Abstract
Background:
C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) is a paracrine growth factor critical in endochondral bone growth. Amino-terminal CNP (NTproCNP), measurable in plasma, correlates with growth-plate activity and can be used as a biomarker of growth velocity in children. Because severe inflammation in adults increases CNP, we studied CNP peptides and inflammatory markers in children with acute illness.
Methods:
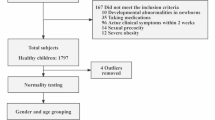
Forty-two children aged 2 mo to 5 y with acute illness warranting admission to an acute assessment unit were studied. Fifteen age-matched healthy children attending an outpatient clinic served as controls. Venous CNP concentrations were measured at admission, along with markers of acute inflammation (body temperature, C-reactive protein (CRP), and white blood cell count) in children with acute illness.
Results:
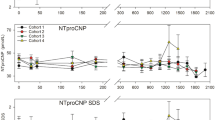
NTproCNP and CNP SD scores (SDSs) in the acutely ill group were significantly suppressed (P < 0.001) as compared with those of healthy children or healthy population norms. NTproCNP SDS was significantly inversely related to body temperature (r = −0.42, P < 0.01) and CRP (r = −0.56, P < 0.001).
Conclusion:
Acute inflammation in young children potently reduces CNP production, which needs to be considered when screening for growth disorders. Our data raise the possibility that the adverse effects of inflammatory cytokines on skeletal growth may be mediated in part by reduced CNP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Minamino N, Aburaya M, Kojima M, Miyamoto K, Kangawa K, Matsuo, H . Distribution of C-type natriuretic peptide and its messenger RNA in rat central nervous system and peripheral tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1993;197:326–35.
Prickett TC, Yandle TG, Nicholls MG, Espiner EA, Richards AM . Identification of amino-terminal pro-C-type natriuretic peptide in human plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001;286:513–7.
Prickett TC, Lynn AM, Barrell GK, et al. Amino-terminal proCNP: a putative marker of cartilage activity in postnatal growth. Pediatr Res 2005;58:334–40.
Prickett TC, Bothwell JC, Yandle TG, Richards AM, Espiner EA . Pharmacodynamic responses of plasma and tissue C-type natriuretic peptide to GH: correlation with linear growth in GH-deficient rats. J Endocrinol 2012;212:217–25.
Chusho H, Tamura N, Ogawa Y, et al. Dwarfism and early death in mice lacking C-type natriuretic peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001;98:4016–21.
Olney RC . C-type natriuretic peptide in growth: a new paradigm. Growth Horm IGF Res 2006;16:Suppl A:S6–14.
Kilpeläinen L, Ivaska KK, Kuiri-Hänninen T, et al. Urinary osteocalcin and serum pro-C-type natriuretic peptide predict linear catch-up growth in infants. J Bone Miner Res 2012;27:1528–35.
Xiao Y, Dong Z, Lu W, et al. Measurement of amino-terminal propeptide of C-type natriuretic peptide in patients with idiopathic short stature or isolated growth hormone deficiency. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2011;24:989–94.
Olney RC, Permuy JW, Prickett TC, Han JC, Espiner EA . Amino-terminal propeptide of C-type natriuretic peptide (NTproCNP) predicts height velocity in healthy children. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2012;77:416–22.
Olney RC, Prickett TC, Yandle TG, Espiner EA, Han JC, Mauras N . Amino-terminal propeptide of C-type natriuretic peptide and linear growth in children: effects of puberty, testosterone, and growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:4294–8.
Prickett TC, Lyver A, Wilson R, Espiner EA, Sullivan MJ . C-type Natriuretic Peptide: a novel biomarker of steroid induced bone toxicity in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Peptides 2012;36:54–9.
Czech-Kowalska J, Pludowski P, Dobrzanska A, et al. Impact of vitamin D supplementation on markers of bone mineral metabolism in term infants. Bone 2012;51:781–6.
Prickett TC, Olney RC, Cameron VA, Ellis MJ, Richards AM, Espiner EA . Impact of age, phenotype and cardio-renal function on plasma C-type and B-type natriuretic peptide forms in an adult population. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2013;78:783–9.
Suga S, Nakao K, Itoh H, et al. Endothelial production of C-type natriuretic peptide and its marked augmentation by transforming growth factor-beta. Possible existence of “vascular natriuretic peptide system”. J Clin Invest 1992;90:1145–9.
Hama N, Itoh H, Shirakami G, et al. Detection of C-type natriuretic peptide in human circulation and marked increase of plasma CNP level in septic shock patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994;198:1177–82.
Bahrami S, Pelinka L, Khadem A, et al. Circulating NT-proCNP predicts sepsis in multiple-traumatized patients without traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med 2010;38:161–6.
Koch A, Voigt S, Sanson E, et al. Prognostic value of circulating amino-terminal pro-C-type natriuretic peptide in critically ill patients. Crit Care 2011;15:R45.
Gabay C, Kushner I . Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 1999;340:448–54.
Cuschieri J, Bulger E, Schaeffer V, et al.; Inflammation and the Host Response to Injury Collaborative Research Program. Early elevation in random plasma IL-6 after severe injury is associated with development of organ failure. Shock 2010;34:346–51.
Suga SI, Itoh H, Komatsu Y, et al. Regulation of endothelial production of C-type natriuretic peptide by interaction between endothelial cells and macrophages. Endocrinology 1998;139:1920–6.
Prickett TC, Barrell GK, Wellby M, Yandle TG, Richards AM, Espiner EA . Response of plasma CNP forms to acute anabolic and catabolic interventions in growing lambs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2007;292:E1395–400.
Prickett TC, McNeill BA, Oliver MH, Harding JE, Espiner EA . Effect of cortisol on C-type natriuretic peptide in ovine pregnancy: differential responses in fetal and placental tissues. Pediatr Res 2010;68:462–5.
Simsa-Maziel S, Monsonego-Ornan E . Interleukin-1ß promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of chondrocytes through a mechanism involving down-regulation of FGFR-3 and p21. Endocrinology 2012;153:2296–310.
Nakajima S, Naruto T, Miyamae T, et al. Interleukin-6 inhibits early differentiation of ATDC5 chondrogenic progenitor cells. Cytokine 2009;47:91–7.
Mårtensson K, Chrysis D, Sävendahl L . Interleukin-1beta and TNF-alpha act in synergy to inhibit longitudinal growth in fetal rat metatarsal bones. J Bone Miner Res 2004;19:1805–12.
Prickett TC, Dixon B, Frampton C, et al. Plasma amino-terminal pro C-type natriuretic Peptide in the neonate: relation to gestational age and postnatal linear growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:225–32.
Marchini G, Berggren V, Djilali-Merzoug R, Hansson LO . The birth process initiates an acute phase reaction in the fetus-newborn infant. Acta Paediatr 2000;89:1082–6.
Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, et al. 2000 CDC Growth Charts for the United States: methods and development. Series 11, Data from the national health survey. Vital Health Stat 2002:1–190.
Yandle TG, Fisher S, Charles C, Espiner EA, Richards AM . The ovine hypothalamus and pituitary have markedly different distribution of C-type natriuretic peptide forms. Peptides 1993;14:713–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prickett, T., Hector-Taylor, J., Olney, R. et al. Acute inflammation in young children inhibits C-type natriuretic peptide. Pediatr Res 74, 191–195 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.92
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.92