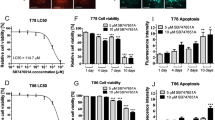
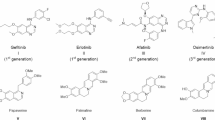
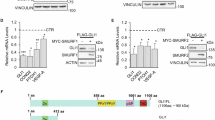
Abstract
Targeted inhibition of Hedgehog signaling at the cell membrane has been associated with anticancer activity in preclinical and early clinical studies. Hedgehog signaling involves activation of Gli transcription factors that can also be induced by alternative pathways. In this study, we identified an interaction between Gli proteins and a transcription coactivator TBP-associated factor 9 (TAF9), and validated its functional relevance in regulating Gli transactivation. We also describe a novel, synthetic small molecule, FN1-8, that efficiently interferes with Gli/TAF9 interaction and downregulate Gli/TAF9-dependent transcriptional activity. More importantly, FN1-8 suppresses cancer cell proliferation in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Our results suggest that blocking Gli transactivation, an important control point of multiple oncogenic pathways, may be an effective anticancer strategy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varjosalo M, Taipale J . Hedgehog: functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 2454–2472.
Merchant AA, Matsui W . Targeting Hedgehog—a cancer stem cell pathway. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 3130–3140.
Kalderon D . Transducing the hedgehog signal. Cell 2000; 103: 371–374.
Hooper JE, Scott MP . Communicating with Hedgehogs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 306–317.
Huangfu D, Anderson KV . Signaling from Smo to Ci/Gli: Hedgehog pathways from Drosophila to vertebrates. Development 2006; 133: 3–14.
Ruiz i Altaba A, Mas C, Stecca B . The Gli code: and information nexus regulating cell fate, stemness and cancer. Trends Cell Biol 2007; 17: 438–447.
Mullor JL, Dahmane N, Sun T, Ruiz i Altaba A . Wnt signals are targets and mediators of Gli function. Curr Biol 2001; 1: 769–773.
Yang L, Xie G, Fan Q, Xie J . Activation of the Hedgehog-signaling pathway in human cancer and the clinical implications. Oncogene 2010; 29: 469–481.
Scales SJ, de Sauvage FJ . Mechanisms of Hedgehog pathway activation in cancer and implications for therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2009; 30: 303–312.
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN et al. Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by Hedgehog pathway blockade. Science 2002; 297: 1559–1561.
Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang B, Beachy PA, Baylin SB . Hedgehog signalling within airway epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2003; 422: 313–317.
Karhadkar SS, Bova GS, Abdallah N, Dhara S, Gardner D, Maitra A et al. Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration, neoplasia and metastasis. Nature 2004; 431: 707–712.
Feldmann G, Dhara S, Fendrich V, Bedja D, Beaty R, Mullendore M et al. Blockade of hedgehog signaling inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion and metastases: a new paradigm for combination therapy in solid cancers. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2187–2196.
Clement V, Sanchez P, de Tribolet N, Radovanovic I, Ruiz i Altaba A . HEDGEHOG-GLI1 signaling regulates human glioma growth, cancer stem cell self-renewal, and tumorigenicity. Curr Biol 2007; 17: 165–172.
Rudin CM, Hann CL, Laterra J, Yauch RL, Callahan CA, Fu L et al. Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 1173–1178.
LoRusso PM, Rudin CM, Reddy JC, Tibes R, Weiss GJ, Borad MJ et al. Phase I trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with refractory, locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 2502–2511.
Tremblay MR, Lescarbeau A, Grogan MJ, Tan E, Lin G, Austad BC et al. Discovery of a potent and orally active Hedgehog pathway antagonist (IPI-926). J Med Chem 2009; 52: 4400–4418.
Yauch RL, Dijkgraaf GJ, Alicke B, Januario T, Ahn CP, Holcomb T et al. Smoothened mutation confers resistance to a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science 2009; 326: 572–574.
Dijkgraaf GJ, Alicke B, Weinmann L, Januario T, West K, Modrusan Z et al. Small molecule inhibition of GDC-0449 refractory smoothened mutants and downstream mechanisms of drug resistance. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 435–444.
Low JA, de Sauvage FJ . Clinical experience with Hedgehog pathway inhibitors. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 5321–5326.
Dennler S, André J, Alexaki I, Li A, Magnaldo T, ten Dijke P et al. Induction of sonic hedgehog mediators by transforming growth factor-beta: Smad3-dependent activation of Gli2 and Gli1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6981–6986.
Dennler S, André J, Verrecchia F, Mauviel A . Cloning of the human Gli2 promoter: transcriptional activation by Tgf-beta via Smad3/beta-catenin cooperation. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 31523–31531.
Guo X, Wang XF . Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res 2009; 19: 71–88.
Ji ZY, Mei FC, Xie J, Cheng X . Oncogenic KRAS activates hedgehog signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 14048–14055.
Riobo NA, Haines GM, Emerson CP Jr . Protein kinase C-delta and mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1 control GLI activation in hedgehog signaling. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 839–845.
Riobo NA, Lu K, Ai X, Haines GM, Emerson CP Jr . Phosphoinositide 3-kinase and Akt are essential for sonic hedgehog signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 4505–4510.
Schnidar H, Eberl M, Klingler S, Mangelberger D, Kasper M, Hauser-Kronberger C et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling synergizes with Hedgehog/GLI in oncogenic transformation via activation of the MEK/ERK/JUN pathway. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 1284–1292.
Stecca B, Mas C, Clement V, Zbinden M, Correa R, Piguet V et al. Melanomas require HEDGEHOG-GLI signaling reaulated by interactions between GLI1 and the RAS-MEK/AKT pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 5895–5900.
Pasca di Magliano M, Sekine S, Ermilov A, Ferris J, Dlugosz AA, Hebrok M . Hedgehog/Ras interactions regulate early stages of pancreatic cancer. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 3161–3173.
Lauth M, Toftgård R . Non-canonical activation of GLI transcription factors. Cell Cycle 2007; 6: 2458–2463.
Lauth M, Bergstrom A, Shimokawa T, Toftgård R . Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 8455–8460.
Yoon JW, Liu CZ, Yang JT, Swart R, Iannaccone P, Walterhouse D . GLI activates transcription through a herpes simplex viral protein 16-like activation domain. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 3496–3501.
Uesugi M, Verdine GL . The alpha-helical FXXPhiPhi motif in p53:TAF interaction and discrimination by MDM2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 14801–14806.
Choi Y, Asada S, Uesugi M . Divergent hTAFII31-binding motifs hidden in activation domains. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 15912–15916.
Rovnak J, Quackenbush SL . Walleye dermal sarcoma virus retroviral cyclin directly contacts TAF9. J Virol 2006; 80: 12041–12048.
Falgout B, Ketner G . Characterization of adenovirus particles made by deletion mutants lacking the fiber gene. J Virol 1988; 62: 622–625.
He B, Fujii N, You L, Xu Z, Jablons DM . Targeting Gli proteins in human cancer by small molecules US Patent No. 7714014 2010.
Ogryzko VV, Kotani T, Zhang X, Schiltz RL, Howard T, Yang XJ et al. Histone-like TAFs within the PCAF histone acetylase complex. Cell 1998; 94: 35–44.
Hoffmann A, Chiang CM, Oelgeschläger T, Xie X, Burley SK, Nakatani Y et al. A histone octamer-like structure within TFIID. Nature 1996; 380: 356–359.
Shao H, Revach M, Moshonov S, Tzuman Y, Gazit K, Albeck S et al. Core promoter binding by histone-like TAF complexes. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 206–219.
Yauch RL, Gould SE, Scales SJ, Tang T, Tian H, Ahn CP et al. A paracrine requirement for hedgehog signaling in cancer. Nature 2008; 455: 406–410.
Hosoya T, Arai MA, Koyano T, Kowithayakorn T, Ishibashi M . Naturally occurring small-molecule inhibitors of hedgehog/GLI-mediated transcription. Chembiochem 2008; 9: 1082–1092.
Hyman JM, Firestone AJ, Heine VM, Zhao Y, Ocasio CA, Han K et al. Small-molecule inhibitors reveal multiple strategies for Hedgehog pathway blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 14132–14137.
Rifai Y, Arai M, Sadhu S, Ahmed F, Ishibashi M . New Hedgehog/GLI signaling inhibitors from Excoecaria agallocha. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2011; 21: 718–722.
Arai M, Tateno C, Koyano T, Kowithayakorn T, Kawabe S, Ishibashi M . New Hedgehog/GLI-signaling inhibitors from Adenium obesum. Org Biomol Chem 2011; 9: 1133–1139.
Jung D, Choi Y, Uesugi M . Small organic molecules that modulate gene transcription. Drug Discov Today 2006; 11: 452–457.
Shimogawa H, Kwon Y, Mao Q, Kawazoe Y, Choi Y, Asada S et al. A wrench-shaped synthetic molecule that modulates a transcription factor–coactivator interaction. J Am Chem Soc 2004; 126: 3461–3471.
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004; 303: 844–848.
Reguart N, He B, Xu Z, You L, Lee AY, Mazieres J et al. Cloning and characterization of the promoter of human Wnt inhibitory factor-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 323: 229–234.
Okamoto J, Hirata T, Chen Z, Zhou HM, Mikami I, Li H et al. EMX2 is epigenetically silenced and suppresses growth in human lung cancer. Oncogene 2010; 29: 5969–5975.
Raz D, Ray MR, Kim JY, He B, Taron M, Skrzypski M et al. A multi-gene assay is prognostic of survival in patients with early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 5565–5570.
Okamoto J, Kratz JR, Hirata T, Mikami I, Raz D, Segal M et al. Downregulation of EMX2 is associated with clinical outcomes in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Clin Lung Cancer 2011; 12: 237–244.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Joan’s Legacy: Uniting Against Lung Cancer Research Grant, NIH/NCI Grant R01CA125030, and the Eileen D Ludwig Endowed for Thoracic Oncology Research (to BH); NIH/NCI Grant R01CA132566, the Bonnie J Addario Lung Cancer Foundation, the Kazan, McClain, Abrams, Fernandez, Lyons, Greenwood, Harley and Oberman Foundation, Honeywell Foundation and the Barbara Isackson Lung Cancer Research Fund (to DMJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
BH, MM and DMJ have an ownership interest in Rescue Therapeutics. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosco-Clément, G., Zhang, F., Chen, Z. et al. Targeting Gli transcription activation by small molecule suppresses tumor growth. Oncogene 33, 2087–2097 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.164
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.164
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Advances in Targeted Therapies for Pediatric Brain Tumors
Current Treatment Options in Neurology (2020)
-
Measurement of genome-wide DNA methylation predicts survival benefits from chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2015)
-
Hedgehog/Gli promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung squamous cell carcinomas
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2014)