Abstract
Background:
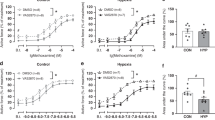
Intestinal circulation and mesenteric arterial (MA) reactivity may play a role in preparing the fetus for enteral nutrition. We hypothesized that MA vasoreactivity changes with gestation and vasodilator pathways predominate in the postnatal period.
Methods:
Small distal MA rings (0.5-mm diameter) were isolated from fetal (116-d, 128-d, 134-d, and 141-d gestation, term ~ 147 d) and postnatal lambs. Vasoreactivity was evaluated using vasoconstrictors (norepinephrine (NE) after pretreatment with propranolol and endothelin-1(ET-1)) and vasodilators (NO donors A23187 and s-nitrosopenicillamine (SNAP)). Protein and mRNA assays for receptors and enzymes (endothelin receptor A, alpha-adrenergic receptor 1A (ADRA1A), endothelial NO synthase (eNOS), soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC), and phosphodiesterase5 (PDE5)) were performed in mesenteric arteries.
Results:
MA constriction to NE and ET-1 peaked at 134 d. Relaxation to A23187 and SNAP was maximal after birth. Basal eNOS activity was low at 134 d. ADRA1A mRNA and protein increased significantly at 134 d and decreased postnatally. sGC and PDE5 protein increased from 134 to 141 d.
Conclusion:
Mesenteric vasoconstriction predominates in late-preterm gestation (134 d; the postconceptional age with the highest incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)) followed by a conversion to vasodilatory influences near the time of full-term birth. Perturbations in this ontogenic mechanism, including preterm birth, may be a risk factor for NEC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Coombs RC, Morgan ME, Durbin GM, Booth IW, McNeish AS. Doppler assessment of human neonatal gut blood flow velocities: postnatal adaptation and response to feeds. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1992;15:6–12.
Nankervis CA, Giannone PJ, Reber KM. The neonatal intestinal vasculature: contributing factors to necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Perinatol 2008;32:83–91.
Patel RM, Kandefer S, Walsh MC, et al.; Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Causes and timing of death in extremely premature infants from 2000 through 2011. N Engl J Med 2015;372:331–40.
McGrady GA, Rettig PJ, Istre GR, Jason JM, Holman RC, Evatt BL. An outbreak of necrotizing enterocolitis. Association with transfusions of packed red blood cells. Am J Epidemiol 1987;126:1165–72.
Mohamed A, Shah PS. Transfusion associated necrotizing enterocolitis: a meta-analysis of observational data. Pediatrics 2012;129:529–40.
Nair J, Gugino SF, Nielsen LC, et al. Packed red cell transfusions alter mesenteric arterial reactivity and nitric oxide pathway in preterm lambs. Pediatr Res 2013;74:652–7.
Upperman JS, Potoka D, Grishin A, Hackam D, Zamora R, Ford HR. Mechanisms of nitric oxide-mediated intestinal barrier failure in necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg 2005;14:159–66.
La Gamma EF, Feldman A, Mintzer J, Lakshminrusimha S, Alpan G. Red blood cell storage in transfusion-related acute gut injury. NeoReviews 2015;16:e420–e30.
Nankervis CA, Nowicki PT. Role of nitric oxide in regulation of vascular resistance in postnatal intestine. Am J Physiol 1995;268:G949–58.
Reber KM, Su BY, Clark KR, Pohlman DL, Miller CE, Nowicki PT. Developmental expression of eNOS in postnatal swine mesenteric artery. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2002;283:G1328–35.
Moonen RM, Villamor E. Developmental changes in mesenteric artery reactivity in embryonic and newly hatched chicks. J Comp Physiol B 2011;181:1063–73.
Clark DA, Munshi UK. Development of the gastrointestinal circulation in the fetus and newborn. In: Polin RA, Fox WW, Abman SH, eds. Fetal and Neonatal Physiology. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2011:773–6.
Fronek K, Stahlgren LH. Systemic and regional hemodynamic changes during food intake and digestion in nonanesthetized dogs. Circ Res 1968;23:687–92.
Vatner SF, Franklin D, Van Citters RL. Mesenteric vasoactivity associated with eating and digestion in the conscious dog. Am J Physiol 1970;219:170–4.
Dawes GS. Foetal and Neonatal Physiology—A Comparative Study of the Changes at Birth. Chicago, IL: Year Book Medical Publishers, 1968.
Zoetis T, Hurtt ME. Species comparison of lung development. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol 2003;68:121–4.
Pitt BR, Brookens MA, Steve AR, et al. Expression of pulmonary metallothionein genes in late gestational lambs. Pediatr Res 1992;32:424–30.
Strang LB. Neonatal Respiration—Physiological and Clinical Studies. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1977.
Sangild PT. Gut responses to enteral nutrition in preterm infants and animals. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2006;231:1695–711.
Bisset WM, Watt JB, Rivers RP, Milla PJ. Ontogeny of fasting small intestinal motor activity in the human infant. Gut 1988;29:483–8.
Bueno L, Ruckebusch Y. Perinatal development of intestinal myoelectrical activity in dogs and sheep. Am J Physiol 1979;237:E61–7.
Martí D, Miquel R, Ziani K, et al. Correlation between mRNA levels and functional role of alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes in arteries: evidence of alpha1L as a functional isoform of the alpha1A-adrenoceptor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2005;289:H1923–32.
Martínez-Salas SG, Campos-Peralta JM, Pares-Hipolito J, Gallardo-Ortíz IA, Ibarra M, Villalobos-Molina R. Alpha1A-adrenoceptors predominate in the control of blood pressure in mouse mesenteric vascular bed. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol 2007;27:137–42.
Rudner XL, Berkowitz DE, Booth JV, et al. Subtype specific regulation of human vascular alpha(1)-adrenergic receptors by vessel bed and age. Circulation 1999;100:2336–43.
Haynes WG, Webb DJ. Contribution of endogenous generation of endothelin-1 to basal vascular tone. Lancet 1994;344:852–4.
Nankervis CA, Nowicki PT. Role of endothelin-1 in regulation of the postnatal intestinal circulation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000;278:G367–75.
Fan WQ, Smolich JJ, Wild J, Yu VY, Walker AM. Major vasodilator role for nitric oxide in the gastrointestinal circulation of the mid-gestation fetal lamb. Pediatr Res 1998;44:344–50.
Fan WQ, Smolich JJ, Wild J, Yu VY, Walker AM. Nitric oxide modulates regional blood flow differences in the fetal gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol 1996;271:G598–604.
González-Rivera R, Culverhouse RC, Hamvas A, Tarr PI, Warner BB. The age of necrotizing enterocolitis onset: an application of Sartwell’s incubation period model. J Perinatol 2011;31:519–23.
Llanos AR, Moss ME, Pinzòn MC, Dye T, Sinkin RA, Kendig JW. Epidemiology of neonatal necrotising enterocolitis: a population-based study. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 2002;16:342–9.
Neu J. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: an update. Acta Paediatr Suppl 2005;94:100–5.
Becker RM, Wu G, Galanko JA, et al. Reduced serum amino acid concentrations in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 2000;137:785–93.
Amin HJ, Zamora SA, McMillan DD, et al. Arginine supplementation prevents necrotizing enterocolitis in the premature infant. J Pediatr 2002;140:425–31.
Nowicki PT, Dunaway DJ, Nankervis CA, et al. Endothelin-1 in human intestine resected for necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 2005;146:805–10.
Lakshminrusimha S, Russell JA, Steinhorn RH, et al. Pulmonary arterial contractility in neonatal lambs increases with 100% oxygen resuscitation. Pediatr Res 2006;59:137–41.
Schindler MB, Hislop AA, Haworth SG. Postnatal changes in response to norepinephrine in the normal and pulmonary hypertensive lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004;170:641–6.
Irish MS, Glick PL, Russell J, et al. Contractile properties of intralobar pulmonary arteries and veins in the fetal lamb model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 1998;33:921–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, J., Gugino, S., Nielsen, L. et al. Fetal and postnatal ovine mesenteric vascular reactivity. Pediatr Res 79, 575–582 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.260
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.260