuan CT, Wikstrand CJ, Bigner DD . (2001). EGF mutant receptor vIII as a molecular target in cancer therapy. Endocr Relat Cancer 8: 83–96.
Learn CA, Hartzell TL, Wikstrand CJ, Archer GE, Rich JN, Friedman AH et al. (2004). Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition by mutant epidermal growth factor receptor variant III contributes to the neoplastic phenotype of glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res 10: 3216–3224.
Li W, Nishimura R, Kashishian A, Batzer AG, Kim WJ, Cooper JA et al. (1994). A new function for a phosphotyrosine phosphatase: linking GRB2-Sos to a receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol 14: 509–517.
Lorimer IA, Lavictoire SJ . (2001). Activation of extracellular-regulated kinases by normal and mutant EGF receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1538: 1–9.
Lu W, Gong D, Bar-Sagi D, Cole PA . (2001). Site-specific incorporation of a phosphotyrosine mimetic reveals a role for tyrosine phosphorylation of SHP-2 in cell signaling. Mol Cell 8: 759–769.
Luo Y, Liang F, Zhang ZY . (2009). PRL1 promotes cell migration and invasion by increasing MMP2 and MMP9 expression through Src and ERK1/2 pathways. Biochemistry 48: 1838–1846.
Madan R, Smolkin MB, Cocker R, Fayyad R, Oktay MH . (2006). Focal adhesion proteins as markers of malignant transformation and prognostic indicators in breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol 37: 9–15.
Malchinkhuu E, Sato K, Horiuchi Y, Mogi C, Ohwada S, Ishiuchi S et al. (2005). Role of p38 mitogen-activated kinase and c-Jun terminal kinase in migration response to lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine-1-phosphate in glioma cells. Oncogene 24: 6676–6688.
Minoo P, Chughtai N, Campiglio M, Stein-Gerlach M, Lebrun JJ, Ullrich A et al. (2003). The adaptor function of SHP-2 downstream of the prolactin receptor is required for the recruitment of p29, a substrate of SHP-2. Cell Signal 15: 319–326.
Mitra SK, Schlaepfer DD . (2006). Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18: 516–523.
Moscatello DK, Holgado-Madruga M, Godwin AK, Ramirez G, Gunn G, Zoltick PW et al. (1995). Frequent expression of a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor in multiple human tumors. Cancer Res 55: 5536–5539.
Moscatello DK, Montgomery RB, Sundareshan P, McDanel H, Wong MY, Wong AJ . (1996). Transformational and altered signal transduction by a naturally occurring mutant EGF receptor. Oncogene 13: 85–96.
Motegi S, Okazawa H, Ohnishi H, Sato R, Kaneko Y, Kobayashi H et al. (2003). Role of the CD47-SHPS-1 system in regulation of cell migration. EMBO J 22: 2634–2644.
Oh ES, Gu H, Saxton TM, Timms JF, Hausdorff S, Frevert EU et al. (1999). Regulation of early events in integrin signaling by protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2. Mol Cell Biol 19: 3205–3215.
Pedersen MW, Meltorn M, Damstrup L, Poulsen HS . (2001). The type III epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Biological significance and potential target for anti-cancer therapy. Ann Oncol 12: 745–760.
Pedersen MW, Tkach V, Pedersen N, Berezin V, Poulsen HS . (2004). Expression of a naturally occurring constitutively active variant of the epidermal growth factor receptor in mouse fibroblasts increases motility. Int J Cancer 108: 643–653.
Qi JH, Ito N, Claesson-Welsh L . (1999). Tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 is involved in regulation of platelet-derived growth factor-induced migration. J Biol Chem 274: 14455–14463.
Qin JM, Yan HX, Liu SQ, Wan XW, Zeng JZ, Cao HF et al. (2006). Negatively regulating mechanism of Sirpalpha1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: an experimental study. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 5: 246–251.
Retta SF, Barry ST, Critchley DR, Defilippi P, Silengo L, Tarone G . (1996). Focal adhesion and stress fiber formation is regulated by tyrosine phosphatase activity. Exp Cell Res 229: 307–317.
Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N et al. (2005). Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature 437: 1173–1178.
Sampaio C, Dance M, Montagner A, Edouard T, Malet N, Perret B et al. (2008). Signal strength dictates phosphoinositide 3-kinase contribution to Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 activation via differential Gab1/Shp2 recruitment: consequences for resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Mol Cell Biol 28: 587–600.
Sampson JH, Archer GE, Mitchell DA, Heimberger AB, Bigner DD . (2008). Tumor-specific immunotherapy targeting the EGFRvIII mutation in patients with malignant glioma. Semin Immunol 20: 267–275.
Schulze WX, Deng L, Mann M . (2005). Phosphotyrosine interactome of the ErbB-receptor kinase family. Mol Syst Biol 1: 2005 0008.
Shi ZQ, Yu DH, Park M, Marshall M, Feng GS . (2000). Molecular mechanism for the Shp-2 tyrosine phosphatase function in promoting growth factor stimulation of Erk activity. Mol Cell Biol 20: 1526–1536.
Takeda H, Matozaki T, Fujioka Y, Takada T, Noguchi T, Yamao T et al. (1998). Lysophosphatidic acid-induced association of SHP-2 with SHPS-1: roles of RHO, FAK, and a SRC family kinase. Oncogene 16: 3019–3027.
Tsuda M, Matozaki T, Fukunaga K, Fujioka Y, Imamoto A, Noguchi T et al. (1998). Integrin-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of SHPS-1 and its association with SHP-2. Roles of Fak and Src family kinases. J Biol Chem 273: 13223–13229.
Tsutsumi R, Takahashi A, Azuma T, Higashi H, Hatakeyama M . (2006). Focal adhesion kinase is a substrate and downstream effector of SHP-2 complexed with Helicobacter pylori CagA. Mol Cell Biol 26: 261–276.
Vadlamudi RK, Adam L, Nguyen D, Santos M, Kumar R . (2002). Differential regulation of components of the focal adhesion complex by heregulin: role of phosphatase SHP-2. J Cell Physiol 190: 189–199.
Vogel W, Ullrich A . (1996). Multiple in vivo phosphorylated tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 engages binding to Grb2 via tyrosine 584. Cell Growth Differ 7: 1589–1597.
Wang FM, Liu HQ, Liu SR, Tang SP, Yang L, Feng GS . (2005). SHP-2 promoting migration and metastasis of MCF-7 with loss of E-cadherin, dephosphorylation of FAK and secretion of MMP-9 induced by IL-1beta in vivo and in vitro. Breast Cancer Res Treat 89: 5–14.
Wikstrand CJ, Hale LP, Batra SK, Hill ML, Humphrey PA, Kurpad SN et al. (1995). Monoclonal antibodies against EGFRvIII are tumor specific and react with breast and lung carcinomas and malignant gliomas. Cancer Res 55: 3140–3148.
Wu CJ, Chen Z, Ullrich A, Greene MI, O'Rourke DM . (2000). Inhibition of EGFR-mediated phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase (PI3-K) signaling and glioblastoma phenotype by signal-regulatory proteins (SIRPs). Oncogene 19: 3999–4010.
Yan HX, Wang HY, Zhang R, Chen L, Li BA, Liu SQ et al. (2004). Negative regulation of hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by signal regulatory protein alpha1. Hepatology 40: 618–628.
Yu DH, Qu CK, Henegariu O, Lu X, Feng GS . (1998). Protein-tyrosine phosphatase Shp-2 regulates cell spreading, migration, and focal adhesion. J Biol Chem 273: 21125–21131.
Yuan L, Yu WM, Xu M, Qu CK . (2005). SHP-2 phosphatase regulates DNA damage-induced apoptosis and G2/M arrest in catalytically dependent and independent manners, respectively. J Biol Chem 280: 42701–42706.
Yuan L, Yu WM, Yuan Z, Haudenschild CC, Qu CK . (2003). Role of SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase in the DNA damage-induced cell death response. J Biol Chem 278: 15208–15216.
Zhan Y, Counelis GJ, O′Rourke DM . (2009). The protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 is required for EGFRvIII oncogenic transformation in human glioblastoma cells. Exp Cell Res 315: 2343–2357.
Zhan Y, O'Rourke DM . (2004). SHP-2-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase activation regulates EGFRvIII but not wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation and glioblastoma cell survival. Cancer Res 64: 8292–8298.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants to DMO from the National Institutes of Health R01 CA-90586, R01 2R56CA0905896-06A1 and from the Terri Ann for a Cure and For Pete's Sake Funds to the University of Pennsylvania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapoor, G., O'Rourke, D. SIRPα1 receptors interfere with the EGFRvIII signalosome to inhibit glioblastoma cell transformation and migration. Oncogene 29, 4130–4144 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.164
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.164
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bayesian methods for expression-based integration of various types of genomics data
EURASIP Journal on Bioinformatics and Systems Biology (2013)