Abstract
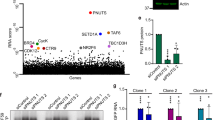
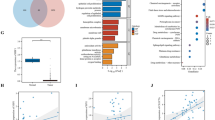
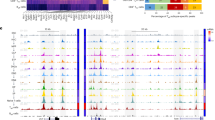
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), which is an aggressive subgroup of B-cell lymphoma associated with Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus/human herpes virus-8, is refractory to the standard treatment, and exhibits a poor survival. Although PU.1 is downregulated in PEL, the potential role of its reduction remains to be elucidated. In this investigation, we analyzed the DNA methylation of PU.1 cis-regulatory elements in PEL and the effect of restoring PU.1 on PEL cells. The mRNA level of PU.1 was downregulated in PEL cells. The methylated promoter and enhancer regions of the PU.1 gene were detected in PEL cells. Suppression of cell growth and apoptosis were caused by the restoration of PU.1 in PEL cells. A microarray analysis revealed that interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) including pro-apoptotic ISGs were strongly increased in BCBL-1 cells after the induction of PU.1. Reporter assays showed that PU.1 transactivated pro-apoptotic ISG promoters, such as the XAF1, OAS1 and TRAIL promoters. Mutations at the PU.1 binding sequences suppressed its transactivation. We confirmed the binding of PU.1 to the XAF1, OAS1 and TRAIL promoters in a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. PU.1 suppressed ORF57 activation by inducing IRF7. The reinduction of PU.1 reduced formation of ascites and lymphoma cell infiltration of distant organs in PEL xenograft model mice. Collectively, PU.1 has a role in tumor suppression in PEL and its down-regulation is associated with PEL development. Restoring PU.1 with demethylation agents may be a novel therapeutic approach for PEL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nador RG, Cesarman E, Chadburn A, Dawson DB, Ansari MQ, Sald J et al. Primary effusion lymphoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity associated with the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus. Blood 1996; 88: 645–656.
Ansari MQ, Dawson DB, Nador R, Rutherford C, Schneider NR, Latimer MJ et al. Primary body cavity-based AIDS-related lymphomas. Am J Clin Pathol 1996; 105: 221–229.
Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM . Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med 1995; 332: 1186–1191.
Gradoville L, Gerlach J, Grogan E, Shedd D, Nikiforow S, Metroka C et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus open reading frame 50/Rta protein activates the entire viral lytic cycle in the HH-B2 primary effusion lymphoma cell line. J Virol 2000; 74: 6207–6212.
Wang S, Liu S, Wu M, Geng Y, Wood C . Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus-8 ORF50 gene product contains a potent C-terminal activation domain which activates gene expression via a specific target sequence. Arch Virol 2001; 146: 1415–1426.
Boulanger E, Gerard L, Gabarre J, Molina JM, Rapp C, Abino JF et al. Prognostic factors and outcome of human herpesvirus 8-associated primary effusion lymphoma in patients with AIDS. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 4372–4380.
Okada S, Goto H, Yotsumoto M . Current status of treatment for primary effusion lymphoma. Intractable Rare Dis Res 2014; 3: 65–74.
Arguello M, Sgarbanti M, Hernandez E, Mamane Y, Sharma S, Servant M et al. Disruption of the B-cell specific transcriptional program in HHV-8 associated primary effusion lymphoma cell lines. Oncogene 2003; 22: 964–973.
Tatetsu H, Ueno S, Hata H, Yamada Y, Takeya M, Mitsuya H et al. Down-regulation of PU.1 by methylation of distal regulatory elements and the promoter is required for myeloma cell growth. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 5328–5336.
Yuki H, Ueno S, Tatetsu H, Niiro H, Iino T, Endo S et al. PU.1 is a potent tumor suppressor in classical Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Blood 2013; 121: 962–970.
Scott EW, Simon MC, Anastasi J, Singh H . Requirement of transcription factor PU.1 in the development of multiple hematopoietic lineages. Science 1994; 265: 1573–1577.
DeKoter RP, Singh H . Regulation of B lymphocyte and macrophage development by graded expression of PU.1. Science 2000; 288: 1439–1441.
Iwasaki H, Somoza C, Shigematsu H, Duprez EA, Iwasaki-Arai J, Mizuno S et al. Distinctive and indispensable roles of PU.1 in maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells and their differentiation. Blood 2005; 106: 1590–1600.
Nutt SL, Metcalf D, D'Amico A, Polli M, Wu L . Dynamic regulation of PU.1 expression in multipotent hematopoietic progenitors. J Exp Med 2005; 201: 221–231.
Nelsen B, Tian G, Erman B, Gregoire J, Maki R, Graves B et al. Regulation of lymphoid-specific immunoglobulin mu heavy chain gene enhancer by ETS-domain proteins. Science 1993; 261: 82–86.
Pongubala JM, Nagulapalli S, Klemsz MJ, McKercher SR, Maki RA, Atchison ML . PU.1 recruits a second nuclear factor to a site important for immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol 1992; 12: 368–378.
Eisenbeis CF, Singh H, Storb U . PU.1 is a component of a multiprotein complex which binds an essential site in the murine immunoglobulin lambda 2-4 enhancer. Mol Cell Biol 1993; 13: 6452–6461.
Li Y, Okuno Y, Zhang P, Radomska HS, Chen H, Iwasaki H et al. Regulation of the PU.1 gene by distal elements. Blood 2001; 98: 2958–2965.
Rosenbauer F, Wagner K, Kutok JL, Iwasaki H, Le Beau MM, Okuno Y et al. Acute myeloid leukemia induced by graded reduction of a lineage-specific transcription factor, PU.1. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 624–630.
Rosenbauer F, Owens BM, Yu L, Tumang JR, Steidl U, Kutok JL et al. Lymphoid cell growth and transformation are suppressed by a key regulatory element of the gene encoding PU.1. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 27–37.
Goto H, Kojima Y, Matsuda K, Kariya R, Taura M, Kuwahara K et al. Efficacy of anti-CD47 antibody-mediated phagocytosis with macrophages against primary effusion lymphoma. Eur J Cancer 2014; 50: 1836–1846.
Fan W, Bubman D, Chadburn A, Harrington Jr WJ, Cesarman E, Knowles DM . Distinct subsets of primary effusion lymphoma can be identified based on their cellular gene expression profile and viral association. J Virol 2005; 79: 1244–1251.
Samarajiwa SA, Forster S, Auchettl K, Hertzog PJ . INTERFEROME: the database of interferon regulated genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: D852–D857.
Rusinova I, Forster S, Yu S, Kannan A, Masse M, Cumming H et al. Interferome v2.0: an updated database of annotated interferon-regulated genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41: D1040–D1046.
Taniguchi T, Ogasawara K, Takaoka A, Tanaka N . IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu Rev Immunol 2001; 19: 623–655.
Palmeri D, Spadavecchia S, Carroll KD, Lukac DM . Promoter- and cell-specific transcriptional transactivation by the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57/Mta protein. J Virol 2007; 81: 13299–13314.
Majerciak V, Zheng ZM . Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 in viral RNA processing. Front Biosci 2009; 14: 1516–1528.
Wang J, Zhang J, Zhang L, Harrington Jr W, West JT, Wood C . Modulation of human herpesvirus 8/Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus replication and transcription activator transactivation by interferon regulatory factor 7. J Virol 2005; 79: 2420–2431.
Goto H, Kariya R, Shimamoto M, Kudo E, Taura M, Katano H et al. Antitumor effect of berberine against primary effusion lymphoma via inhibition of NF-κB pathway. Cancer Sci 2012; 103: 775–781.
Uddin S, Hussain AR, Al-Hussein KA, Manogaran PS, Wickrema A, Gutierrez MI et al. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase/AKT signaling promotes apoptosis of primary effusion lymphoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 3102–3108.
Uddin S, Hussain AR, Manogaran PS, Al-Hussein K, Platanias LC, Gutierrez MI et al. Curcumin suppresses growth and induces apoptosis in primary effusion lymphoma. Oncogene 2005; 24: 7022–7030.
Hussain AR, Ahmed SO, Ahmed M, Khan OS, Al Abdulmohsen S, Platanias LC et al. Cross-talk between NFkB and the PI3-kinase/AKT pathway can be targeted in primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cell lines for efficient apoptosis. PLoS One 2012; 7: e39945.
Will B, Vogler TO, Narayanagari S, Bartholdy B, Todorova TI, da Silva Ferreira M et al. Minimal PU.1 reduction induces a preleukemic state and promotes development of acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med 2015; 21: 1172–1181.
Pang SH, Minnich M, Gangatirkar P, Zheng Z, Ebert A, Song G et al. PU.1 cooperates with IRF4 and IRF8 to suppress pre-B-cell leukemia. Leukemia 2016; 30: 1375–1387.
Chawla-Sarkar M, Lindner DJ, Liu YF, Williams BR, Sen GC, Silverman RH et al. Apoptosis and interferons: role of interferon-stimulated genes as mediators of apoptosis. Apoptosis 2003; 8: 237–249.
Liston P, Fong WG, Kelly NL, Toji S, Miyazaki T, Conte D et al. Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-Caspase activity. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 128–133.
Leaman DW, Chawla-Sarkar M, Vyas K, Reheman M, Tamai K, Toji S et al. Identification of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor-1 as an interferon-stimulated gene that augments TRAIL Apo2L-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 28504–28511.
Dong B, Silverman RH . 2-5 A-dependent RNase molecules dimerize during activation by 2-5 A. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 4133–4137.
Castelli JC, Hassel BA, Maran A, Paranjape J, Hewitt JA, Li XL et al. The role of 2'-5' oligoadenylate-activated ribonuclease L in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 1998; 5: 313–320.
Domingo-Gil E, Esteban M . Role of mitochondria in apoptosis induced by the 2-5 A system and mechanisms involved. Apoptosis 2006; 11: 725–738.
Ueno S, Tatetsu H, Hata H, Iino T, Niiro H, Akashi K et al. PU.1 induces apoptosis in myeloma cells through direct transactivation of TRAIL. Oncogene 2009; 28: 4116–4125.
Takaoka A, Hayakawa S, Yanai H, Stoiber D, Negishi H, Kikuchi H et al. Integration of interferon-alpha/beta signalling to p53 responses in tumour suppression and antiviral defence. Nature 2003; 424: 516–523.
Zou B, Chim CS, Pang R, Zeng H, Dai Y, Zhang R et al. XIAP-associated factor 1 (XAF1), a novel target of p53, enhances p53-mediated apoptosis via post-translational modification. Mol Carcinog 2012; 51: 422–432.
Solomon LA, Li SK, Piskorz J, Xu LS, DeKoter RP . Genome-wide comparison of PU.1 and Spi-B binding sites in a mouse B lymphoma cell line. BMC Genomics 2015; 16: 76.
Moore PS, Chang Y . Molecular virology of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2001; 356: 499–516.
Deng H, Liang Y, Sun R . Regulation of KSHV lytic gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2007; 312: 157–183.
Goto H, Kojima Y, Nagai H, Okada S . Establishment of a CD4-positive cell line from an AIDS-related primary effusion lymphoma. Int J Hematol 2013; 97: 624–633.
Katano H, Hoshino Y, Morishita Y, Nakamura T, Satoh H, Iwamoto A et al. Establishing and characterizing a CD30-positive cell line harboring HHV-8 from a primary effusion lymphoma. J Med Virol 1999; 58: 394–401.
Miyagi J, Masuda M, Takasu N, Nagasaki A, Shinjyo T, Uezato H et al. Establishment of a primary effusion lymphoma cell line (RM-P1) and in vivo growth system using SCID mice. Int J Hematol 2002; 76: 165–172.
Moreau-Gachelin F . Spi-1/PU.1: an oncogene of the Ets family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1994; 1198: 149–163.
Nishiyama C, Hasegawa M, Nishiyama M, Takahashi K, Akizawa Y, Yokota T et al. Regulation of human Fc epsilon RI alpha-chain gene expression by multiple transcription factors. J Immunol 2002; 168: 4546–4552.
Goto H, Kudo E, Kariya R, Taura M, Katano H, Okada S . Targeting VEGF and interleukin-6 for controlling malignant effusion of primary effusion lymphoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2015; 141: 465–474.
Ueda K, Ishikawa K, Nishimura K, Sakakibara S, Do E, Yamanishi K . Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) replication and transcription factor activates the K9 (vIRF) gene through two distinct cis elements by a non-DNA-binding mechanism. J Virol 2002; 76: 12044–12054.
Katano H, Sato Y, Kurata T, Mori S, Sata T . High expression of HHV-8-encoded ORF73 protein in spindle-shaped cells of Kaposi's sarcoma. Am J Pathol 1999; 155: 47–52.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research program on HIV/AIDS (No. 17fk0410208h0002) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED, and Grants-in-Aid for Science Research (No. 16K08742) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan.
Author contributions
HG and RK performed the experiments; HG, RK, EK, YO, KU and SO interpreted experimental data; HK performed the analysis of immunohistochemistry; HG and SO designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goto, H., Kariya, R., Kudo, E. et al. Restoring PU.1 induces apoptosis and modulates viral transactivation via interferon-stimulated genes in primary effusion lymphoma. Oncogene 36, 5252–5262 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.138
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.138
This article is cited by
-
Dual targeting PD-L1 and 4-1BB to overcome dendritic cell-mediated lenalidomide resistance in follicular lymphoma
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2025)
-
GNAS knockout potentiates HDAC3 inhibition through viral mimicry-related interferon responses in lymphoma
Leukemia (2024)
-
LncRNA018392 promotes the proliferation of Liaoning cashmere goat skin fibroblasts by upregulating CSF1R through binding to SPI1
Molecular Biology Reports (2024)
-
PU.1 negatively regulates tumorigenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer
Medical Oncology (2023)