Abstract
BACKGROUND
Low birth weight is associated with childhood stunting, but equivalent associations for birth body composition (BC) remain unknown. The aim of this study was to assess associations between birth BC and height-for-age z-score (HAZ) at 2 years of age.
METHODS
In a prospective cohort study, fat mass (FM) and fat-free mass (FFM) were measured using air-displacement plethysmography within 48 h of birth. Linear regression models were applied to study the relationship between BC at birth and HAZ at 24 ±3 months.
RESULTS
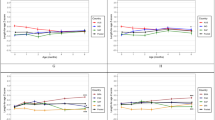
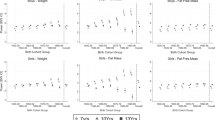
A total of 268 children with height assessment at 2 years were included. Mean±SD HAZ at 2 years of age was −1.2±1.2, with 25.8% classified as stunted (HAZ <−2SD). FFM at birth was positively associated with HAZ at 2 years, independent of length at birth. When adjusted for potential confounders, HAZ at 2 years was 0.73 higher for each additional kg FFM at birth (β=0.73, 95% CI: 0.08, 1.38). FM was not associated with HAZ at 2 years in any model.
CONCLUSION
The FFM component of birth weight, independent of length at birth, explained variability in HAZ at 2 years. Further studies are required to explore how changes in early infant BC are associated with linear growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Black RE, Allen LH, Bhutta ZA et al, Maternal and child undernutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 2008;371:243–60.
Research Institute (IFPRI) IFP Global Nutrition Report 2016 From Promise to Impact Ending Malnutrition by 2030. Washington, DC: International Food Policy Research Institute, 2016. Available at http://ebrary.ifpri.org/cdm/ref/collection/p15738coll2/id/130354. Accessed 1 September 2016.
Central Statistical Agency [Ethiopia]. Ethiopia Mini Demographic and Health Survey 2014. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2014. Available at http://www.measuredhs.com/pubs.pdf. Accessed 19 August 2015.
Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP et al, Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet 2013;382:427–51.
Dewey KG, Begum K . Long-term consequences of stunting in early life. Matern Child Nutr 2011;7:5–18.
Allen L, Gillespie S . What works? A Review of the Efficacy and Effectiveness of Nutrition Interventions. Geneva: United Nations, Administrative Committee on Coordination, Sub-Committee on Nutrition, 2001.
Bhutta ZA, Salam RA . Global nutrition epidemiology and trends. Ann Nutr Metab 2012;61:19–27.
Prendergast AJ, Humphrey JH . The stunting syndrome in developing countries. Paediatr Int Child Health 2014;34:250–65.
Iannotti LL, Zavaleta N, León Z, Caulfield LE . Growth and body composition of Peruvian infants in a periurban setting. Food Nutr Bull 2009;30:245–53.
Padonou G, Le Port A, Cottrell G et al, Factors associated with growth patterns from birth to 18 months in a Beninese cohort of children. Acta Trop 2014;135:1–9.
Wells JCK . Measuring body composition. Arch Dis Child 2005;91:612–7.
Dencker M, Wollmer P, Karlsson MK, Lindén C, Andersen LB, Thorsson O . Body fat, abdominal fat and body fat distribution related to cardiovascular risk factors in prepubertal children. Acta Paediatr 2012;101:852–7.
Gishti O, Gaillard R, Durmus B et al, Body mass index, total and abdominal fat distribution and cardiovascular risk factors in school-age children. Pediatr Res 2015;77:710–8.
Hanieh S, Ha TT, De Livera AM et al, Antenatal and early infant predictors of postnatal growth in rural Vietnam: a prospective cohort study. Arch Dis Child 2015;100:165–73.
Medhin G, Hanlon C, Dewey M et al, Prevalence and predictors of undernutrition among infants aged six and twelve months in Butajira, Ethiopia: the P-MaMiE Birth Cohort, BMC Public Health 2010;10:27.
Lourenço BH, Villamor E, Augusto RA, Cardoso MA . Determinants of linear growth from infancy to school-aged years: a population-based follow-up study in urban Amazonian children. BMC Public Health 2012;12:265.
Wells JC . A critique of the expression of paediatric body composition data. Arch Dis Child 2001;85:67–72.
Andersen GS, Girma T, Wells JCK, Kæstel P, Michaelsen KF, Friis H . Fat and fat-free mass at birth: air displacement plethysmography measurements on 350 Ethiopian newborns. Pediatr Res 2011;70:501–6.
Andersen GS, Girma T, Wells JC et al, Body composition from birth to 6 mo of age in Ethiopian infants: reference data obtained by air-displacement plethysmography. Am J Clin Nutr 2013;98:885–94.
World Health Organization Training Course on Child Growth Assessment. Geneva: WHO, 2008.
WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/ Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2006.
Urlando A, Dempster P, Aitkens S . A new air displacement plethysmograph for the measurement of body composition in infants. Pediatr Res 2003;53:486–92.
Ellis KJ, Yao M, Shypailo RJ, Urlando A, Wong WW, Heird WC . Body-composition assessment in infancy: air-displacement plethysmography compared with a reference 4-compartment model. Am J Clin Nutr 2007;85:90–5.
Lorey J zscore06: Stata Command for the Calculation of Anthropometric z-Scores Using the 2006 WHO Child Growth Standards, 2006. Available at http://www.stata.com/statalist/archive/2011-04/msg01386.html. Accessed 31 August 31 2015.
Arimond M, T. Ruel M . International Food Policy Research Institute Report: Progress in Developing an Infant and Child Feeding Index: an Example Using The Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey 2000, 2002. http://www.ifpri.org/publication/progress-developing-infant-and-child-feeding-index-0. Accessed 19 March 2016.
Barker DJ, Bull AR, Osmond C, Simmonds SJ . Fetal and placental size and risk of hypertension in adult life. BMJ 1990;301:259–62.
Wells JCK . The programming effects of early growth. Early Hum Dev 2007;83:743–8.
Longo S, Bollani L, Decembrino L, Di Comite A, Angelini M, Stronati M . Short-term and long-term sequelae in intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR). J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;26:222–5.
Joglekar CV, Fall CHD, Deshpande VU et al, Newborn size, infant and childhood growth, and body composition and cardiovascular disease risk factors at the age of 6 years: the Pune Maternal Nutrition Study. Int J Obes 2007;31:1534–44.
Burrows R, Correa-Burrows P, Reyes M, Blanco E, Albala C, Gahagan S . Healthy Chilean adolescents with HOMA-IR≥ 2.6 have increased cardiometabolic risk: Association with Genetic, Biological, and Environmental Factors. J Diabetes Res 2015;2015:1–8.
Thornburg K, O’Tierney P, Louey S . The placenta is a programming agent for cardiovascular disease. Placenta 2010;31:S54–9.
Jansson T, Powell TL . Role of the placenta in fetal programming: underlying mechanisms and potential interventional approaches. Clin Sci 2007;113:1–13.
Gabory A, Attig L, Junien C . Developmental programming and epigenetics. Am J Clin Nutr 2011;94:1943S–52S.
Carberry AE, Raynes-Greenow CH, Turner RM, Askie LM, Jeffery HE . Is body fat percentage a better measure of undernutrition in newborns than birth weight percentiles? Pediatr Res 2013;74:730–6.
Haggarty P . Placental regulation of fatty acid delivery and its effect on fetal growth—a review. Placenta 2002;23:S28–38.
Wells JCK . Toward body composition reference data for infants, children, and adolescents. Adv Nutr Int Rev J 2014;5:320S–9S.
Aguayo VM, Badgaiyan N, Paintal K . Determinants of child stunting in the Royal Kingdom of Bhutan: an in-depth analysis of nationally representative data: Determinants of child stunting in Bhutan. Matern Child Nutr 2015;11:333–45.
Aguayo VM, Nair R, Badgaiyan N, Krishna V . Determinants of stunting and poor linear growth in children under 2 years of age in India: an in-depth analysis of Maharashtra’s comprehensive nutrition survey: child stunting in Maharashtra, India. Matern Child Nutr 2016;12:121–40.
Wamani H, Åstrøm AN, Peterson S, Tumwine JK, Tylleskär T . Boys are more stunted than girls in sub-Saharan Africa: a meta-analysis of 16 demographic and health surveys. BMC Pediatr 2007;7:17.
Stein AD, Wang M, Martorell R et al, Growth patterns in early childhood and final attained stature: data from five birth cohorts from low- and middle-income countries. Am J Hum Biol 2010;22:353–9.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the supervisors, research nurses and respondents, and Jimma University Specialized Hospital. We would like to thank Jimma University for giving us permission to conduct the study and publish the result.
Author contributions
The authors’ responsibilities were as follows—BA, HF, JCKW, TG, GSA and PK designed the study; BA, GSA, PK, MA and RW supervised the data collection; BA. analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript, and had primary responsibility for the final content of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the manuscript revisions and read the final manuscript and approved for submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL SUPPORT
Danish Council for Strategic Research—Programme Commission on Food and Health; Danida through the Consultative Research Committee for Development Research (104.Dan.8-1207).
Supplementary material is linked to the online version of the paper at http://www.nature.com/pr
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Admassu, B., Wells, J., Girma, T. et al. Body composition at birth and height at 2 years: a prospective cohort study among children in Jimma, Ethiopia. Pediatr Res 82, 209–214 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2017.59
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2017.59
This article is cited by
-
Heat shocks, maize yields, and child height in Tanzania
Food Security (2022)
-
Higher fat mass and fat mass accretion during the first six months of life in exclusively breastfed infants
Pediatric Research (2020)
-
Body composition during early infancy and its relation with body composition at 4 years of age in Jimma, an Ethiopian prospective cohort study
Nutrition & Diabetes (2018)