Abstract
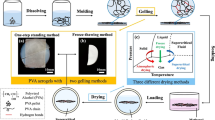
Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels (PVA-Hs) are promising materials for various biomedical applications and have been studied extensively. Low-temperature crystallization is the most popular method used to prepare PVA-Hs with excellent mechanical properties. However, this method uses dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) as a solvent, which is toxic and difficult to handle. In this study, a novel hot-pressing method was developed for preparing transparent PVA-Hs in order to eliminate the need of DMSO for solubilizing PVA during gelation. Unlike the conventional methods, this method used high initial concentrations of PVA, which made the molding of the gels easy and enhanced their gelation. The hydrogels prepared by hot-pressing showed rapid gelation of the PVA molecules along with an enhanced crystallinity, unlike the hydrogels prepared by freezing and thawing. The efficiency of different solvents (water and DMSO/water mixtures) for the preparation of PVA-Hs by the hot-pressing method was tested. The total amount of crystallites was the same for all the gels irrespective of the solvent used. However, the gels solubilized in only water showed a decrease in the net crystal size. This method not only eliminates the use of DMSO in preparing PVA-Hs but also produces gels with high mechanical properties for future use.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ratner, B. & Hoffman, A. Hydrogels for medical related applications. ACS Symp. Ser. 1–36 (1976).
Hoffman, A. S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 64, 18–23 (2012).
Bohl Masters, K. S., Leibovich, S. J., Belem, P., West, J. L. & Poole-Warren, L. A. Effects of nitric oxide releasing poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel dressings on dermal wound healing in diabetic mice. Wound Repair Regen. 10, 286–294 (2002).
Peppas, N. A., Bures, P., Leobandung, W. & Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 50, 27–46 (2000).
Brannon-Peppas, L. in Absorbent Polymer Technology (eds Brannon-Peppas L. & Harland, R. S.) 45–66 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1990).
Oliveira, J. T. & Reis, R. L. Hydrogels from polysaccharide-based materials: fundamentals and applications in regenerative medicine. in Natural-Based Polymers for Biomedical Applications. (eds Reis, R. L., Neves, N. M., Mano, J. F., Gomes, M. E., Marques, A. P., & Azevedo, H. S.) Ch. 18, 485–514. (Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, UK, 2008)
Wichterle, O. & Lím, D. in Natural-Based Polymers for Biomedical Applications. (eds Reis, R. L., Neves, N. M., Mano, J. F., Gomes, M. E., Marques, A. P., & Azevedo, H. S.) Ch. 18, 485–514. (Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, UK, 2008).
Kirker, K. R., Luo, Y., Nielson, J. H., Shelby, J. & Prestwich, G. D. Glycosaminoglycan hydrogel films as bio-interactive dressings for wound healing. Biomaterials 23, 3661–3671 (2002).
Obara, K., Ishihara, M., Fujita, M., Kanatani, Y., Hattori, H., Matsui, T., Takase, B., Ozeki, Y., Nakamura, S., Ishizuka, T., Tominaga, S., Hiroi, S., Kawai, T. & Maehara, T. Acceleration of wound healing in healing-impaired db/db mice with a photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogel containing fibroblast growth factor-2. Wound Repair Regen. 13, 390–397 (2005).
Xie, Y., Zhao, J., Huang, R., Qi, W., Wang, Y., Su, R. & He, Z. Calcium-ion-triggered co-assembly of peptide and polysaccharide into a hybrid hydrogel for drug delivery. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 184 (2016).
Yu, Z., Xu, Q., Dong, C., Lee, S. S., Gao, L., Li, Y., D’Ortenzio, M. & Wu, J. Self-assembling peptide nanofibrous hydrogel as a versatile drug delivery platform. Curr. Pharm. Des. 21, 4342–4354 (2015).
Bigot, M., Guterres, J., Rossato, L., Pudmenzky, A., Doley, D., Whittaker, M., Pillai-McGarry, U. & Schmidt, S. Metal-binding hydrogel particles alleviate soil toxicity and facilitate healthy plant establishment of the native metallophyte grass Astrebla lappacea in mine waste rock and tailings. J. Hazard. Mater. 248–249, 424–434 (2013).
Tolentino, F. I., Roldan, M., Nassif, J. & Refojo, M. F. Hydrogel implant for scleral buckling. Long-term observations. Retina 5, 38–41 (1985).
Koreen, I. V., McClintic, E. A., Mott, R. T., Stanton, C. & Yeatts, R. P. Evisceration with injectable hydrogel implant in a rabbit model. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. (e-pub ahead of print 24 March 2016; doi:10.1097/IOP.0000000000000679)
Gulrez, Syed K. H., Al-Assaf, S., G. O, P. in Prog. Mol. Environ. Bioeng.—From Anal. Moddelling to Technol. Appl. (ed. Angelo Carpi.) 117–150 (InTech, 2011).
Hennink, W. E. & van Nostrum, C. F. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 64, 223–236 (2012).
Bray, J. C. & Merrill, E. W. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for synthetic articular cartilage material. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 7, 431–443 (1973).
Spiller, K. L., Maher, S. A. & Lowman, A. M. Hydrogels for the repair of articular cartilage defects. Tissue Eng. B. Rev. 17, 281–299 (2011).
Lowman, A. M. & Peppas, N. in Encyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery (ed. Mathiowitz, E.) 397-418 (Wiley, NY, USA, 1999)
Bodugoz-Senturk, H., Macias, C. E., Kung, J. H. & Muratoglu, O. K. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-acrylamide hydrogels as load-bearing cartilage substitute. Biomaterials 30, 589–596 (2009).
Stauffer, S. R. & Peppast, N. A. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared by freezing-thawing cyclic processing. Polymer (Guildf) 33, 3932–3936 (1992).
Yokoyama, F., Masada, I., Shimamura, K., Ikawa, T. & Monobe, K. Morphology and structure of highly elastic poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel prepared by repeated freezing-and-melting. Colloid Polym. Sci. 264, 595–601 (1986).
Komatsu, M., Inoue, T. & Miyasaka, K. Light-scattering studies on the sol–gel transition in aqueous solutions of poly(vinyl alcohol). J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 24, 303–311 (1986).
Peppas, N. A. [Turbidimetric studies of aqueous poly(vinyl alcohol) solutions]. Die Makromol. Chem. 176, 3433–3440 (1975).
Hassan, C. M. & Peppas, N. A. Structure and applications of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels produced by conventional crosslinking or by freezing / thawing methods. Adv. Polym. Sci. 153, 37–65 (2000).
Nishinari, K., Watase, M., Ogino, K. & Nambu, M. Simple extension of poly(vinyl alcohol) gels. Polym. Commun. 24, 345–347 (1983).
Mano, I., Goshima, H., Nambu, M. & Iio, M. New polyvinyl alcohol gel material for MRI phantoms. Magn. Reson. Med. 3, 921–926 (1986).
Watase, M. & Nishinari, K. Rheological and DSC changes in poly(viny alcohol) gels induced by immersion in water. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 23, 1803–1811 (1985).
Watase, M. & Nishinari, K. [Effect of the degree of saponification on the rheological and thermal properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) gels]. Die Makromol. Chem. 190, 155–163 (1989).
Hassan, C. M. & Peppas, N. A. Structure and morphology of freeze/thawed PVA hydrogels. Macromolecules 33, 2472–2479 (2000).
Hyon, S. H., Cha, W. I. & Ikada, Y. Preparation of transparent poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel. Polym. Bull. 22, 119–122 (1989).
Cha, W.-I., Hyon, S.-H., Oka, M. & Ikada, Y. Mechanical and wear properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Macromol. Symp. 109, 115–126 (1996).
Kobayashi, M. & Hyon, S. H. Development and evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol-hydrogels as an artificial atrticular cartilage for orthopedic implants. Materials (Basel) 3, 2753–2771 (2010).
Otsuka, E., Komiya, S., Sasaki, S., Xing, J. W., Bando, Y., Hirashima, Y., Sugiyama, M. & Suzuki, A. Effects of preparation temperature on swelling and mechanical properties of PVA cast gels. Soft Matter 8, 8129–8136 (2012).
Tubbs, R. K. Melting point and heat of fusion of poly(vinyl alcohol). J. Polym. Sci. A Gen. Pap. 3, 4181–4189 (1965).
Hou, Y., Chen, C., Liu, K., Tu, Y., Zhang, L. & Li, Y. Preparation of PVA hydrogel with high-transparence and investigations of its transparent mechanism. RSC Adv. 5, 24023–24030 (2015).
Takeshita, H., Kanaya, T., Nishida, K. & Kaji, K. Spinodal decomposition and syneresis of PVA gel. Macromolecules 34, 7894–7898 (2001).
Sasaki, S., Otsuka, E., Hirashima, Y. & Suzuki, A. Elution of polymers from poly(vinyl alcohol) cast gels with different degrees of polymerization and hydrolysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 126, E233–E241 (2012).
Tretinnikov, O. N., Sushko, N. I. & Zagorskaya, S. A. Detection and quantitative determination of the crystalline phase in poly(vinyl alcohol) cryogels by ATR FTIR spectroscopy. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 55, 91–97 (2013).
Gupta, S., Webster, T. J. & Sinha, A. Evolution of PVA gels prepared without crosslinking agents as a cell adhesive surface. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 22, 1763–1772 (2011).
COLVIN, B. G. Crystal structure of polyvinyl alcohol. Nature 248, 756–759 (1974).
Takahashi, N., Kanaya, T., Nishida, K. & Kaji, K. Effects of cononsolvency on gelation of poly(vinyl alcohol) in mixed solvents of dimethyl sulfoxide and water. Polymer (Guildf) 44, 4075–4078 (2003).
Keller, A. in Growth and Perfection of Crystals (eds Doremus, R. H., Roberts, B. W. & Turnbull, D. 499–532 (Wiley, Hoboken, NY, USA, 1958).
Kamata, H., Akagi, Y., Kayasuga-Kariya, Y., Chung, U. & Sakai, T. ‘Nonswellable’ hydrogel without mechanical hysteresis. Science 343, 873–875 (2014).
Bin Imran, A., Esaki, K., Gotoh, H., Seki, T., Ito, K., Sakai, Y. & Takeoka, Y. Extremely stretchable thermosensitive hydrogels by introducing slide-ring polyrotaxane cross-linkers and ionic groups into the polymer network. Nat. Commun. 5, 5124 (2014).
Okumura, Y. & Ito, K. The polyrotaxane gel: a topological gel by figure-of-eight cross-links. Adv. Mater. 13, 485–487 (2001).
Oka, M., Noguchi, T., Kumar, P. & Ikeuchi, K. Development of an artificial articular cartilage. Clin. Mater. 6, 361–381 (1990).
Acknowledgements
We thank Japan VAM & POVAL for kindly donating PVA. This work was partly supported by Nanotechnology Platform Program (Nagoya University, Molecule and Material Synthesis) of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Polymer Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakaguchi, T., Nagano, S., Hara, M. et al. Facile preparation of transparent poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with uniform microcrystalline structure by hot-pressing without using organic solvents. Polym J 49, 535–542 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2017.18
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2017.18
This article is cited by
-
Totally transparent hydrogel-based subdural electrode with patterned salt bridge
Biomedical Microdevices (2020)
-
Dispersibility and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol–coated magnetic nanoparticles in poly(glycerol sebacate) for biomedical applications
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2019)